Loop type heat pipe and waste heat recovery device
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
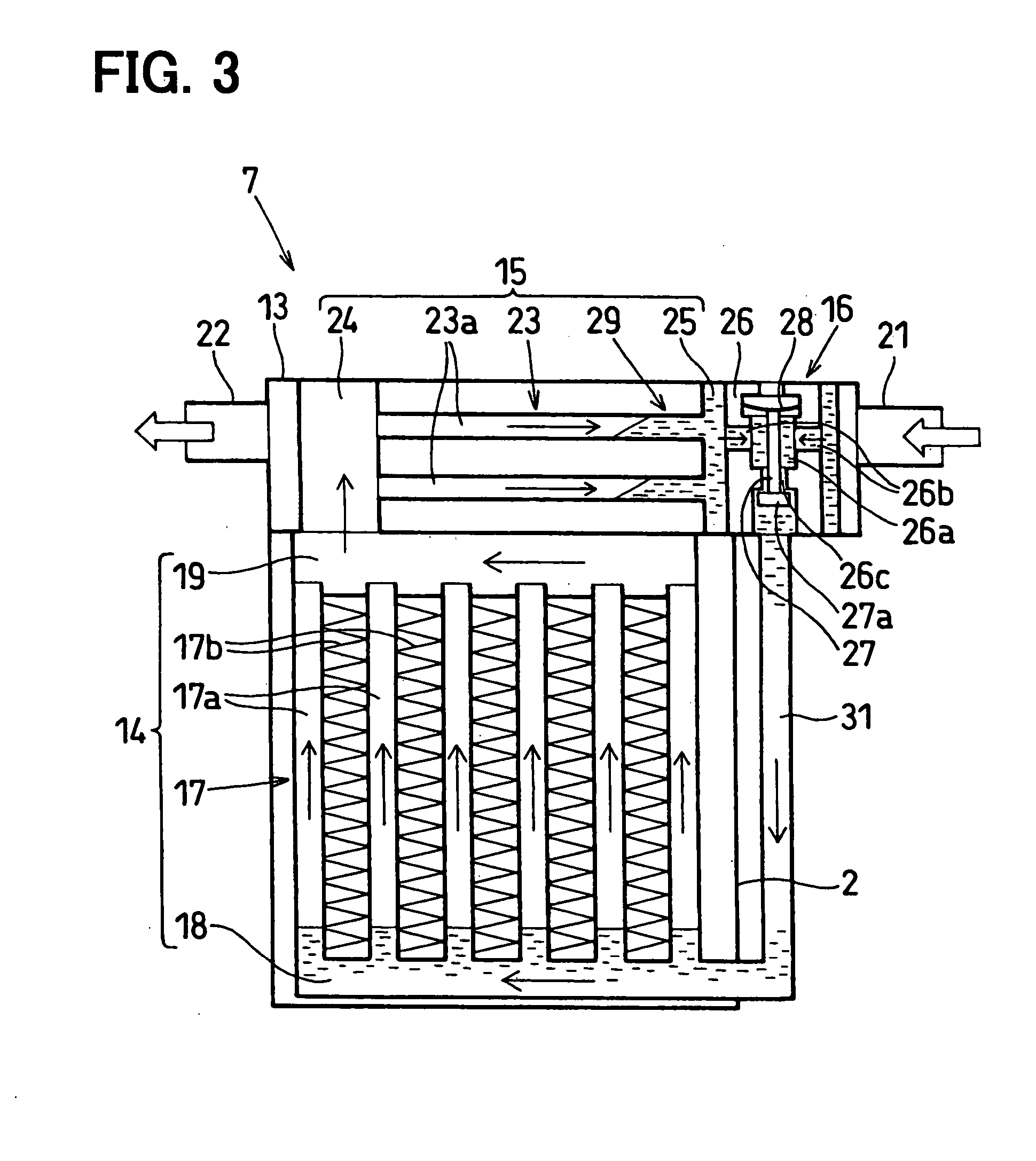
[0018] A first embodiment will be now described with reference to FIGS. 1 and 2. In this embodiment, a loop type heat pipe is typically used for a waste heat recovery device.
[0019] First, a basic structure of the waste heat recovery device will be now described. An engine (internal combustion engine) 1 is located for generating a rotation output for a vehicle running by fuel combustion. The engine 1 is generally provided with a coolant circuit for controlling heat generated in the engine 1, and an exhaust pipe 2 for discharging exhaust gas to atmosphere.
[0020] The coolant circuit includes a radiator circuit 3, a heater circuit 4 and a waste heat recovery circuit 5. Furthermore, a catalytic converter 6 for purifying the exhaust gas and the waste heat recovery device 7 are located in the exhaust pipe 2.
[0021] Next, the coolant circuit including the radiator circuit 3, the heater circuit 4 and the waste heat recovery circuit 5 will be described.
[0022] A radiator 9 is located to per...
second embodiment
[0061] The second embodiment will be described with reference to FIG. 3. In the second embodiment, members having the same functions as those of the above-described first embodiment are indicated by the same reference numbers.
[0062] In the waste heat recovery device 7 of the above-described first embodiment, the tubes 23a of the condenser 15 are elongated in the vertical direction so that liquid refrigerant moves downwardly by its weight when the waste heat recovery device 7 is mounted on a vehicle. That is, in the above-described first embodiment, the condenser 15 is located on the side surface of the evaporator 14 such that the tubes 17a of the evaporator 14 and the tubes 23a of the condenser 15 are arranged in parallel with each other to be elongated in the vertical direction when the waste heat recovery device 7 is mounted on a vehicle. However, in the second embodiment, the condenser 15 is located such that the longitudinal direction of the tubes 23a of the condenser 15 is app...
third embodiment
[0069] A third embodiment will be now described with reference to FIG. 4. In the above-described first and second embodiments, the differential pressure regulating valve 16 is used as one example of the operation stop means of the waste heat recovery device 7, to open and close the communication passage through which the liquid refrigerant condensed in the condenser 15 flows to the evaporator 14. However, in a waste heat recovery device 7 of the third embodiment, as shown in FIG. 4, the differential pressure regulating valve 16 is not provided. In the third embodiment, an operation stop means for stopping evaporation of the refrigerant in the evaporator 14 is constructed without using the differential pressure regulating means 16. For example, a fluid control means for controlling a supply amount of exhaust gas (first fluid for heating) introduced to the evaporator 14 through the exhaust gas pipe 2 is provided so as to stop the evaporation of refrigerant in the evaporator 14.
[0070]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com