Oligonucleotide linkers comprising a variable cohesive portion and method for the preparation of polynucleotide libraries by using said linkers
a technology of oligonucleotide and polynucleotide, which is applied in the field of oligonucleotide linkers comprising a variable cohesive portion and the preparation of polynucleotide libraries by using said linkers, can solve the problems of reducing the efficiency of sequencing, affecting and difficult control of the number of g residues added
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Linker Evaluation Using a Test cDNA
Linkers Preparation
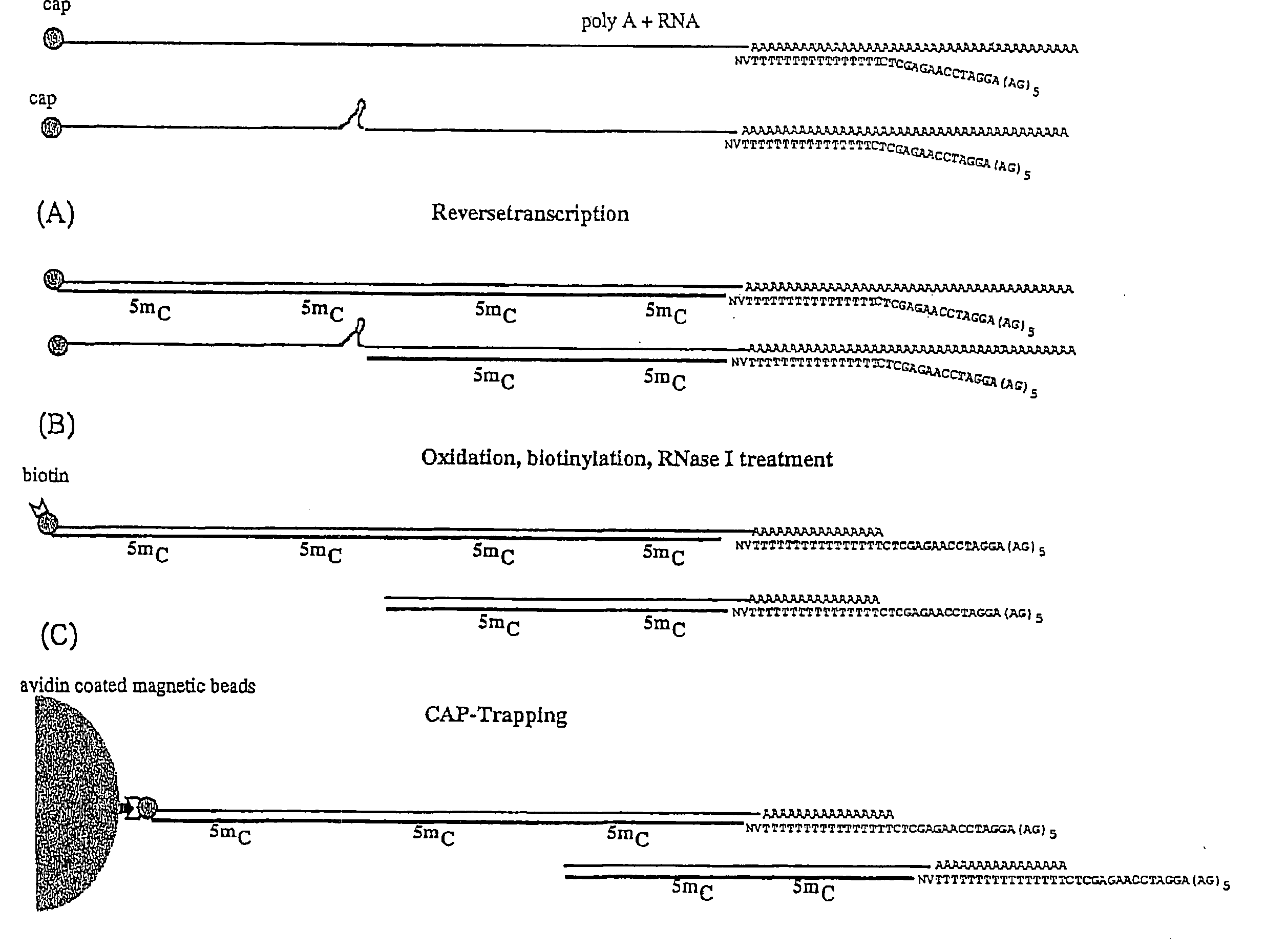
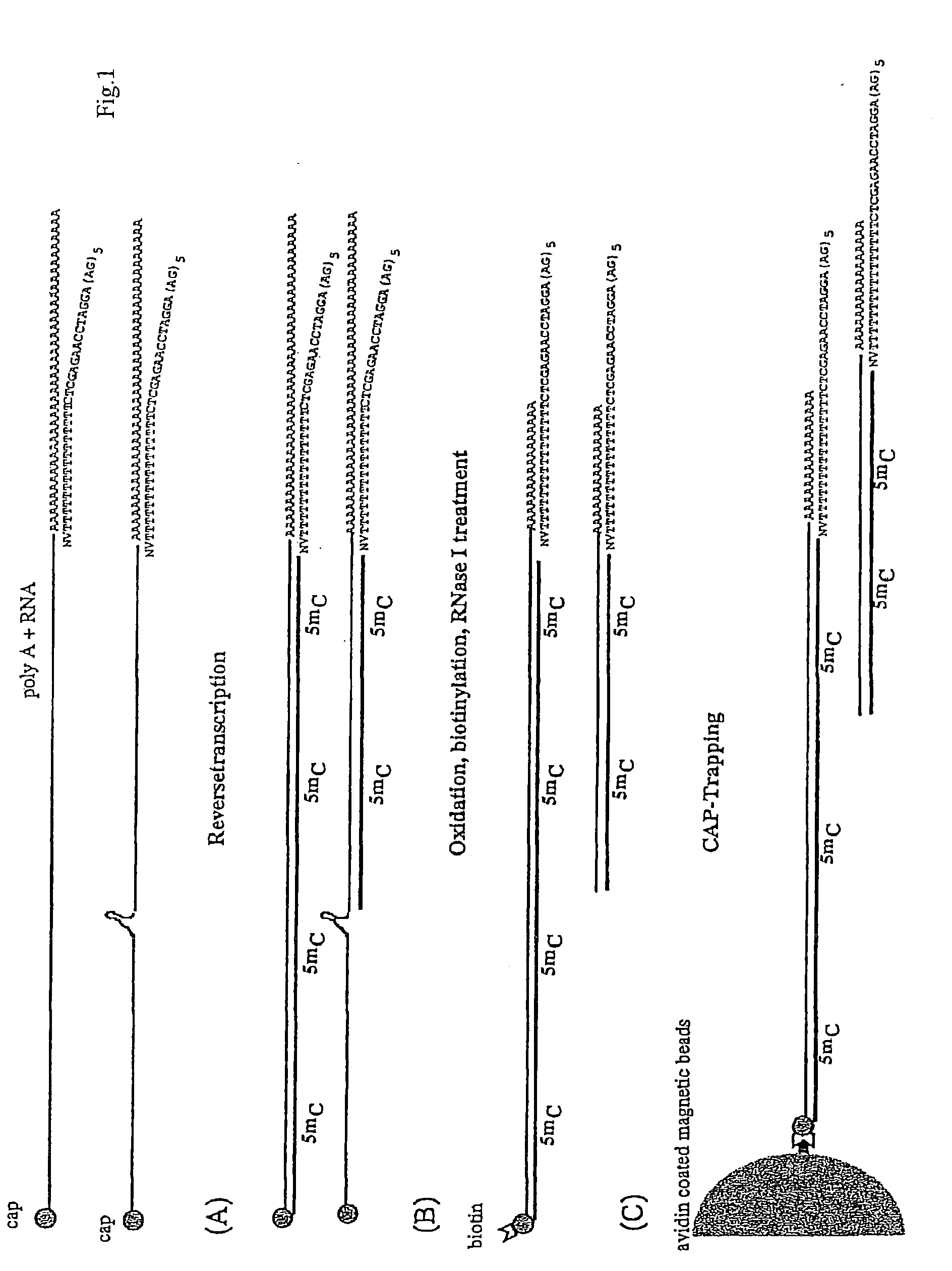
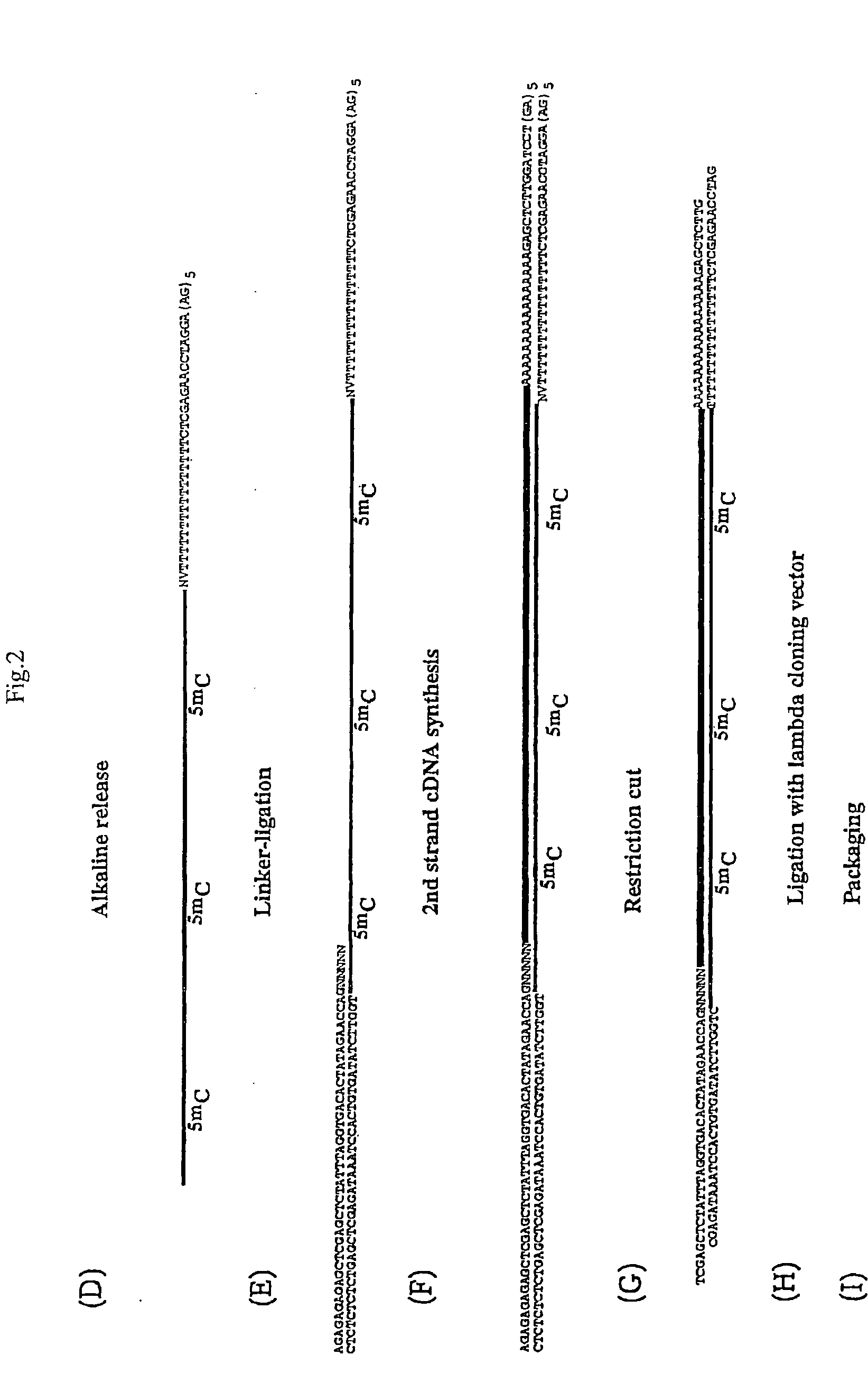
[0199]The population of linker oligonucleotides were purchased from Gibco-BRL Life technologies. The oligonucleotides were distinguished in one single strand (single upper strand) (indicated as A and C, comprising the variable portion) and the other single strand (single lower strand) (indicated as B). Then, one of A and C and B were bound together in order to form two different populations of double strands. The population of linkers A comprises linkers having a fixed portion oligonucleotide (in this case, bases 1-43 of SEQ ID NO:1) and a variable portion (GN5), wherein the first base is G (that is, the base number 44) and the following bases NNNNN (bases from 45 to 49) different for each linker of the population and prepared at random.
[0200]The population of linkers C comprises a constant portion oligonucleotide (bases 1-43 of SEQ ID NO:3) and the variable portion NNNNNN (bases 44 to 49) different for each linker of the populat...
example 2
Full-Length cDNA Library Preparation and cDNA Analysis
Linker Preparation
[0214]Linkers were prepared as above described in Example 1.
Preparation of RNA
[0215]Slices of mouse liver tissue (0.5-1 g) were homogenized in 10 ml of a suspension and extracted with 1 ml of 2M sodium acetate (pH 4.0) and the same amount of a mixture of phenol / chloroform (volume ratio 5:1). After the extraction, the same volume of isopropanol was added to the aqueous layer to precipitate RNA. This sample was incubated on ice for an hour and centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 15 minutes with cooling to collect the precipitates. The resulting precipitates were washed with 70% ethanol and dissolved in 8 ml of water. By adding 2 ml of 5M NaCl and 16 ml of an aqueous solution (pH 7.0) containing 1% CTAB (cetyltrimethylammonium bromide), 4M urea and 50 mM Tris, RNA was precipitated and polysaccharides were removed (CTAB precipitate). After centrifugation at 4000 rpm for 15 minutes at room temperature, the RNA was dissolved ...
example 3
Efficiency of Ligation
[0243]In the ligation of linkers prepared as above to the mouse liver derived cDNAs, 2 μg of mixed linker (N6: GN5=1:4) were ligated to various amounts of cDNAs (1 μg, 0.5 μg and 0.2 μg respectively in Lanes 1, 2 and 3 of FIG. 4). Then, 50 ng of ligated cDNAs were used for the second strand synthesis and analyzed by alkaline gel electrophoresis. All electrophoresis patterns and incorporation rates were the same (Lanes 1-3), suggesting that 2 μg of linker were efficiently ligated to any of the different amount of cDNAs. If the linker amount was not appropriate, excessively expressed cDNA bands would be shifted up to twice size by forming hairpin structures. Instead, the first-strand cDNA and all second-strand cDNAs showed the same pattern (the same size).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic field | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Magnetic field | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com