Thin-film piezoelectric resonator and filter circuit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
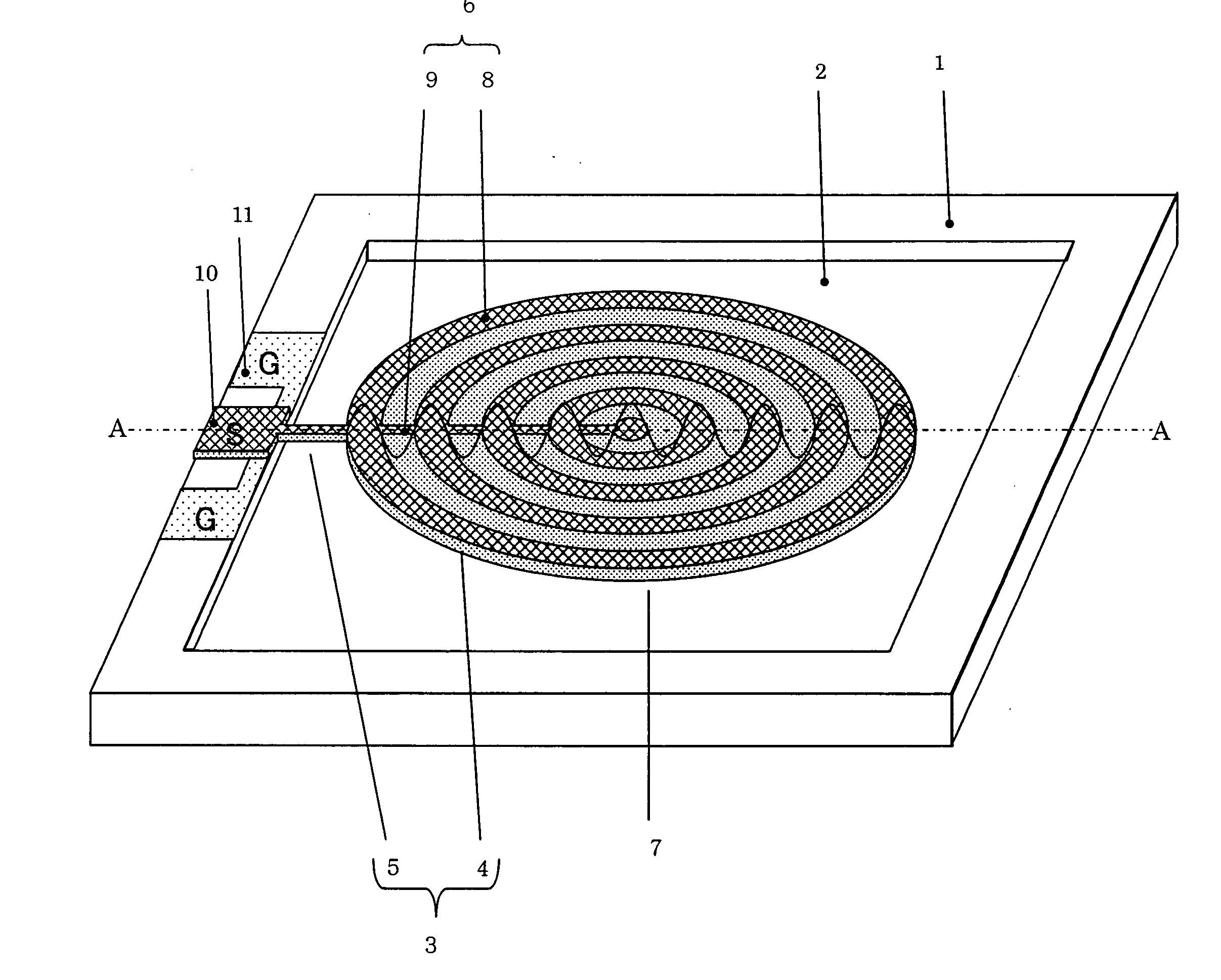
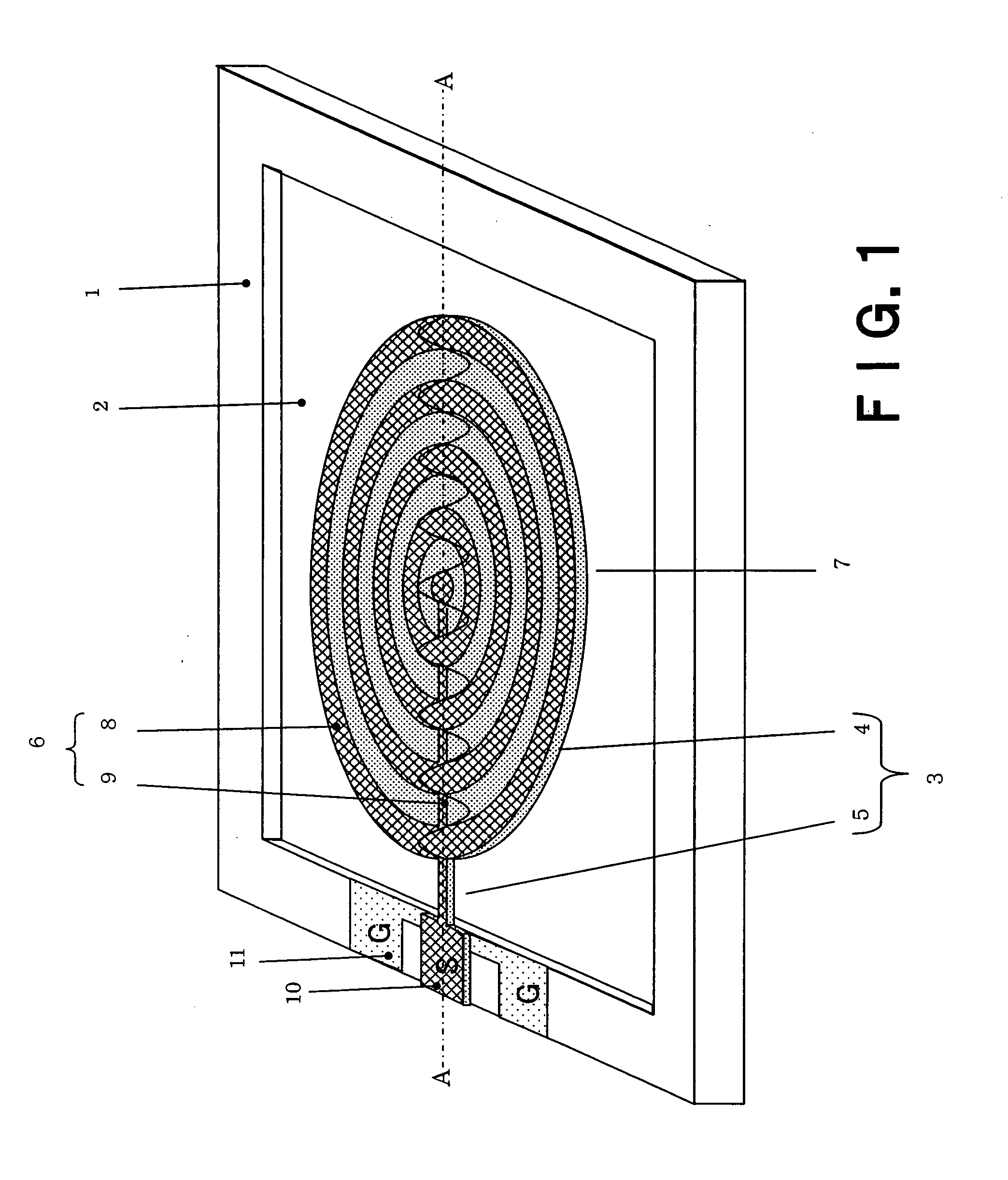
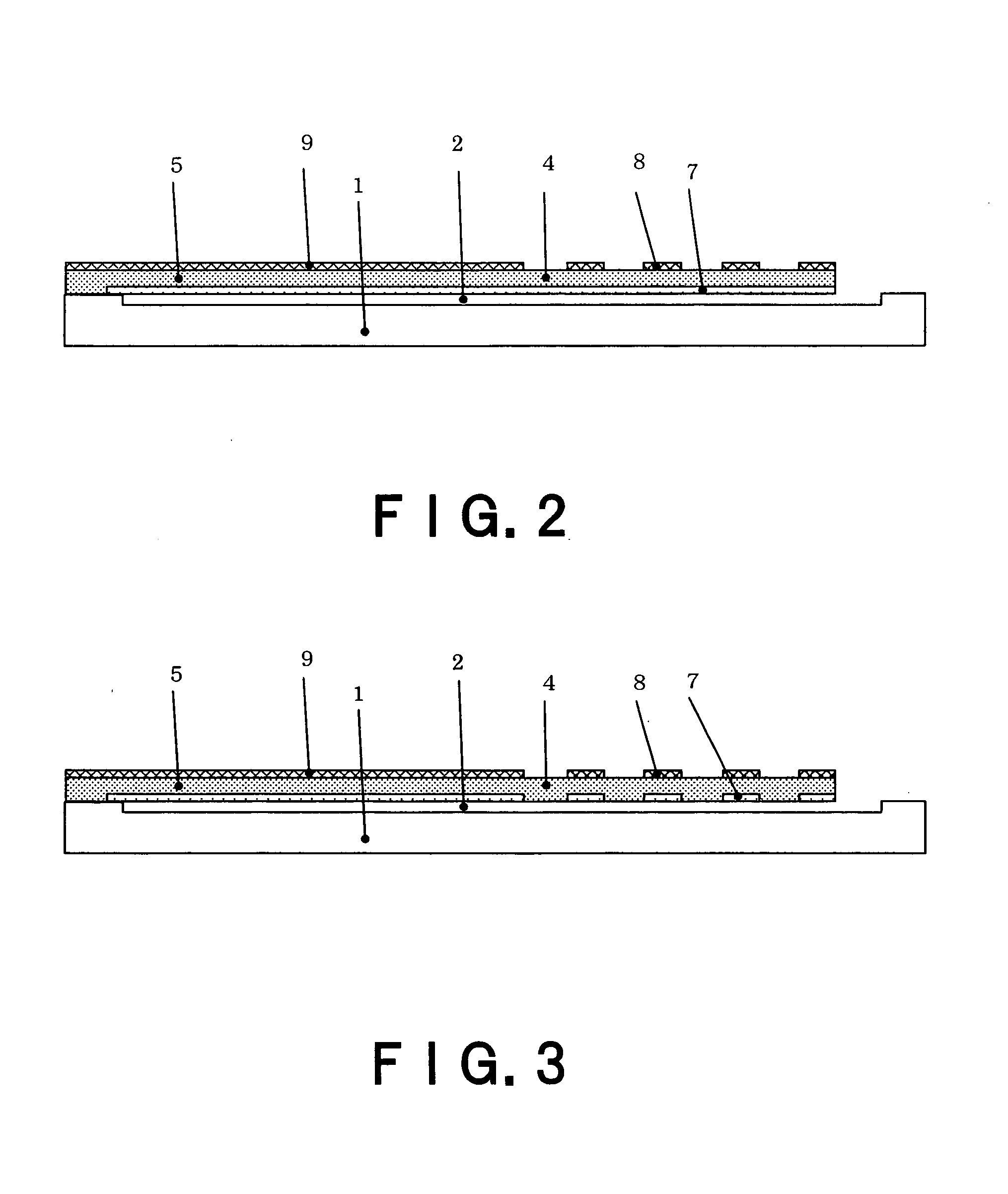
[0097]FIG. 1 is a perspective view of a one-port thin-film piezoelectric resonator according to a first embodiment of the invention. FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view along line A-A in FIG. 1.
[0098] As shown in FIG. 1, a rectangular concave part 2 is formed in the center of a substrate 1. A piezoelectric film 3 is formed above the concave part 2. The piezoelectric film 3 has a disc part 4 and a supporting part 5 that extends from the end of the disc part 4 to the end of a substrate 1 around the concave part 2 and supports the disc part 4. The disc part 4 and the supporting part 5 are integrally formed.
[0099] An upper electrode 6 is formed above the piezoelectric film 3. A lower electrode 7 is formed under the piezoelectric film 3. The upper electrode 6 has plural annular parts 8 of a concentric shape that have the same width and are arranged at the same intervals, respectively, and a bus bar 9 (a connection part) that connects the annular parts 8 one another. The lower electrode 7 ...
application 1
of the First Embodiment
[0113] It is possible to realize various filter circuits by using the plural thin-film piezoelectric resonators in FIG. 1. For example, FIG. 4 is a plan view showing an example of a ladder-type filter constituted by using the thin-film piezoelectric resonator in FIG. 1. FIG. 5 is a circuit diagram of the filter in FIG. 4.
[0114] The ladder-type filter in FIG. 5 has a series resonator 15 including three thin-film piezoelectric resonators connected in series and a parallel resonator 16 including two thin-film piezoelectric resonators connected between connection nodes among the three thin-film piezoelectric resonators and a ground terminal.
[0115] In the ladder-type filter shown in FIGS. 4 and 5, it is necessary to match a resonant frequency of the series resonator 15 with an anti-resonant frequency of the parallel resonator 16. In this embodiment, the resonant frequency and the anti-resonant frequency were matched by setting a diameter of the piezoelectric film...
application 2
of the First Embodiment
[0116]FIG. 6 is a plan view showing an example of a lattice-type high-frequency filter constituted by using the thin-film piezoelectric resonator in FIG. 1. FIG. 7 is a circuit diagram of the filter in FIG. 6. The lattice-type filter has, as shown in FIG. 7, a first resonator 17 including thin-film piezoelectric resonators connected to first opposite sides opposed to each other, respectively, and a second resonator 18 including thin-film piezoelectric resonators connected to second opposite sides opposed to each other, respectively.
[0117] It is necessary to match a resonant frequency of the first resonator 17 with an anti-resonant frequency of the second resonator 18. In this embodiment, the resonant frequency and the anti-resonant frequency were matched by setting a diameter of the piezoelectric films 3 of the second resonator 18 larger than that of the first resonator 17 by 0.65%. When characteristics of the filter manufactured were measured, a minimum inse...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com