Progressive cavity pump/motor stator, and apparatus and method to manufacture same by electrochemical machining
a technology of progressive cavity and motor, which is applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, machines/engines, liquid fuel engines, etc., can solve the problems of limited precision of drive bars and electrodes, limited electrical transfer ability, and very cost-effective threaded joints, so as to reduce adverse effects, improve heat transfer, and reduce insulating effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
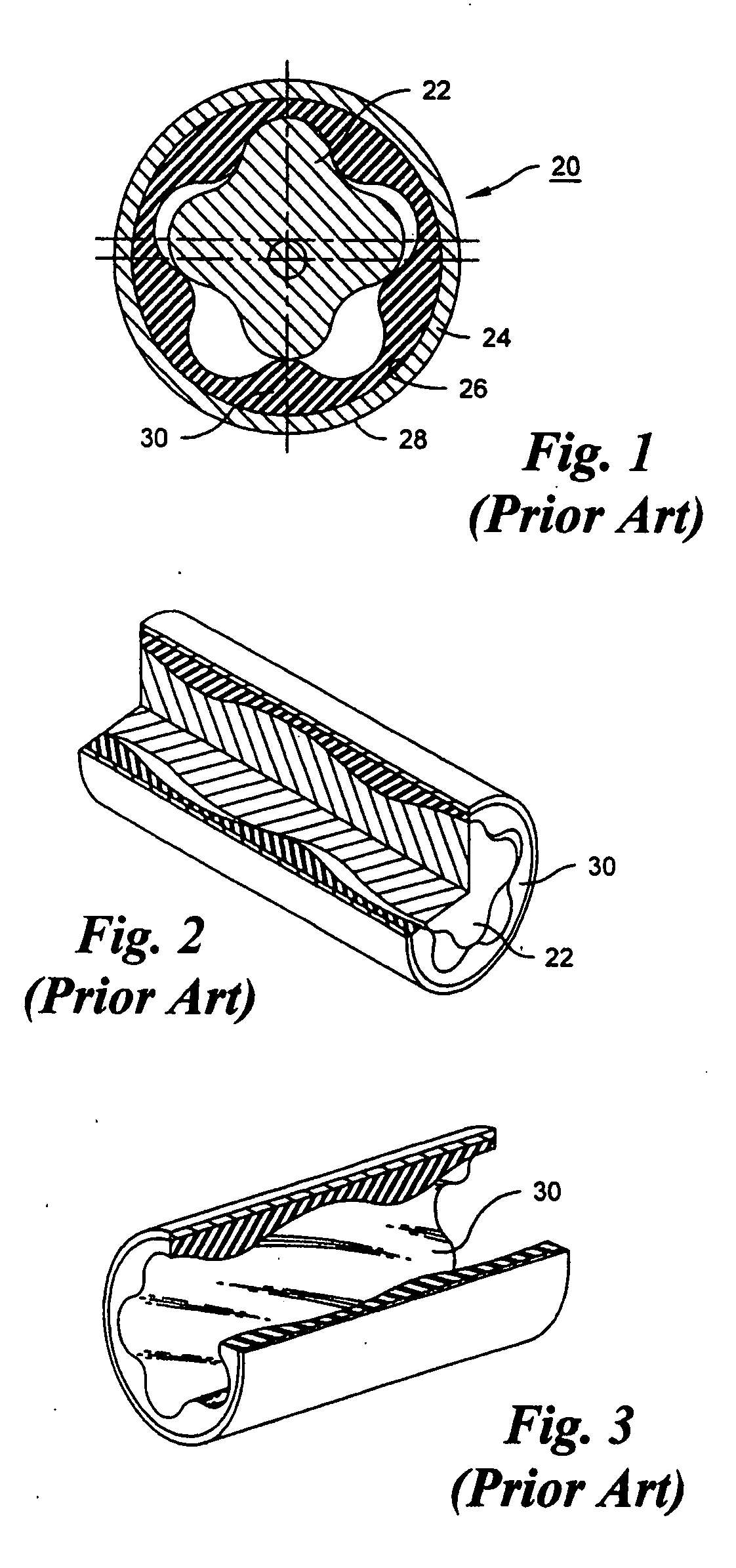
[0031] As shown in FIGS. 1-3, the conventional Moineau motor 20 comprises a helically lobed rotor 22 disposed within a stator, the stator comprising a metal tube 24 having a circular, cylindrical interior wall 26 and a circular, cylindrical exterior wall 28, the interior wall having a molded elastomer liner 30 formed with helical lobes cooperable with the rotor to provide moving fluid chambers as the rotor rotates. As seen in all three of FIGS. 1-3, the thickness of the elastomer liner varies because of the presence of the lobes.
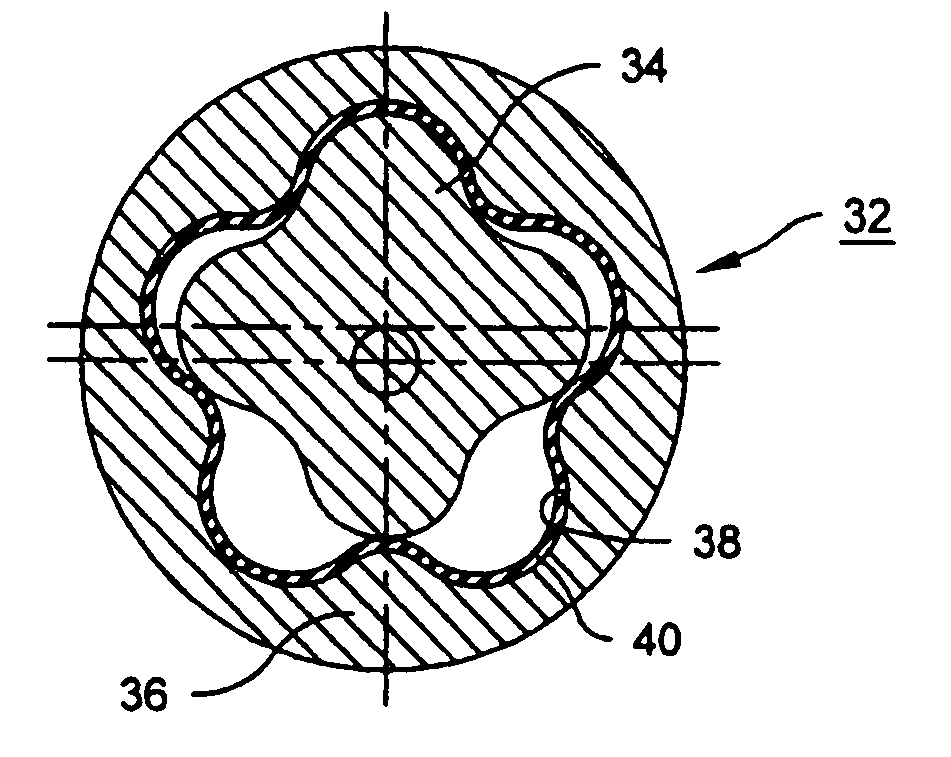
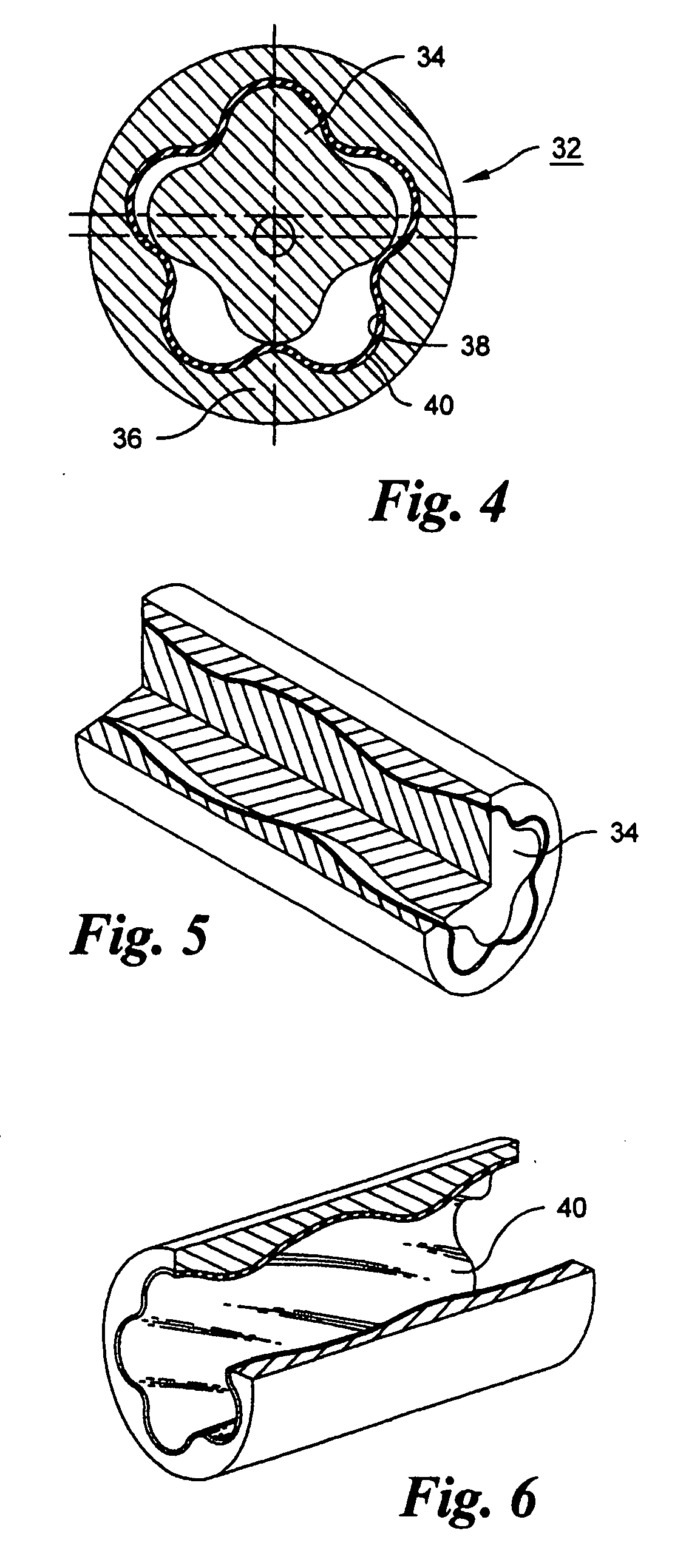
[0032] A Moineau Motor 32 in accordance with the invention, illustrated in FIGS. 4-6, comprises a helically lobed rotor 34 disposed within a stator comprising a tube 36 and a flexible liner 40. The tube 36 is composed of steel or a similar structural material. The tube has an interior wall 38 having helical lobes formed by electrochemical machining, and a circular, cylindrical exterior. Using a suitable mold or core (not shown), the molded liner 40, of rubb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com