Reinforced Soil Retaining Wall System and Method of Construction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
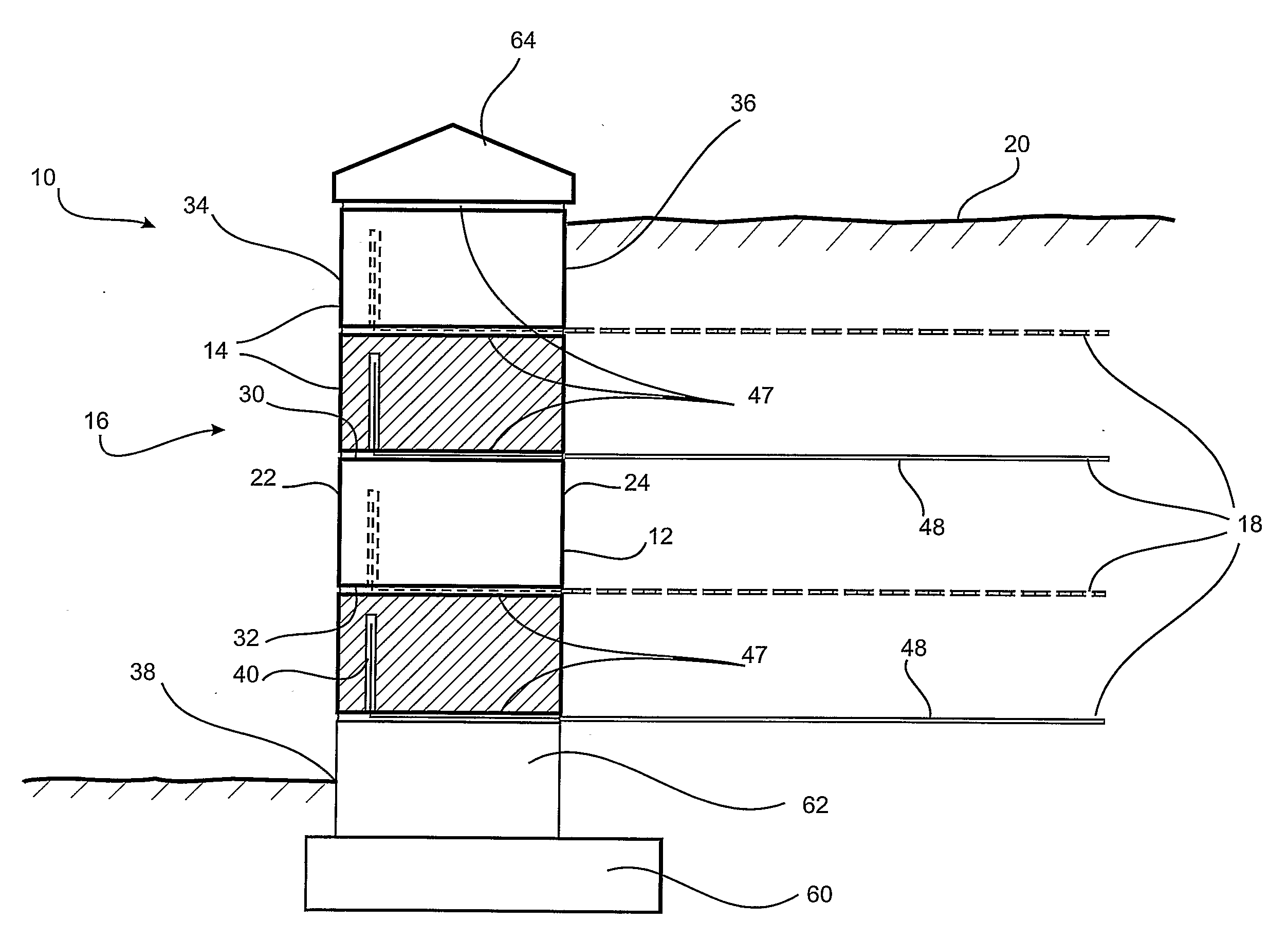
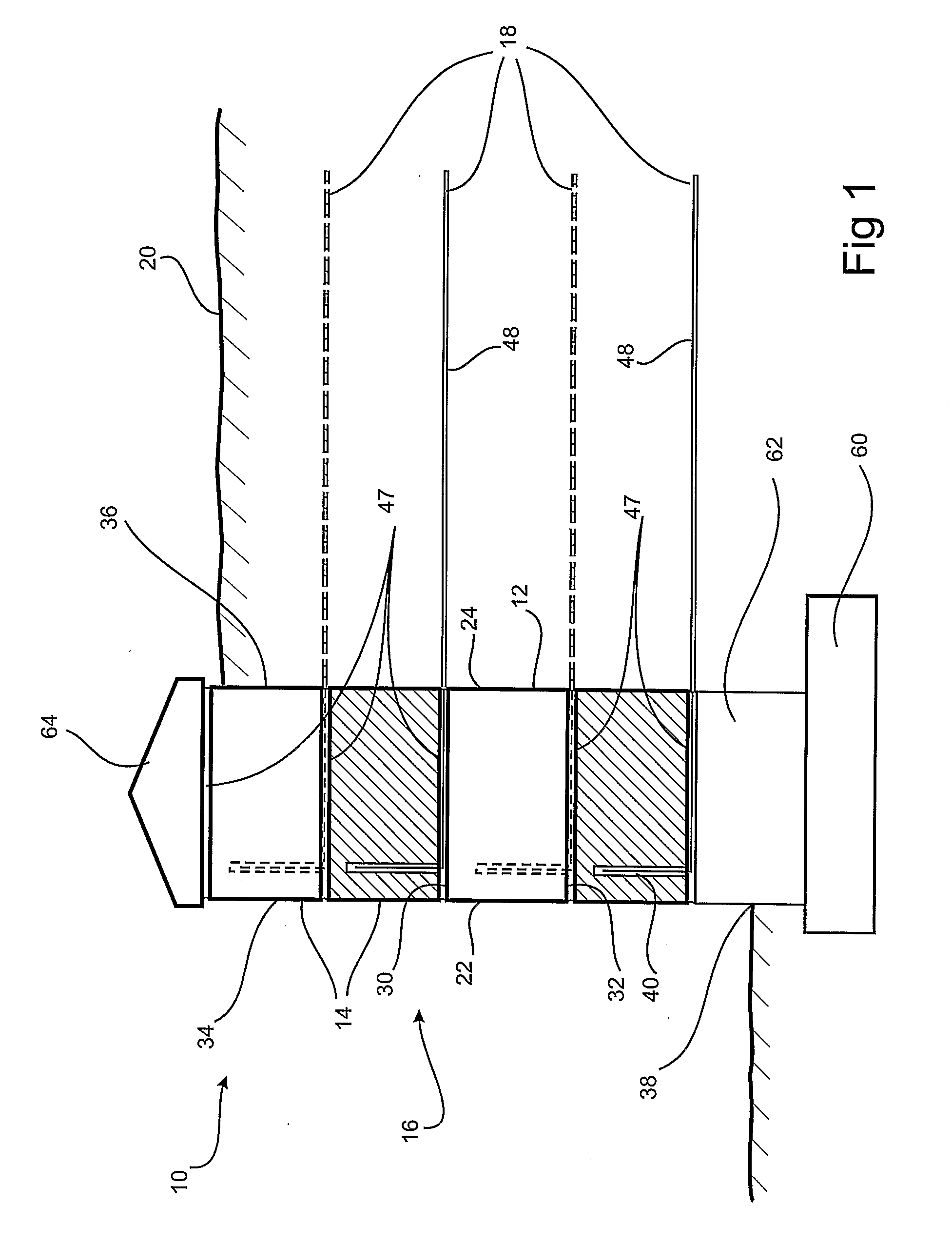
[0077]the reinforced soil retaining wall system 10 of present invention is now described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 7, the reinforced soil retaining wall system 10 comprising a plurality of blocks 12 arranged in courses 14 to form a wall 16. Soil reinforcement is provided to the wall 16 using a plurality of lengths of strip reinforcement 18 inserted in and extending from the blocks 12, the strip reinforcement 18 being buried under compacted backfill 20 either as each course 14 is laid or after construction of the wall 16.
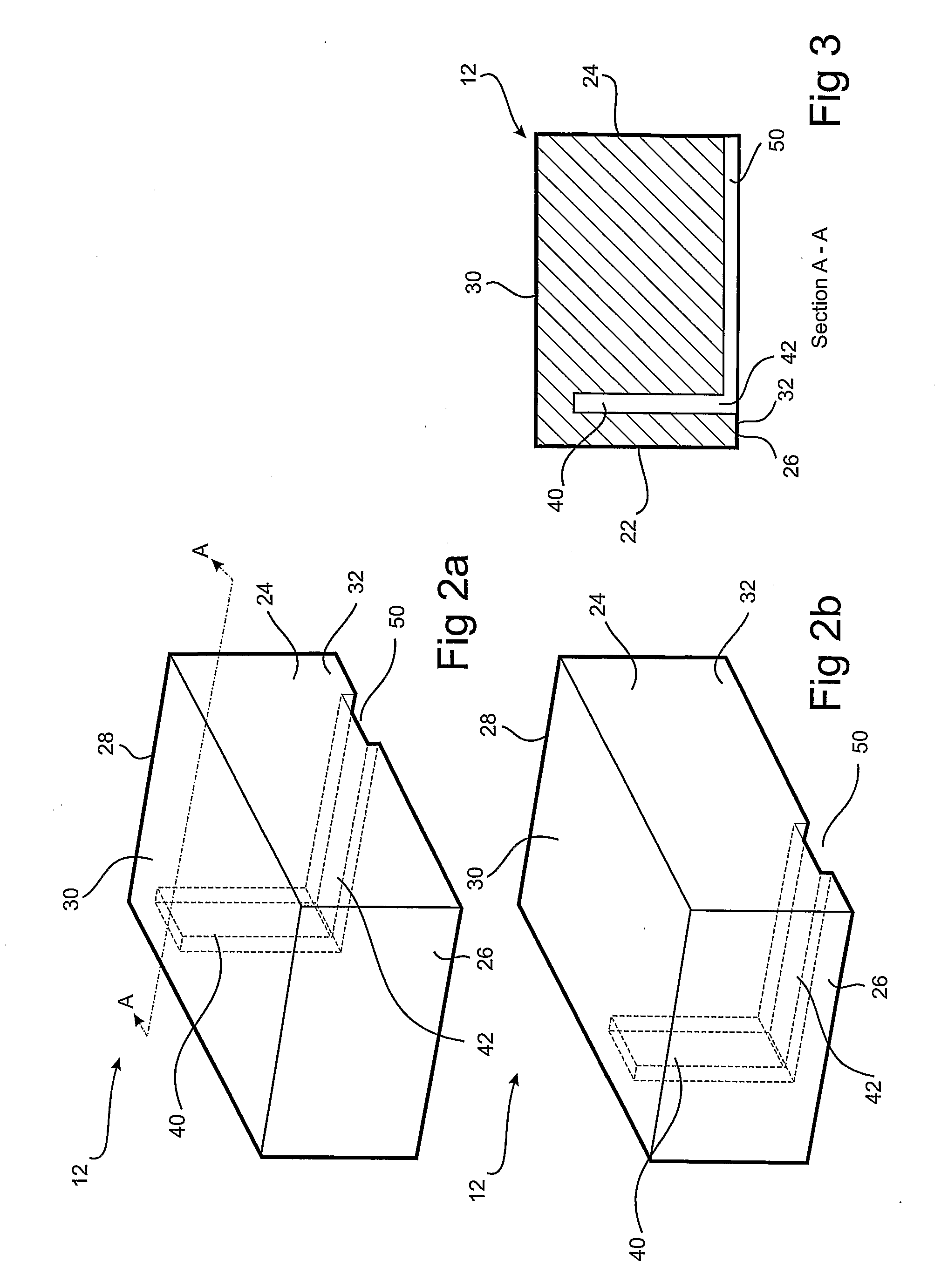
[0078]With reference to FIGS. 1, 2(a) and 2(b), the blocks 12 used in accordance with a first embodiment of the reinforced soil wall system 10 comprise a front face 22, a rear face 24 spaced from said front face by a distance defining the depth of the block 12, opposing side surfaces 26 and 28 respectively, spaced from each other by a distance defining the width of the block 12, a top surface 30 and a bottom surface 32 spaced from the top surface 30 by a distance ...
third embodiment
[0109]This based on a realization that the top 0.1-0.9 meters of the retaining wall is effectively self-supporting. The transition depth 92 depends in part on the anticipated depth of any installations or structures to be constructed on the retained side of the wall, but it is anticipated that the transition depth will not exceed one metre and will more likely be around 0.4 to 0.6 m below the final anticipated height of the composite wall 90.
[0110]A soil reinforcement protection barrier 98 may be installed at the transition depth 92 in general coplanar alignment with respect to the top surface 30 of the uppermost course 14 of the lower section 96. The barrier 98 serves as a visual or physical barrier to protect the strip reinforcement 18 from damage during subsequent building operations adjacent to the completed retaining wall. Accordingly, the barrier 98 may take the form of a thin planar strip of plastic that provides a visual indication that the transition depth has been reached ...
fourth embodiment
[0111]the system 10 and blocks 12 of the present invention is illustrated in FIGS. 12 and 13 for which like reference numerals refer to like parts. This embodiment has been designed specifically to deal with problems associated with using backfill such as clay soils which have a very slow rate of permeation of water. As a result of the low permeability of the soil, the backfill 20 may become saturated over time, for example due to precipitation, resulting in a buildup in water being stored on the retained side 32 of the wall 16. This causes hydrostatic pressure on the wall 16 to increase, effectively pushing against the retained side 32 of the wall 16.
[0112]One way to overcome this problem is to place a vertically oriented permeable layer 104 of permeable material such as drainage aggregate adjacent to the retained side 32 of the wall 16 to allow water to drain under gravity from behind the wall through a drainage channel 106 positioned towards the base of the wall 16 and extending ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com