Genotyping for src-1 predicts for bone loss
a gene and bone loss technology, applied in the field of gene expression for src1, can solve the problems of increasing bone resorption and osteoclast numbers, and achieve the effect of increasing er activity and reducing er activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
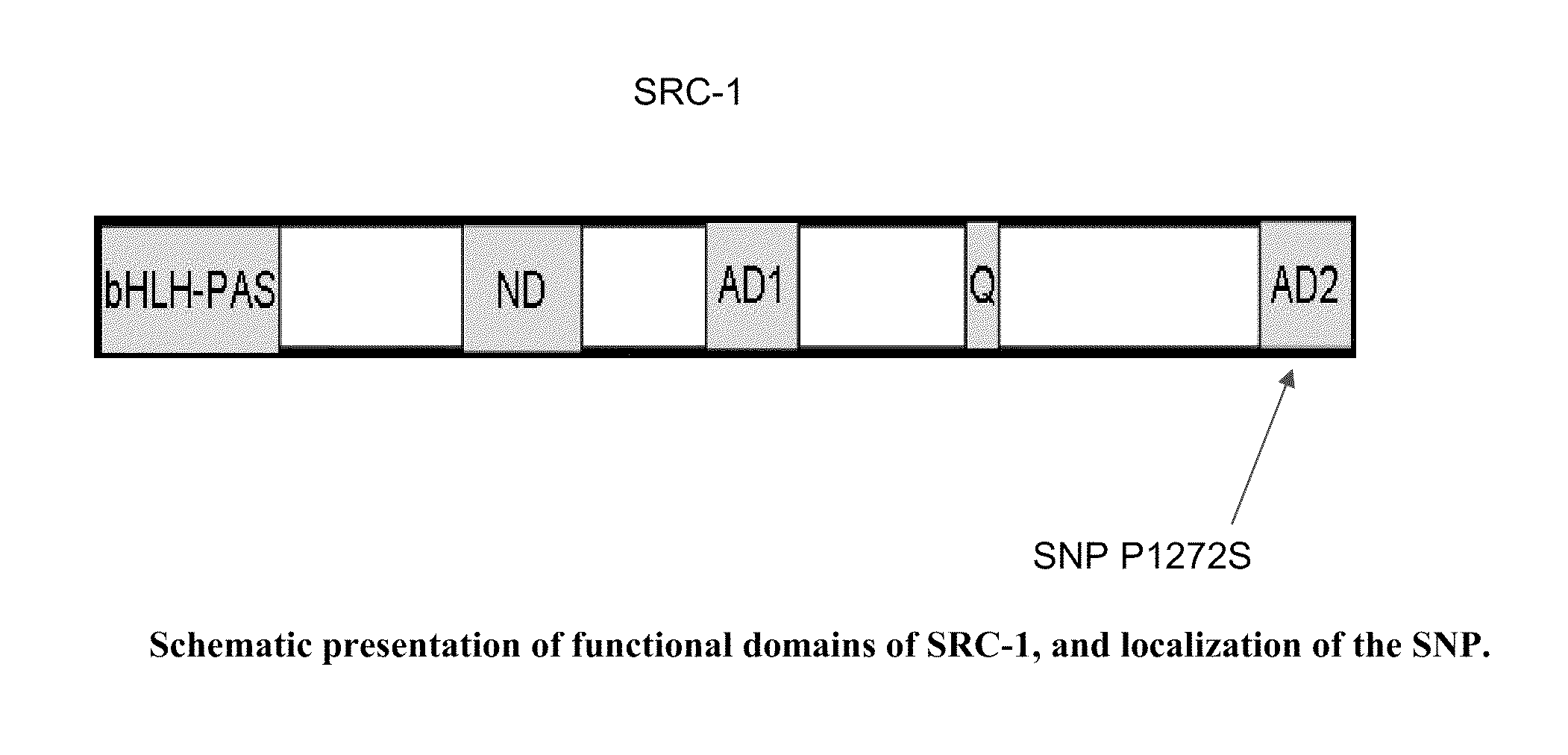
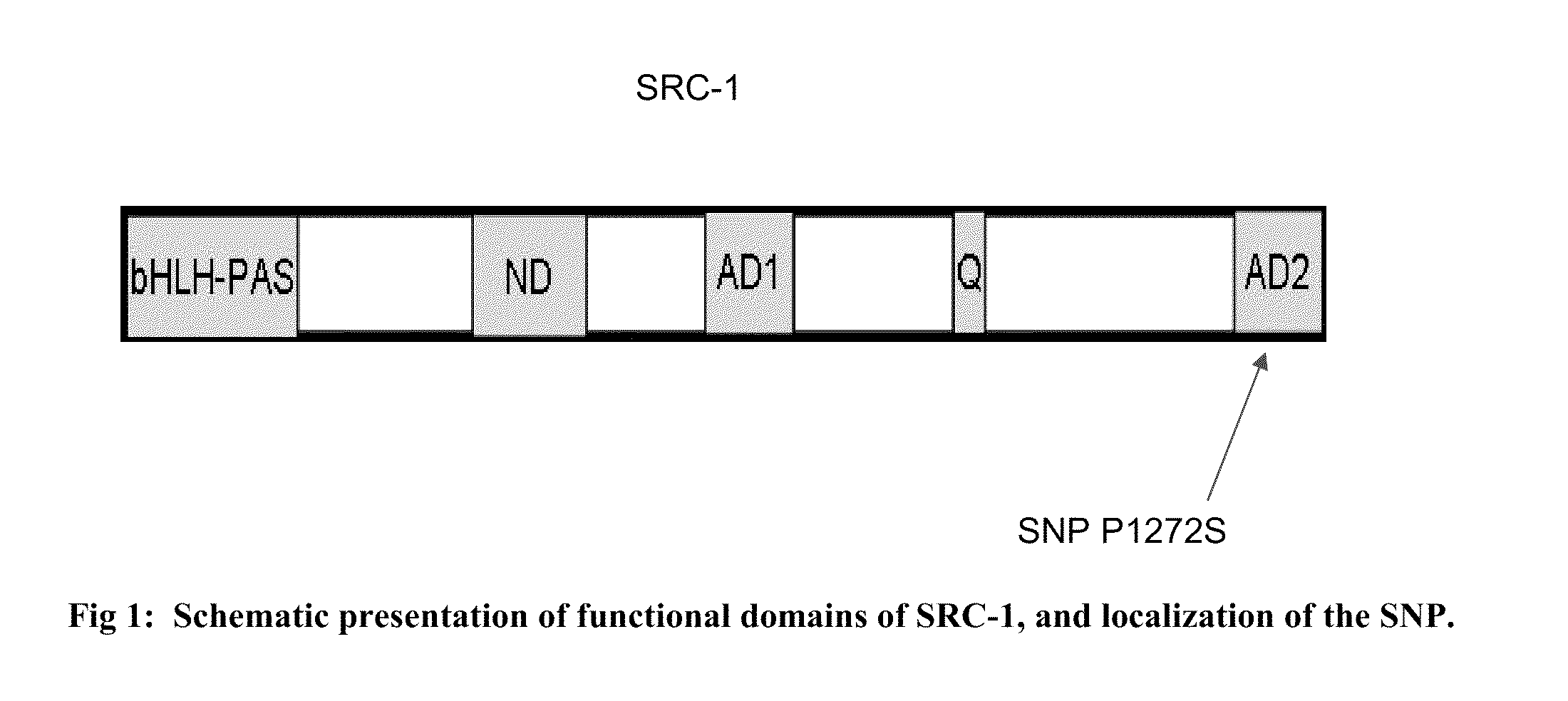
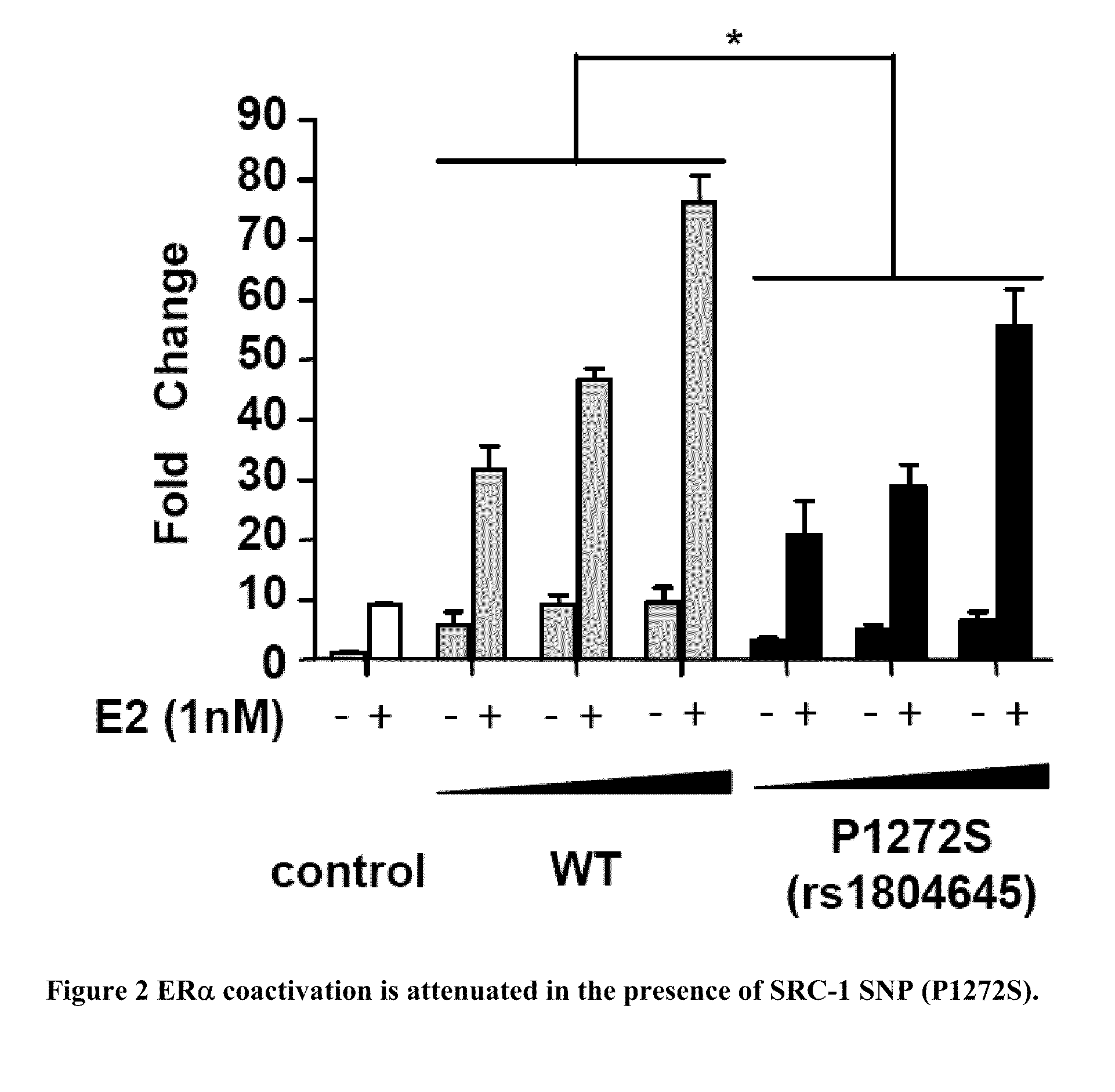
[0041]To investigate the role of variations at the human SRC-1 locus in maintenance of BMD, we initially sought to identify SNPs in the coding regions of SRC-1. First, we carried out direct sequencing of all SRC-1 coding exons in 48 Caucasian and 48 African-American apparently normal individuals to identify novel SNPs, and to gain population-specific SNP information (Coriell Institute, NJ). From this effort we identified a total of six variants (Table 1). SNPs were identified through dbSNP (http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / projects / SNP / ) and by full exon sequencing of (Coriell samples. Our re-sequencing is listed as “Coriell re-sequencing” with AA representing African Americans and CA representing Caucasian Americans. (AGI ASP population is a mixture of African American and Caucasian samples. CEPH, HapMap-CEU, and AFD_EUR_PANEL represent populations of European descent. HapMap-HCB and AFD_CHN_PANEL populations are of Chinese descent. HapMap-YRI and AFD_AFR_PANEL are populations of Africa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| nucleic acid polymorphism | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bone Mass Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| bone mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com