Stem cells from urine and methods for using the same
a technology of stem cells and urine, applied in the field of stem cells from urine, can solve problems such as limiting the supply of viable cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Isolation and Characterization of Stem Cells from Urine
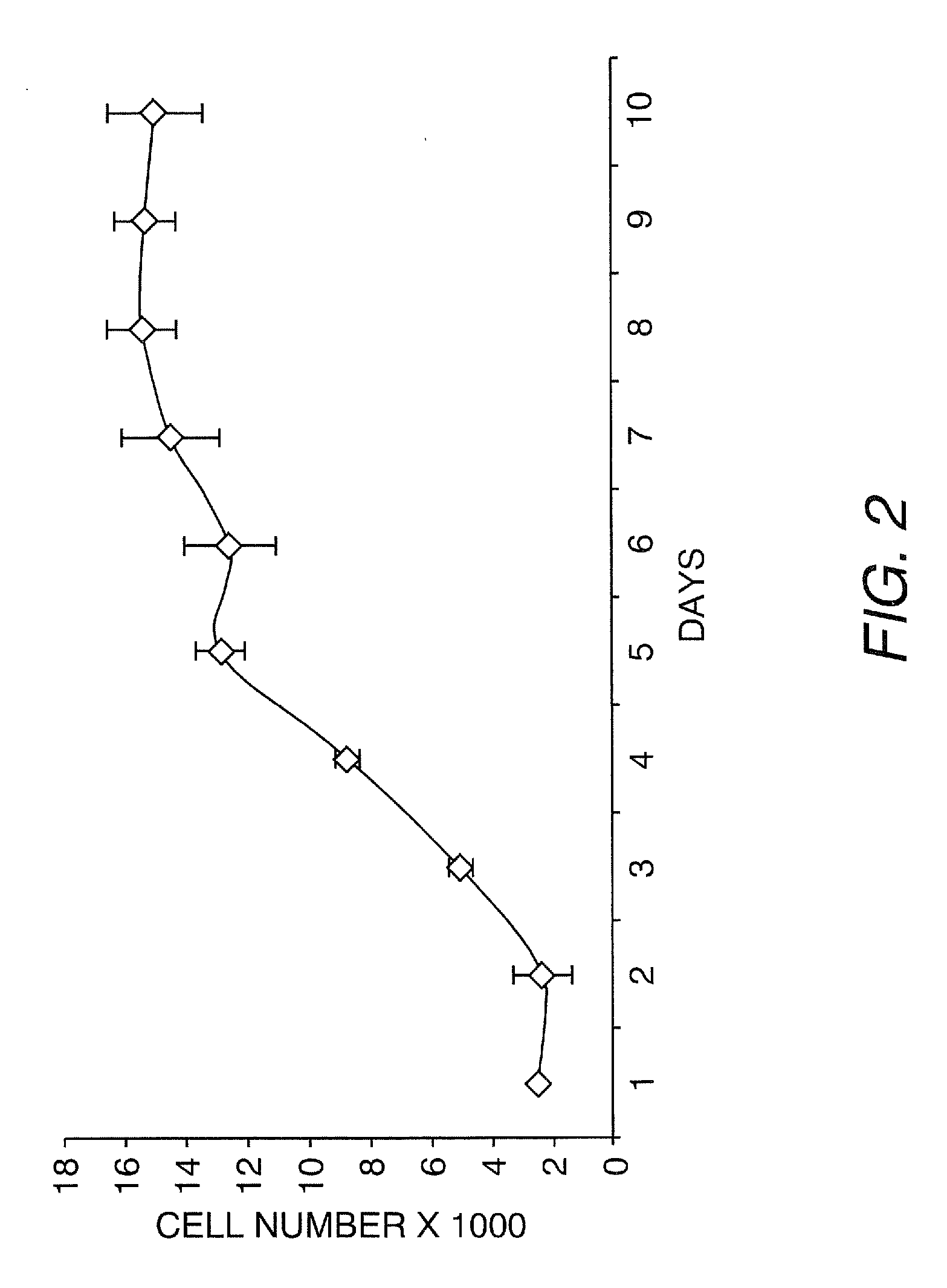
[0127]Fifty-eight human urine samples were collected from 22 male and one female donors (15 healthy individuals and 8 patients), ranging in age from 2 to 50 years. No bacterial contamination was found in any cultures. Urine samples were centrifuged at 1500 RPM for 5 minutes at 4° C. and washed two times with sterile PBS. Cells were plated at an average of 0.5 cell / well in multi-well plates with stem cell medium using a gradual dilution method. The stem cell medium contains ¾ DMEM, ¼ Ham's F12, 10% FBS, 0.4 mg / ml hydrocortisone, 10−10 M, Chron Toxin, 5 mg / ml, insulin, 1.2 mg / ml adenine, 2.5 mg / ml transferrin plus 0.136 mg / ml 3,39,5-triiodo-L-thyronine, 10 mg / ml EGF, and 1% penicillin-streptomycin (Zhang et al., In vitro Cell Dev. Biol.-Animal 37:419, 2001). Single cells were identified and allowed to grow to more than 50% confluence. Cells were subsequently subcultured, transferred to a 6-cm culture dish and expanded.
[0128]Primar...
example 2
Cell Contractility and Tight Junctions of Urine Stem Cells
[0132]Functional characteristics of urine-derived smooth muscle cells are ascertained by determining cell contractility with collagen lattices. Methods for the collagen lattice contraction assay are known in the art (Kropp, et al. (1999) J. Urol. 162:1779). Contractile response to agonists is performed in a similar manner except that agonists are added to the serum-free media immediately prior to lattice release. Agonists which are tested include the Ca-ionophore A23187 (1025 M) and KCl.
[0133]Urine-derived urothelial stem cells are analyzed for tight junctions. Urothelial barrier function is maintained by apical membrane plaques and intercellular tight junctions. Tight junction components within urine stem cells is investigated with conventional methods such as electric microscopy (Zhang, et al. (2003) Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 539:907; Ludwikowski, et al. (1999) BJU hit. 84:507; Sugasi, et al. (2000) J. Urol. 164:951; Zhang, et a...
example 3
Urine Stem Cell Differentiation into Smooth Muscle Cells
[0134]To determine the effect of epithelial-stromal cell interaction or cell-cell interaction on urine stem cell differentiation into smooth muscle cells (Staack, et al. (2005) Differentiation 73:121; DiSandro, et al. (1998) J. Urol. 160:1040), two co-culture methods are used. The first is an indirect co-culture using transwell devices with a 4.5 μm size exclusion. Urine smooth muscle stem cells are plated on the upper chamber wells and bladder smooth muscle cells and / or urothelium from tissue biopsy are seeded on the bottom wells of a transwell unit (Luk, et al. (2005) J. Immunol. Methods 305:39; Gerstenfeld, et al. (2003) Connect Tissue Res. 44(suppl 1):85). The second method is a direct co-culture approach which is performed with a transwell insert of 0.4 μm pore size. The transwell is used as a basement membrane on which urine stem cells are cultured on the lower side, while normal human bladder urothelium and smooth muscle...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com