Copper powder
a technology of copper powder and weatherability, which is applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, solventing apparatus, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of inadequate response to the need for improving the weatherability of copper powder for use in conductive paste, and achieve excellent weatherability, stable operation of electronic equipment, and stable surface condition. , the effect of reducing the risk of aging
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
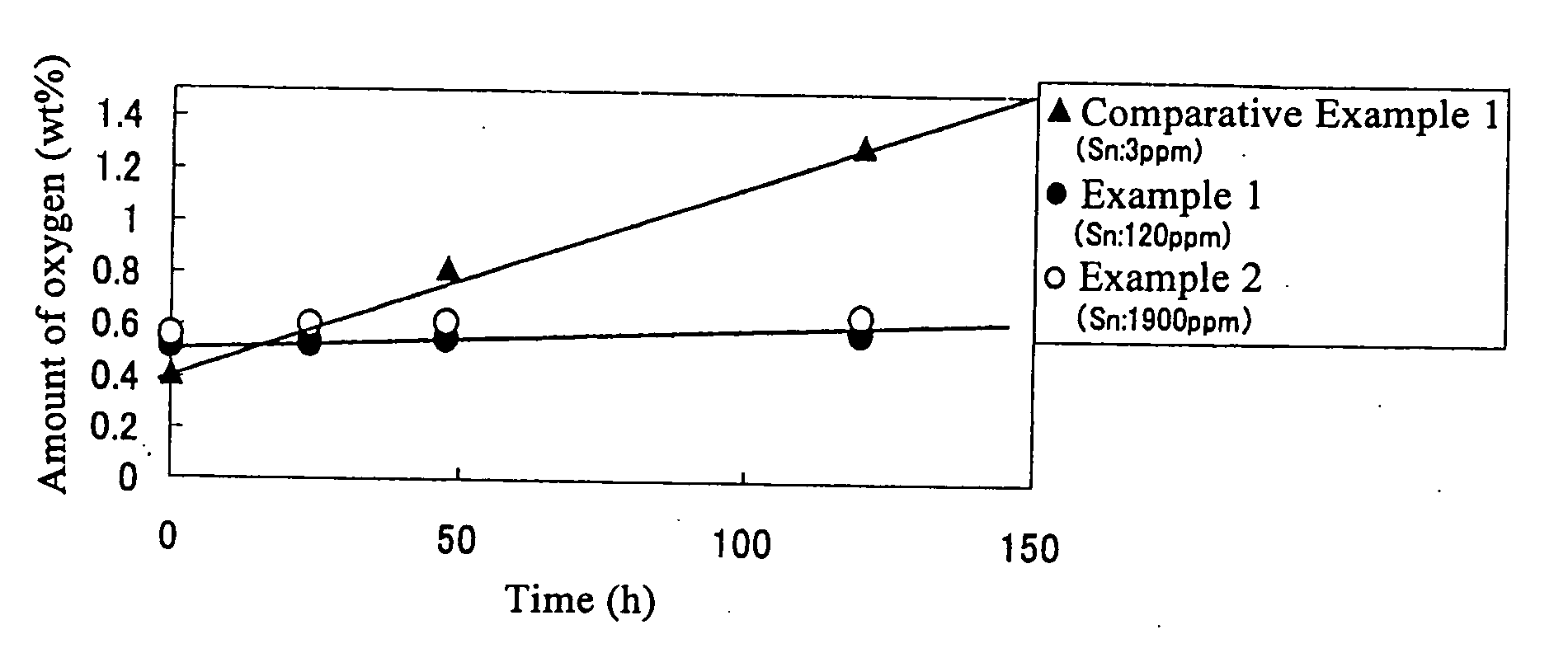
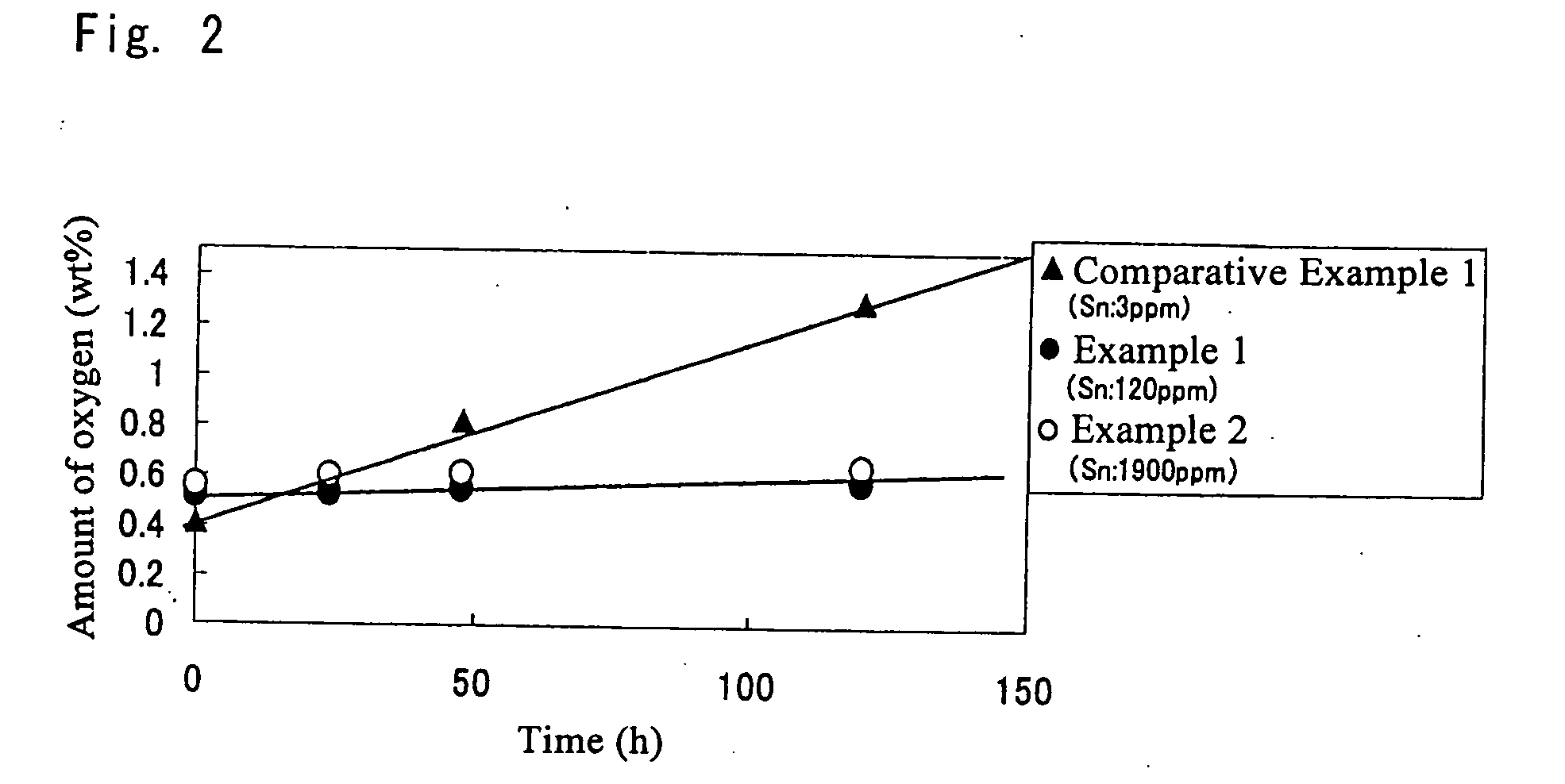
[0027] Electrolytic cuprous oxide of an average particle diameter of 3 μm was prepared. The prepared electrolytic cuprous oxide had a broad particle size distribution, i.e., 50% or more of all particles fell outside the range of 3 μm±1 μm. The Sn content of the electrolytic cuprous oxide was 0.01 mass %. This electrolytic cuprous oxide, 135 g, was dispersed in 3,750 g of pure water. The dispersion was added with 7.5 g of cuprous chloride as water-soluble copper salt and 15 g of polyvinyl alcohol as protective colloid and then heated to 40° C. under stirring. To the heated mixture were added 100 g of 80% hydrazine hydrate as reducing agent and 22.5 g of acetic acid as complexing agent. The resulting liquor was heated to 60° C. over one hour and then held at 60° C. for another hour to allow the reduction reaction to proceed. The liquor after reaction was subjected to solid-liquid separation and the recovered solids were washed with water and dried to obtain a copper powder. The copper...
example 2
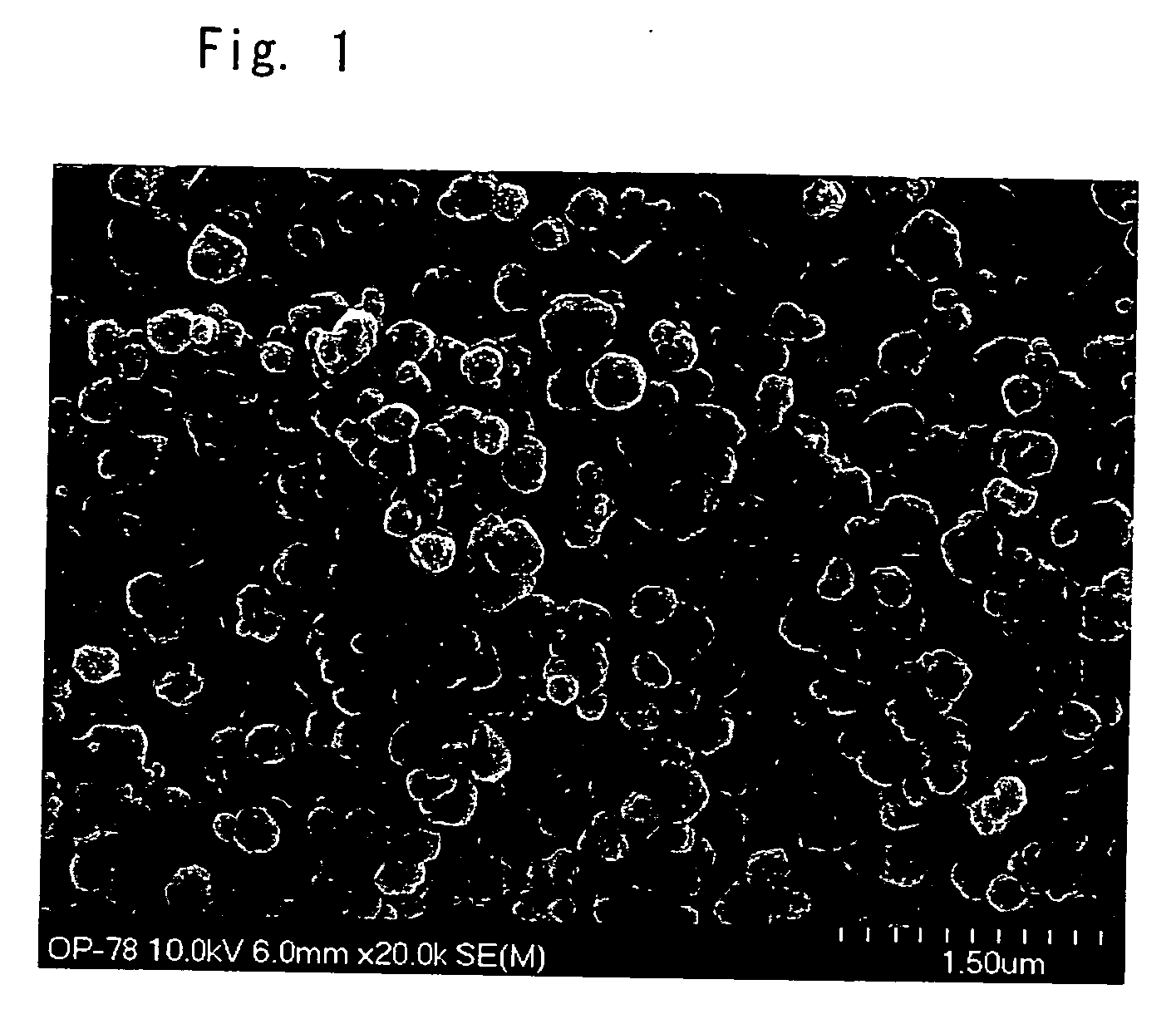
[0029] To 3,750 g of pure water were added 7.5 g of cuprous chloride as water-soluble copper salt and 15 g of polyvinyl alcohol as protective colloid. The result was heated to 40° C. under stirring, whereafter 100 g of hydrazine hydrate was added as reducing agent. To the resulting reaction liquor was added 135 g of the same electrolytic cuprous oxide as used in Example 1, 0.43 g of stannic chloride as stannic salt and 22.5 g of acetic acid as complexing agent. The resulting liquor was heated to 60° C. over one hour and then held at 60° C. for another hour to allow the reduction reaction to proceed. The liquor after reaction was subjected to solid-liquid separation and the recovered solids were washed with water and dried to obtain a copper powder. The copper powder was observed under a scanning electron microscope (SEM) and the diameters of the particles within the field of vision were measured. It was found that the average particle diameter DM was 0.3 μm and that the particle dia...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter DM | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com