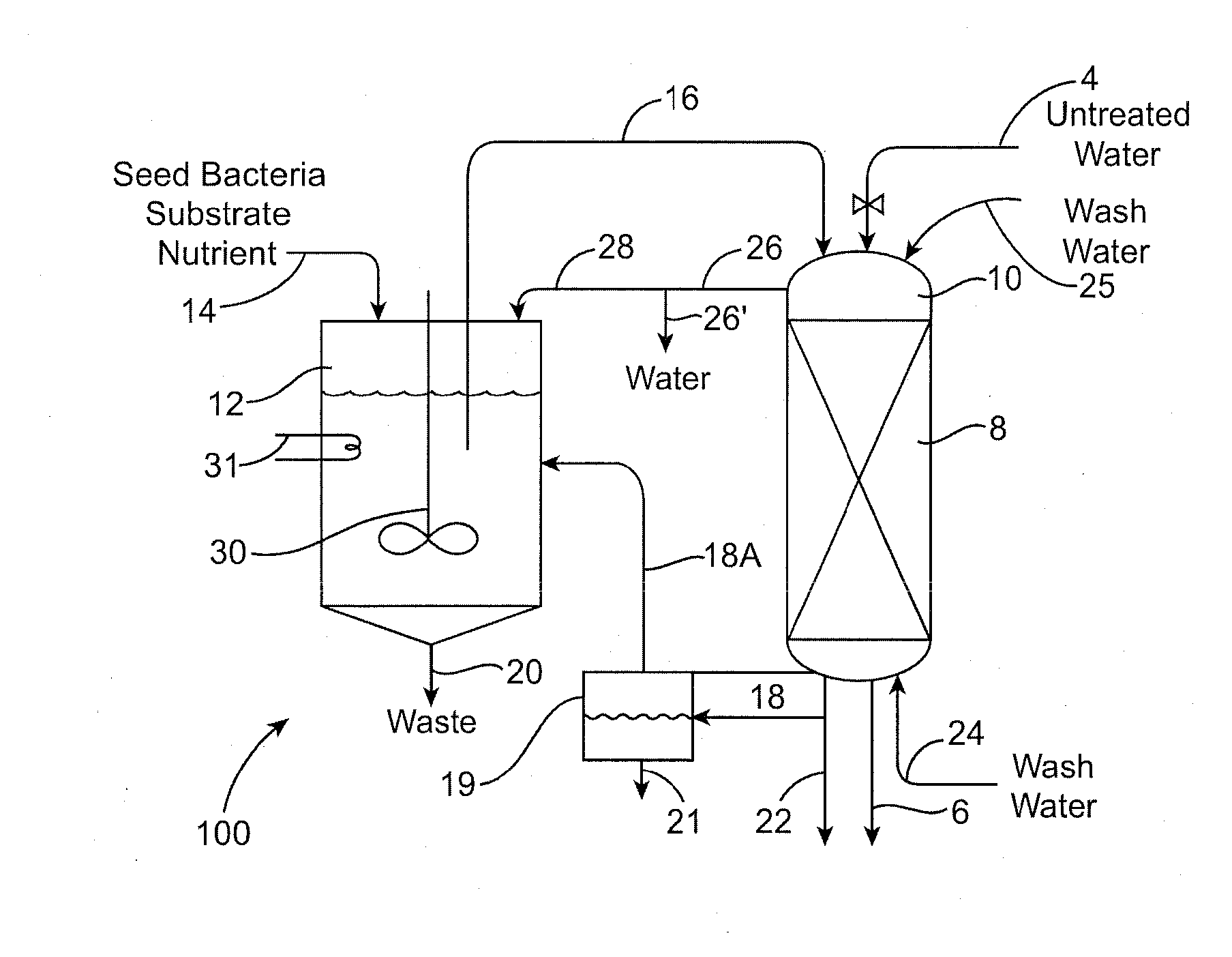
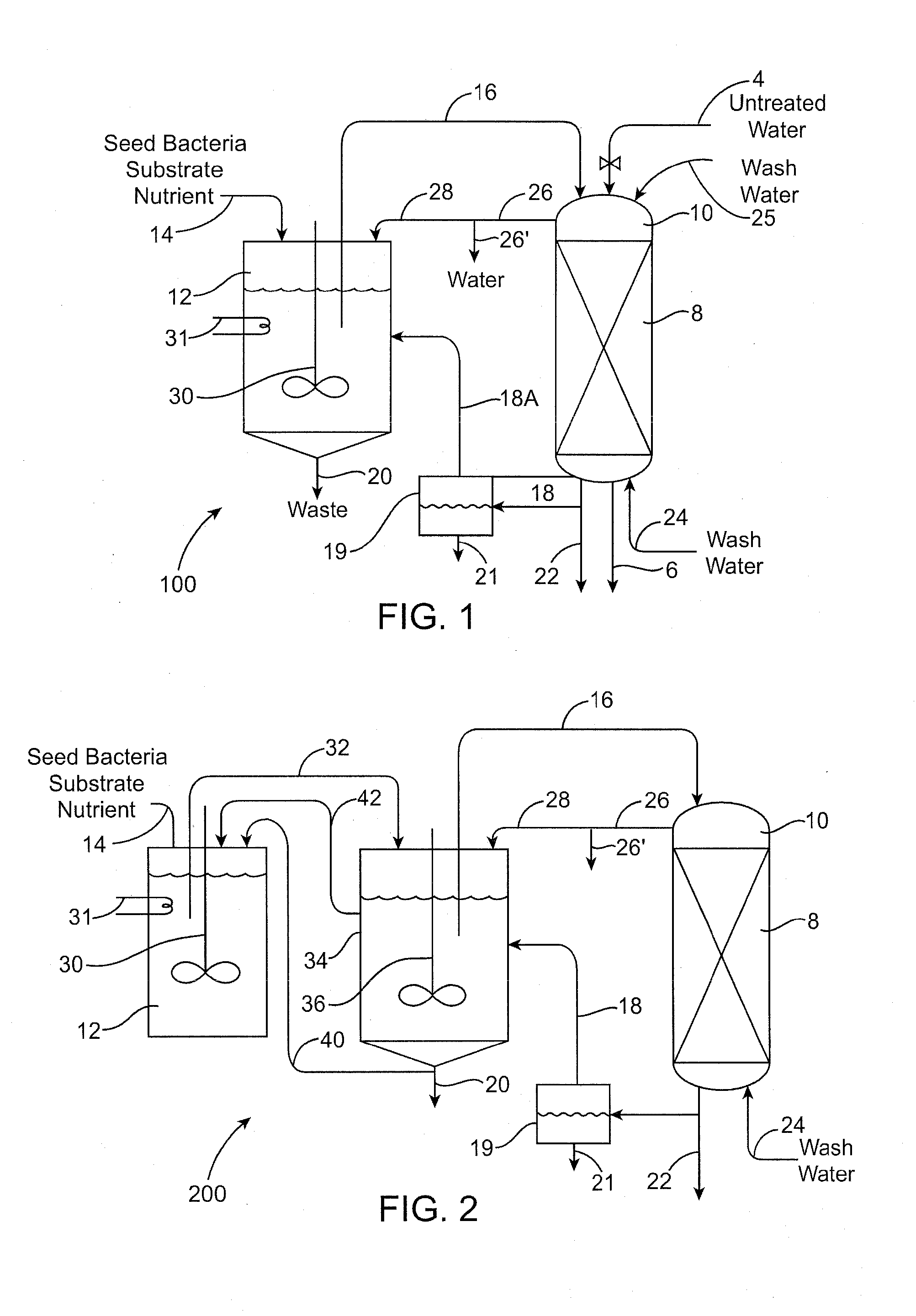
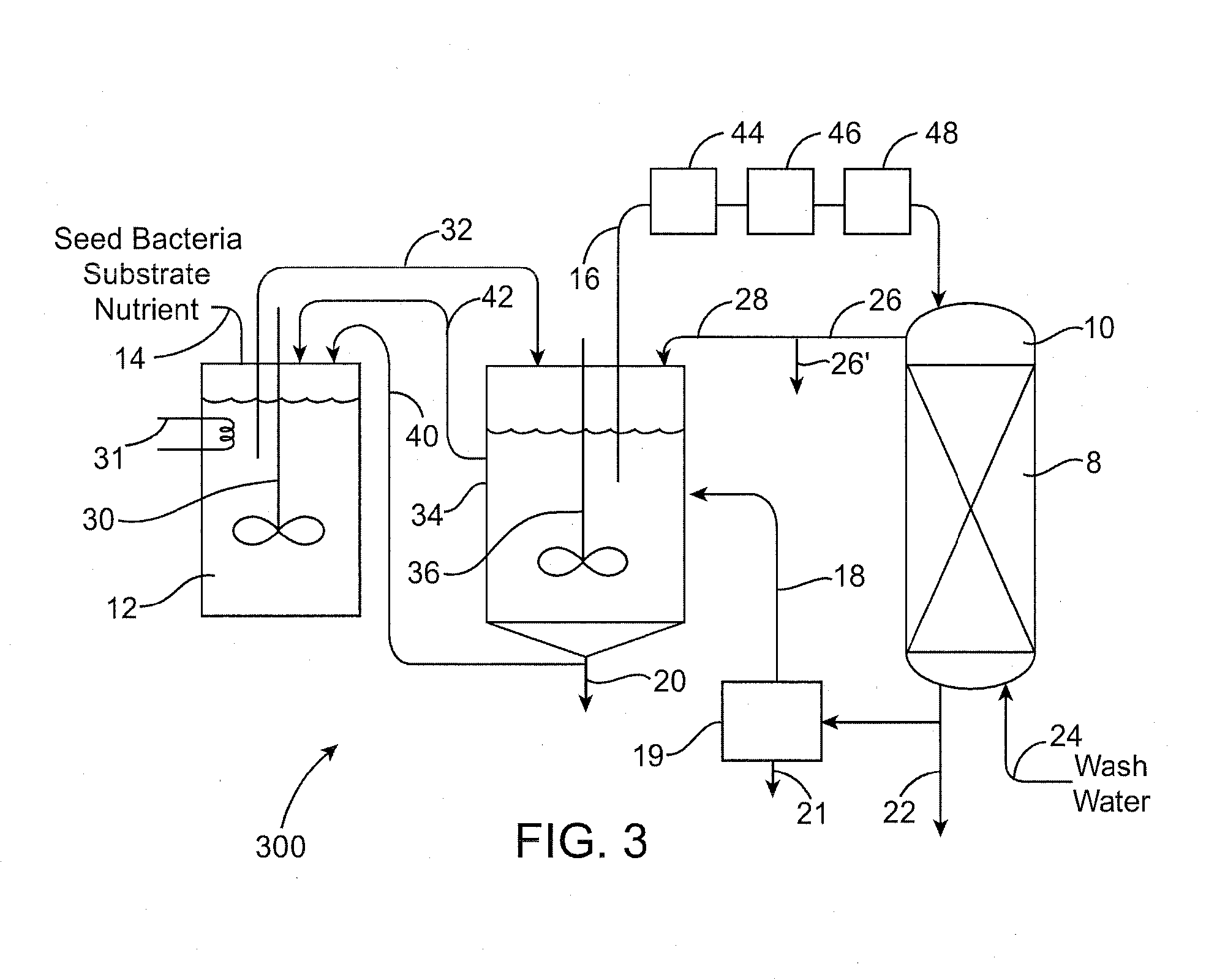
Biodegradation of oxyanions such as perchlorate on ion exchange resins
a technology of oxyanions and ion exchange resins, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve the problems of perchlorate contamination of surface water and ground water supplies, state of the art practice does not provide a practical and convenient method for resin regeneration, and difficult-to-deal-with perchlorate-loaded spent resin formation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Bench Scale Tests
[0156]A microbial culture fluid was developed by seeding 18 L of buffer / mineral media with 500 ml of perchlorate-degrading enrichment culture. The enrichment culture was prepared by selectively aerobically culturing water samples taken from a site heavily contaminated with perchlorate. A ten gallon covered polyethylene tank with a conic bottom was used as the reactor vessel for producing the microbial culture. The reactor was fitted with a mixer that rotated at about 20 rpm. Anaerobic conditions in the reactor were established by covering the reactor and sealing the cover with tape. The solids retention time (SRT) used in operating the reactor was approximately 27 days. After the microbial culture was deemed stable, the bioregeneration tests were started. The microbial fluid product reactor vessel contained the perchlorate-reducing microorganisms and a mineral / nutrient broth that provided an electron donor (i.e. acetate), and buffer solution to keep the pH at 7.0.
[0...
example 2
Effect of Flow Rate on Biodegradation Rate and Resin Expansion
[0162]FIGS. 9 and 10 depict bioregeneration of a spent resin in the laboratory scale apparatus of Example 1 using flow rates of 335 mL / min and 213 mL / min. These flow rates correspond to retention times of 0.30 and 0.47 minutes, respectively. With the faster flow rate more complete bioregeneration was obtained. Bed expansion was 56.8% with the faster flow rate and 44.5% with the slower flow rate.
[0163]FIGS. 9 and 10 show that there exists a relationship between the flow rate applied to the system, the % expansion obtained and the kinetics of the biodegradation process. It will be readily appreciated by those of skill in the art that changes in the geometry of the bioreactor will give rise to different flow conditions being called for to attain these same degrees of bed expansion. The invention described herein is applicable to any flow conditions which give rise to the desired resin bed expansions. FIG. 11 depicts empirica...
example 3
Application to Brine Treatment and Overall Water Treatment Process
[0164]The biological removal of perchlorate from a resin using enriched cultures and expanded beds as described above can be applied to a resin that was loaded with perchlorate from a brine generated in a water treatment resin regeneration process.
[0165]Ground water containing about 20 ppb of perchlorate and part per million levels of nitrate and sulfate can be treated by passage over a bed of chloride-loaded strong base acrylic resin in an ion-exchange vessel. This treatment removes the undesired perchlorate and nitrate and sulfate anions from the water and replaces them with chloride ions. Approximately 500 to 5000 bed-volumes of water can be treated before tests of the effluent water indicate that the resin's capacity is beginning to be used up. The resin is removed from service and regenerated by contact with a strong salt brine (6-8% w NaCl). This treatment can be carried out on the resin in situ in its original ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com