Novel antimicrobial peptides with heparin binding activity
a technology of antimicrobial peptides and heparin, which is applied in the direction of peptide/protein ingredients, peptide sources, applications, etc., can solve the problems of not always the best treatment option for vaccines, no vaccine is available, and localised or generalised acute infections, so as to reduce the risk of allergenic reactions to antimicrobial peptides, reduce production costs, and increase the stability of peptides
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Antimicrobial Peptides
[0093] The antimicrobial peptides shown in the sequence listing and Table 1 below were synthesized by Innovagen AB, Ideon, SE-22370, Lund, Sweden. The purity and molecular weight of these peptides was confirmed by mass spectral analysis (MALDI.TOF Voyager).
TABLE 1OriginPeptideCodeC3aLRKCCEDGMR ENPMRFSCQR RTRFISLRK26C3aLGEACKKVFL DCCNYITELR RQHARASLGE27C3aCNYITELRRQHARASHLGLARCNY21Laminin-α1SRNLSEIKLLISQARKSRN16Laminin-α1SRNLSEIKLL ISQARKQAAS IKVAVSADRSRN29Laminin-α1KDFLSIELFR GRVKVKDF15Laminin-α1SAVRKKLSVE LSIRTSAV15Laminin-α5LGTRLRAQSR QRSRPGRWHK VSVRWLGT25Laminin-α5PPPPLTSASK AIQVFLLGGS RKRVLPPP25Laminin-α5RLRAQSRQRS RPGRWHKVSV RWRLR22Laminin-α1PGRWHKVSVR WPGR11Laminin-β1RIQNLLKITNLRIKFVKLRIQ18FibronectinQPPRARITGY IIKYEKPGQPP18Von Willebrand FactorYIGLKDRKRP SELRRIASQV KYAYIG23VitronectinAKKQRFRHRN RKGYRAKK15Protein C inhibitorSEKTLRKWLK MFKKRQLELYSEK20Histidine-rich glycopro-GHHPHGHHPH GHHPHGHHPHGHH20teinKininogenKHNLGHGHKH ERDQGHGHQRKHN20KininogenGGHVL...
example 2
Antibacterial Effects of Arginine and Lysine-Rich Peptides
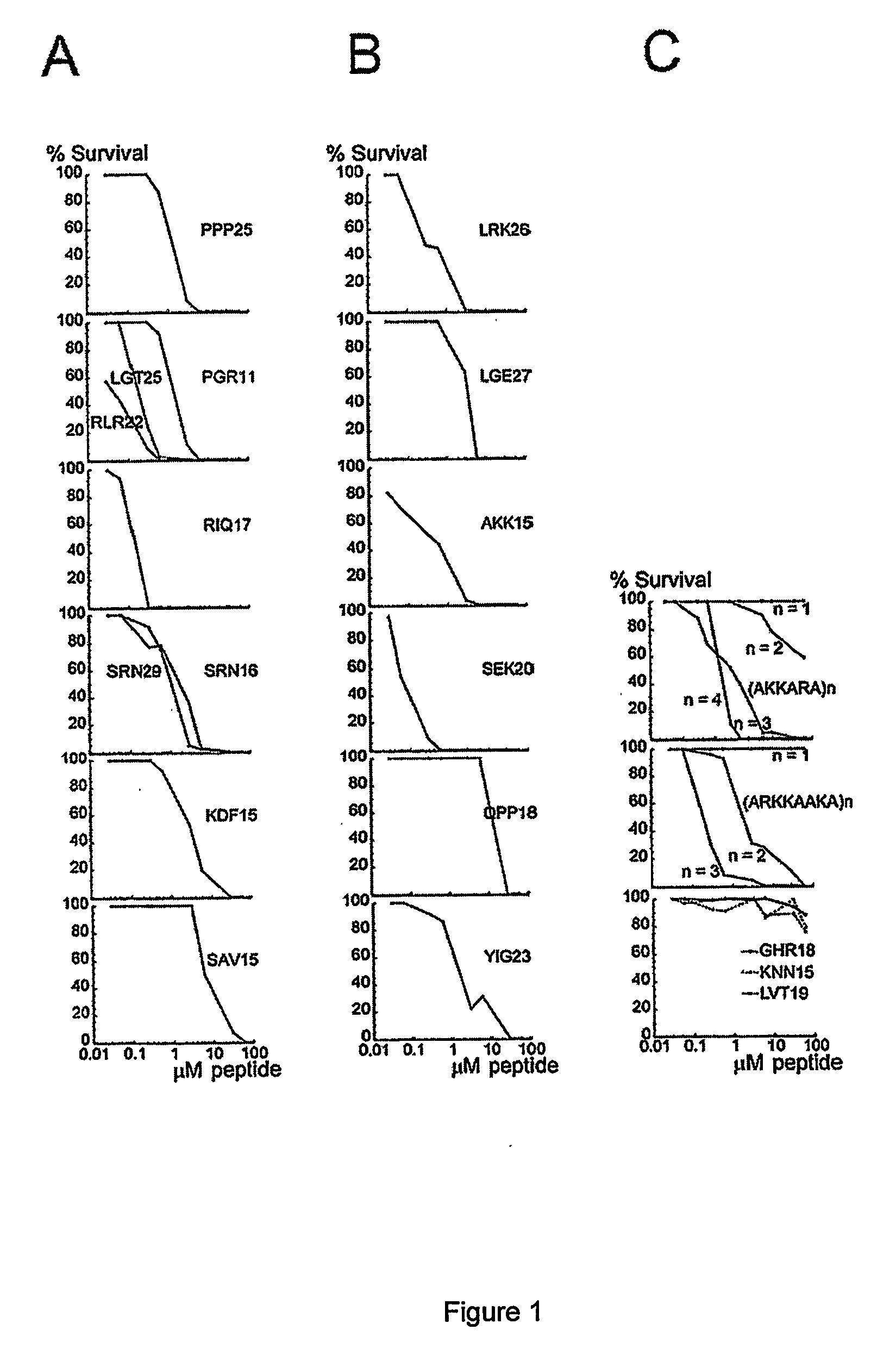
[0094]FIG. 1 describes bactericidal effects of arginine and lysine-rich peptides (Sequence listing) on Enterococcus faecalis. Bacteria were grown to mid-logarithmic phase in Todd-Hewitt (TH) medium. Bacteria were washed and diluted in either 10 mM Tris, pH 7.4, containing 5 mM glucose Bacteria (50 μl; 2×106 cfu / ml) were incubated, at 37° C. for 2 hours, with the synthetic peptide at concentrations ranging from 0.03 to 60 μM. To quantify the bactericidal activity, serial dilutions of the incubation mixture were plated on TH agar, followed by incubation at 37° C. overnight and the number of colony-forming units was determined.
[0095] 2×106 colony-forming units (CFU)×ml−1 of E. faecalis (isolate 2374) were incubated in 50 μl with peptides at concentrations ranging from 0.03 to 60 μM. (A) Synthetic peptides derived from laminin. Effect of peptides from the LG-domain of the α5 chain (PPP25: SEQ ID NO:13, LGT25: SEQ ID NO:12, RLR...
example 3
Radial Diffusion Assay Analysis of Antimicrobial Peptides (Table 2)
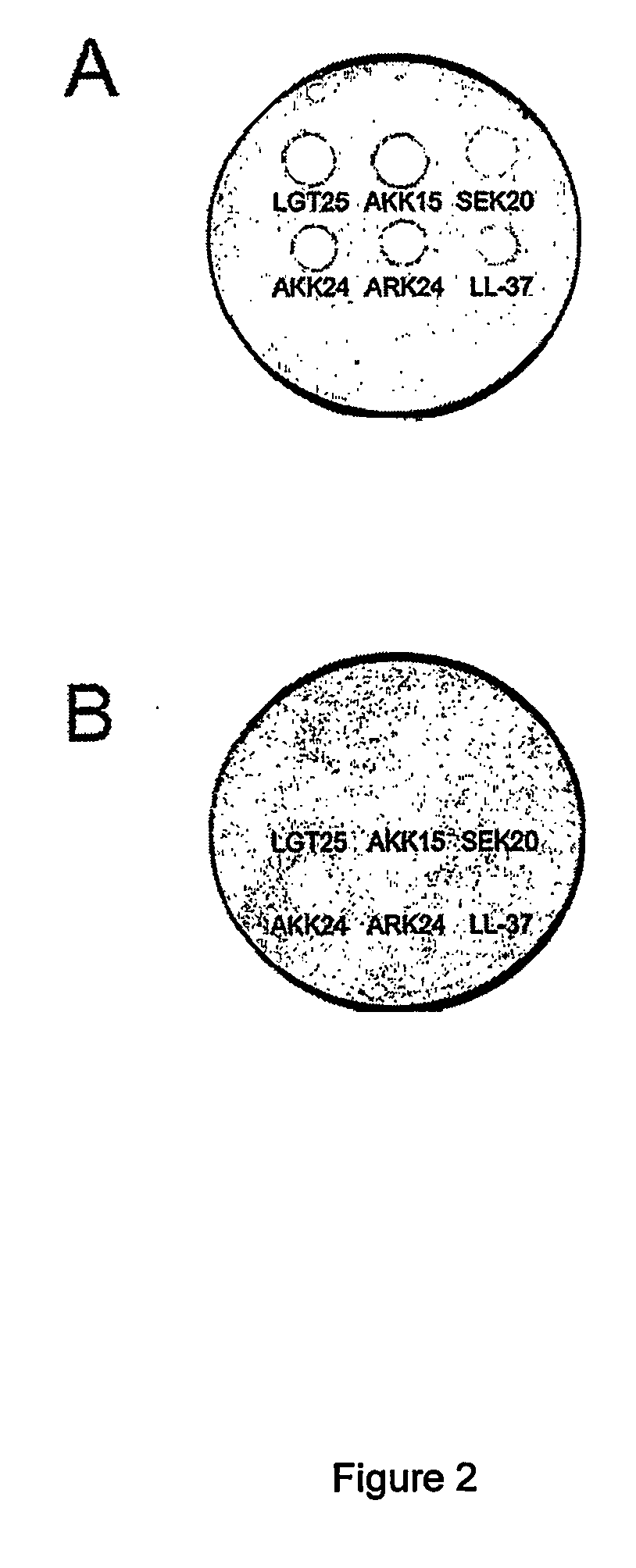
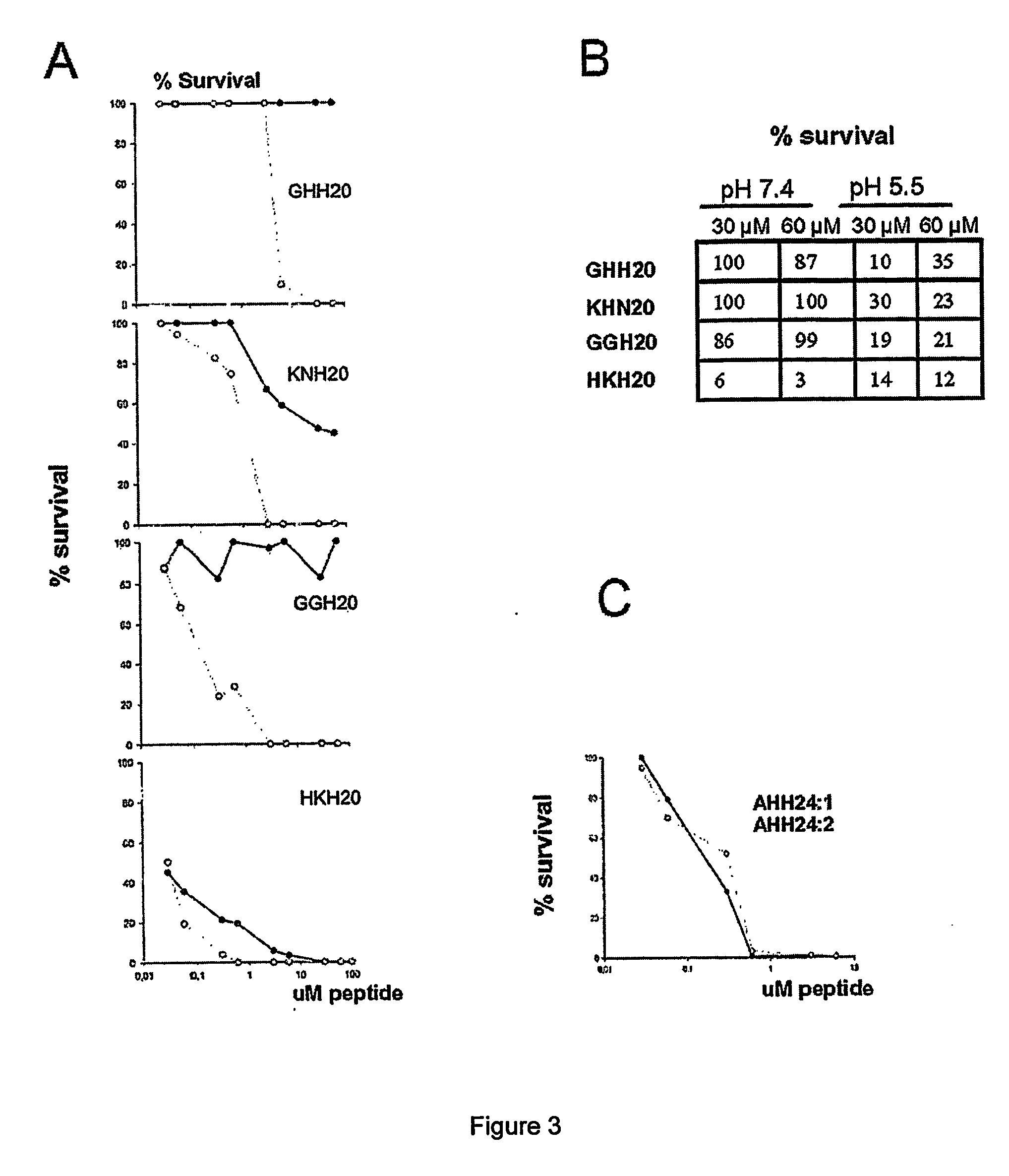
[0096] Radial diffusion assays (RDA) were performed essentially as described earlier (Andersson et al., Eur J Biochem, 2004, 271:1219-1226). Briefly, bacteria (E. coli) or fungi (C. albicans) were grown to mid-logarithmic phase in 10 ml of full-strength (3% w / v) trypticase soy broth (TSB) (Becton-Dickinson, Cockeysville, Md.). The microorganisms were washed once with 10 mM Tris, pH 7.4. 4×106 bacterial cfu or 1×105 fungal cfu was added to 5 ml of the underlay agarose gel, consisting of 0.03% (w / v) TSB, 1% (w / v) low-electroendosmosistype (Low-EEO) agarose (Sigma, St Louise Mo.) and a final concentration of 0.02% (v / v) Tween 20 (Sigma). The underlay was poured into a Ø85 mm petri dish. After agarose solidified, 4 mm-diameter wells were punched and 6 μl of test sample was added to each well. Plates were incubated at 37° C. for 3 hours to allow diffusion of the peptides. The underlay gel was then covered with 5 ml of m...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com