Digital single-lens reflex camera
a digital single-lens, reflex camera technology, applied in the field of digital single-lens reflex cameras, can solve the problems of vignetting cannot be effectively prevented is difficult to prevent vignetting from occurring by using only the micro lens, so as to prevent deterioration of image quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
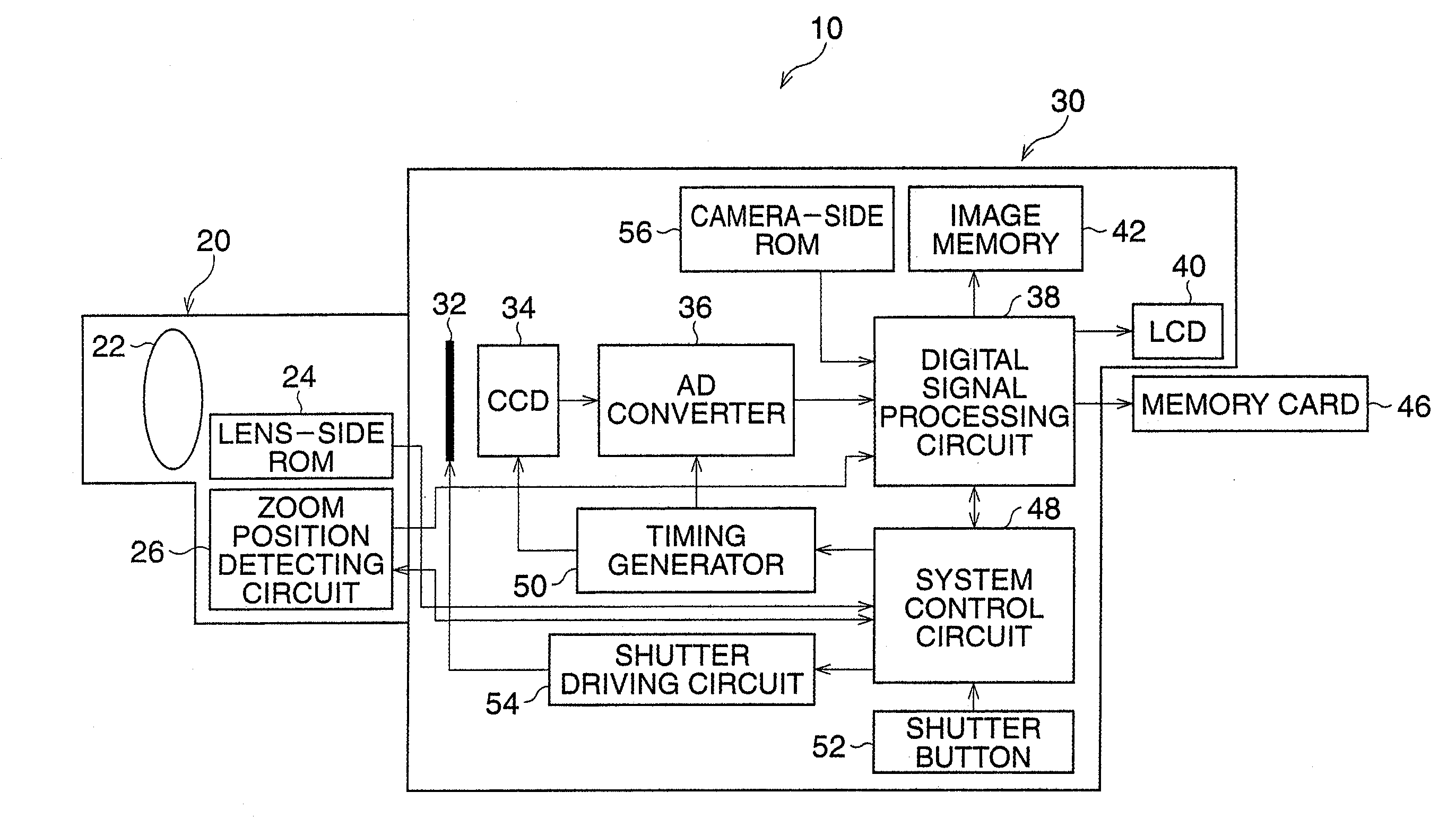
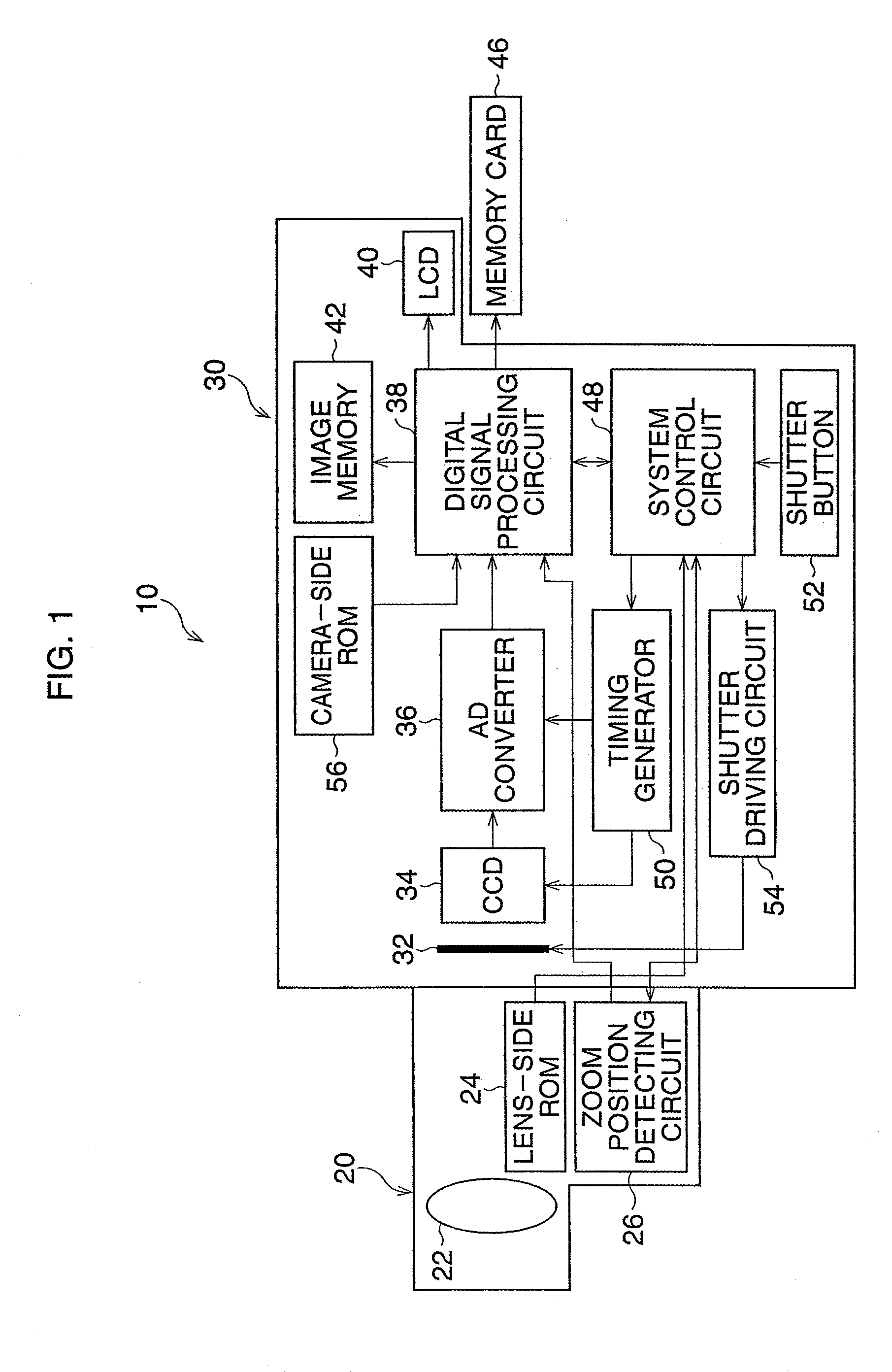
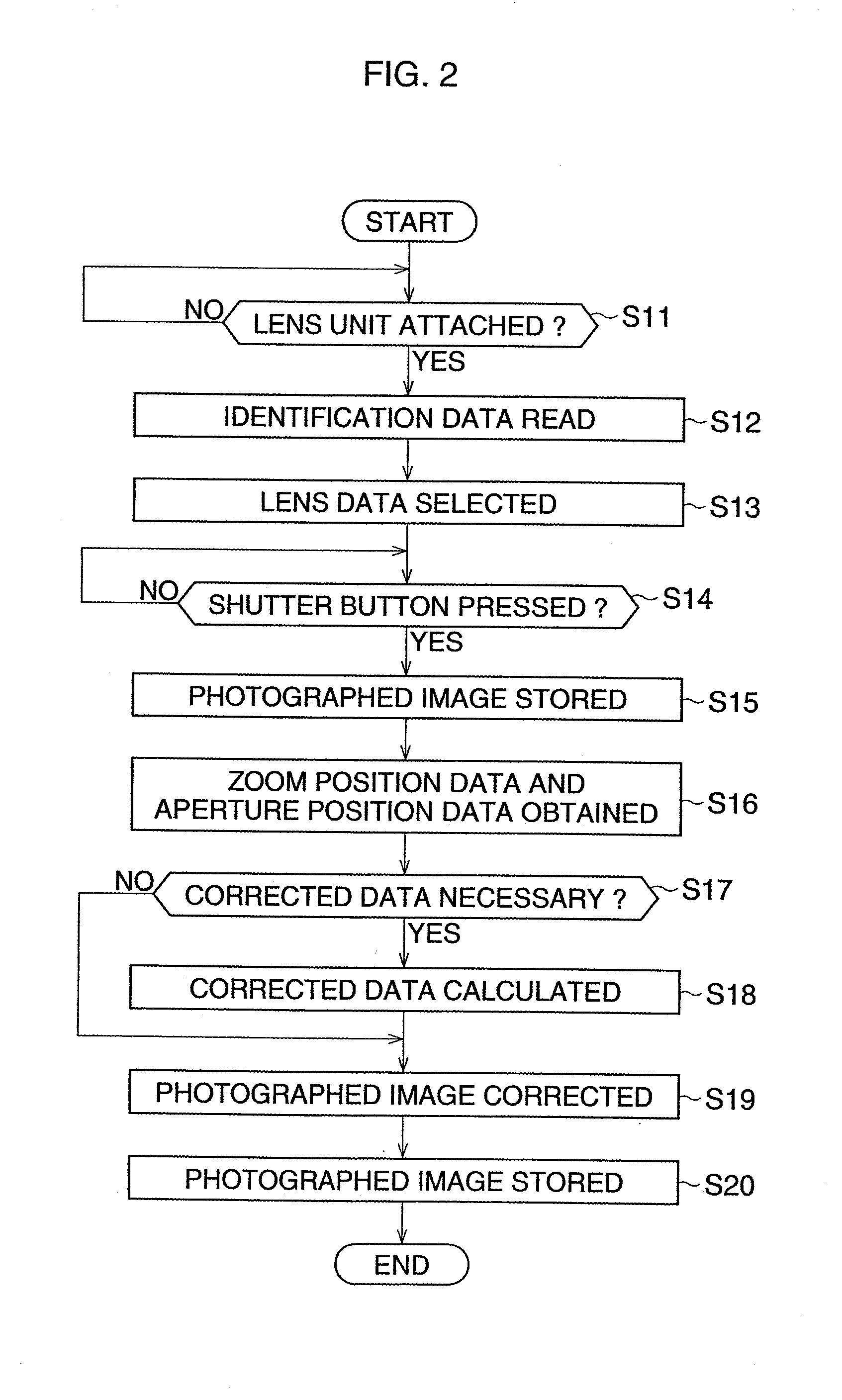
[0036]Hereinafter, the preferred embodiments of the present invention are described with reference to the attached drawings. FIG. 1 is a block diagram of the digital single-lens reflex camera of the
[0037]A digital single-lens reflex camera 10 includes a lens unit 20 having a photographing lens 22 of a zoom lens, and a camera body 30 to which the lens unit 20 is detachably attached. A plurality of lens units including the lens unit 20, can be attached to the camera body 30. The lens unit 20 has a lens-side ROM 24 for storing identification data to identify the photographing lens 22, and a zoom position detecting circuit 26 to detect a zoom position of the photographing lens 22 and transmit zoom position data (focal distance data) indicating the zoom position of the photographing lens 22, to the camera body 30. Further, in the lens unit 20, an aperture position detecting circuit (not shown) to detect an aperture position and transmit aperture position data indicating the aperture posi...
second embodiment
[0058]FIG. 14 is a block diagram of the digital single-lens reflex camera 10 of the
[0059]In this embodiment, there are the following differences from the first embodiment. The lens unit 20 can be attached to and used with a plurality of camera bodies including the camera body 30, and the lens data is stored in the lens unit 20, not in the camera body 30. The lens data is stored in the lens-side ROM 24 with the identification data, and the lens data is stored as full data set. Therefore, when the lens unit 20 is attached to a camera body whose imaging device has the largest format size of the imaging devices included in the camera bodies which can be used with the lens unit 20, such as the camera body 30, the lens data can be used.
[0060]The digital signal processing circuit 38 selectively reads a part of, or all of the lens data stored in the lens-side ROM 24 according to the format size of the CCD 34, and stores the read lens data in the RAM 58. Further, the digital signal processin...
third embodiment
[0068]FIG. 16 is a block diagram of the digital single-lens reflex camera 10 of the
[0069]In this embodiment, there are the following differences from the first and second embodiments. The lens data is stored in the memory card 46, and an EEPROM 62 is provided in the camera body 30 instead of the camera-side ROM 56 and RAM 58. The lens data is read by the digital signal processing circuit 38 from the memory card 46, and stored in the EEPROM 62. The digital signal processing circuit 38 selectively reads the lens data of the photographing lens 22 currently used among the lens data stored in the EEPROM 62, based on the identification data of the photographing lens 22. Further, the digital signal processing circuit 38 reads the imaging device data from the memory 60 in the system control circuit 48, and calculates shading data from the lens data of the photographing lens 22 and imaging device data.
[0070]In this third embodiment, the EEPROM 62 is not necessarily needed. When the EEPROM 62...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com