Low defect group III nitride films useful for electronic and optoelectronic devices and methods for making the same
a technology of nitride films and gan films, which is applied in the direction of polycrystalline material growth, chemically reactive gas growth, crystal growth process, etc., can solve the problems of large number of crystal defects in the gan film and active device layer, unsuitable lifetime, and the dislocation density has a detrimental effect on the performance and lifetime of the device, so as to promote the formation of pits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Low-Defect GaN Film Growth
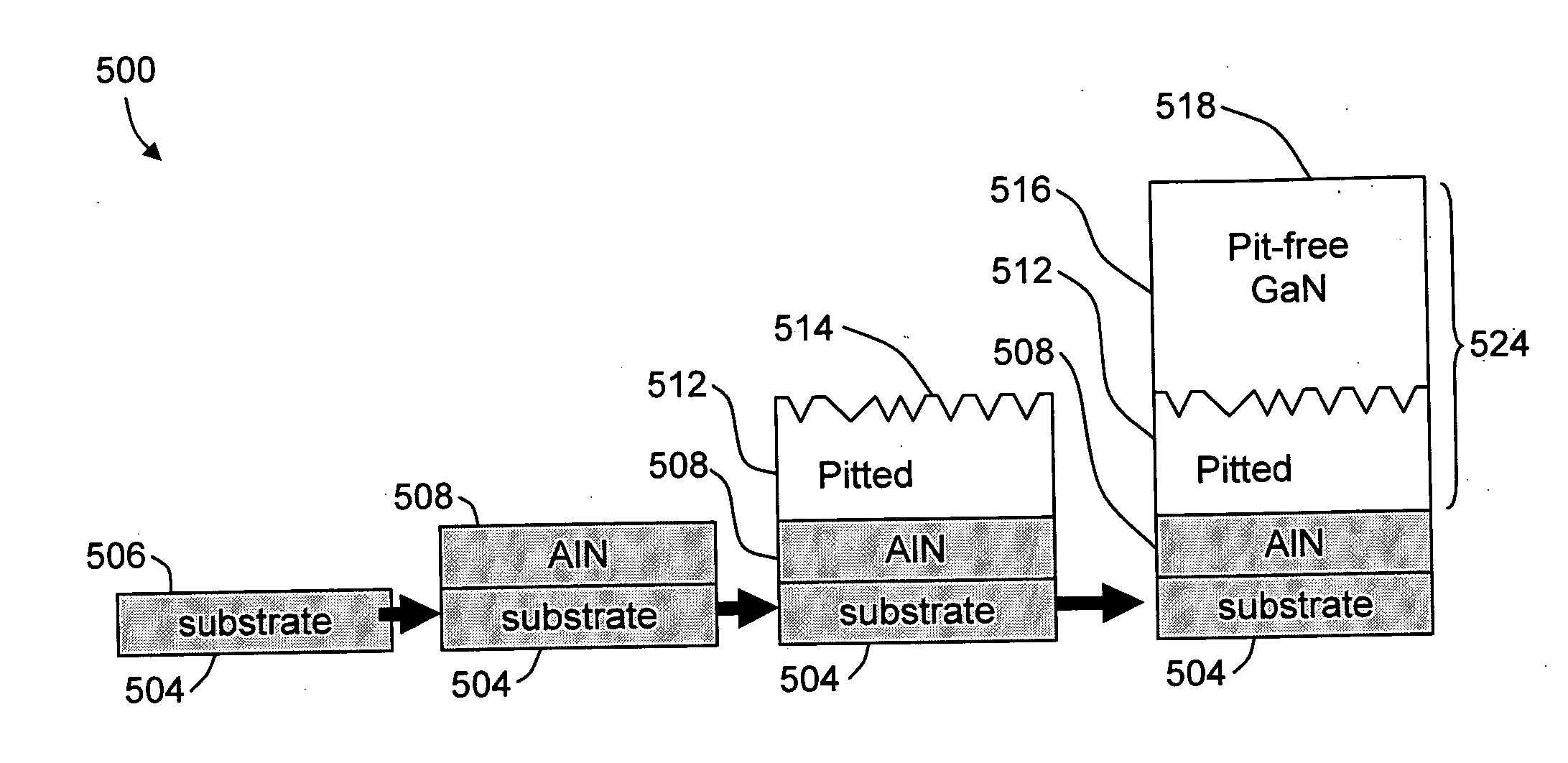
[0071] In this example, we illustrate the growth of a high-quality, low-defect GaN film suitable for the further growth of electronic and optoelectronic devices. A 2″-diameter, 430-micron thick sapphire was used as the starting substrate. Using the sputtering method disclosed in U.S. Pat. No. 6,784,085, an AlN layer approximately 0.7 μm thick was grown on the sapphire substrate for use as a template layer for the HVPE GaN growth. X-ray diffraction was used to verify the AlN film was single-crystal. The AlN / sapphire structure was loaded into a vertical HVPE system and the GaN growth was commenced.
[0072] The HVPE GaN film was grown by a two-step method. The GaN film was first grown under conditions of growth rate of approximately 260 microns per hour, growth temperature of 955° C., HCl flow rate of 92 sccm, and NH3 flow rate of 2500 sccm. After growth of approximately 4 minutes under these growth conditions, the growth rate was reduced to approximately 65 m...
example 2
Low-defect GaN Film Growth
[0074] In this example, we illustrate the growth of another high-quality, low-defect GaN film suitable for the further growth of electronic and optoelectronic devices. A 2″-diameter 430-micron thick sapphire was used as the starting substrate. Using the sputtering method disclosed in U.S. Pat. No. 6,784,085, an AlN layer approximately 0.7 μm thick was grown on the sapphire substrate for use as a template layer for the HVPE GaN growth. The AlN / sapphire structure was loaded into a vertical HVPE system and the GaN growth was commenced.
[0075] The HVPE GaN film was grown by a two-step method. The GaN film was first grown under conditions of growth rate of approximately 260 microns per hour, growth temperature of 955° C., HCl flow rate of 92 sccm, and NH3 flow rate of 2500 sccm. After growth of approximately 3 minutes under these growth conditions, the growth rate was reduced to approximately 30 microns per hour by reducing the HCl flow rate to 10 sccm. At the ...
example 3
Low-defect GaN Film Growth with Lapping Treatment
[0076] The GaN film on sapphire obtained from Example 2 is mounted on a stainless steel plate using wax with the GaN film facing the plate. The backside of the sapphire substrate is lapped on a metal lapping plate with 30-micron diamond slurry. After removing approximately 10 microns from the backside of the sapphire substrate, the wafer bow is reduced from approximately 95 microns to approximately 40 microns.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com