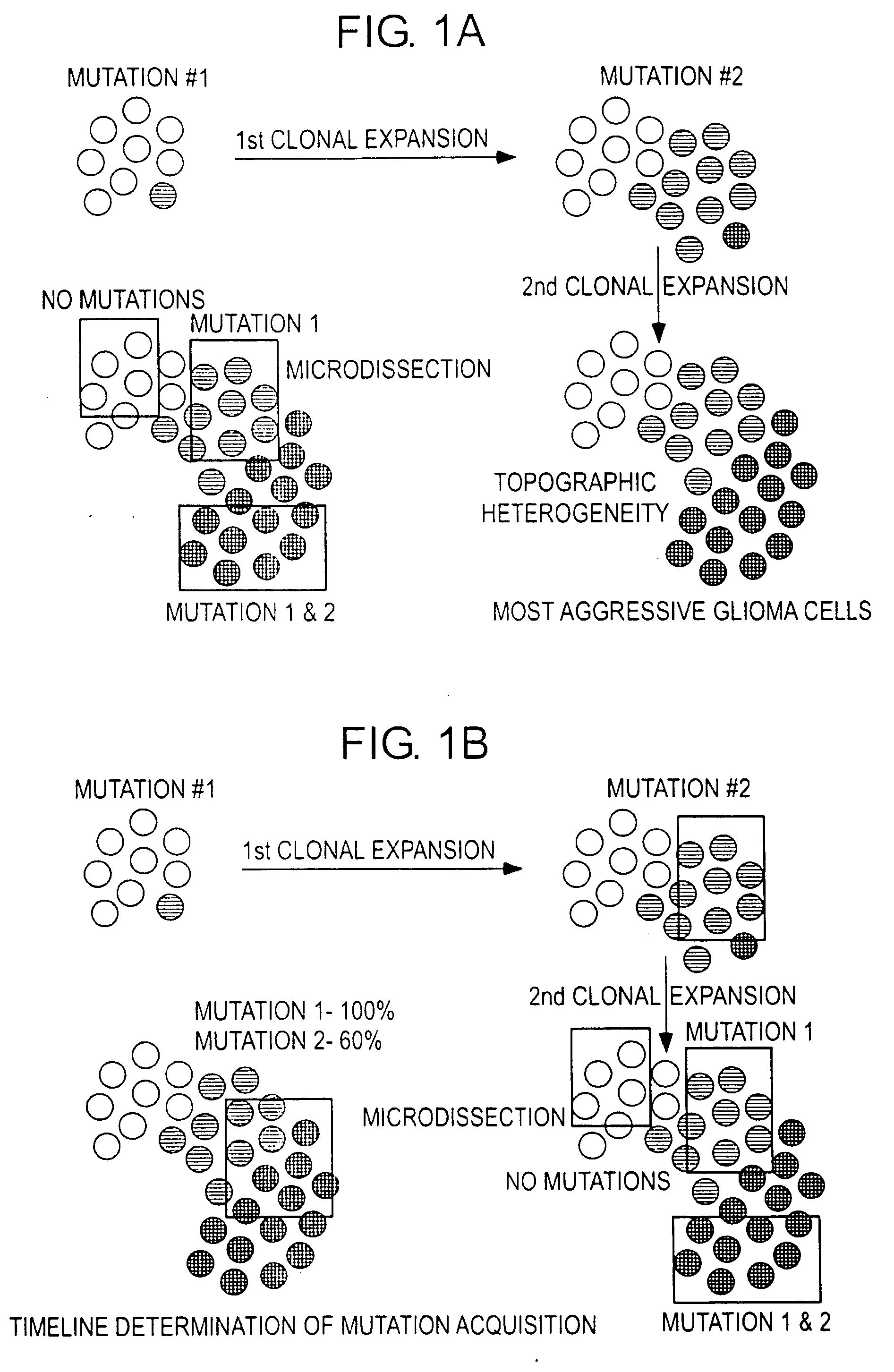
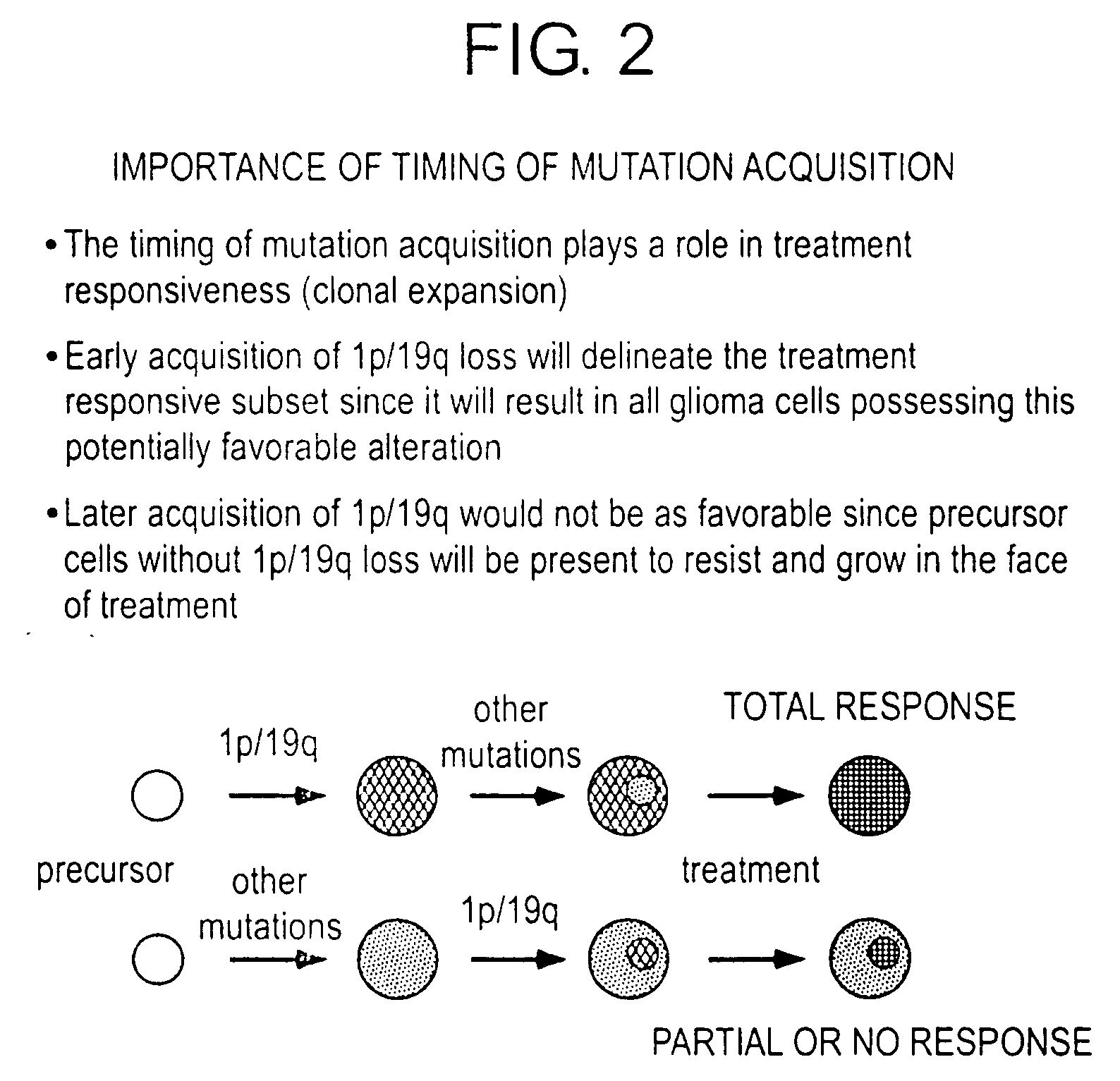
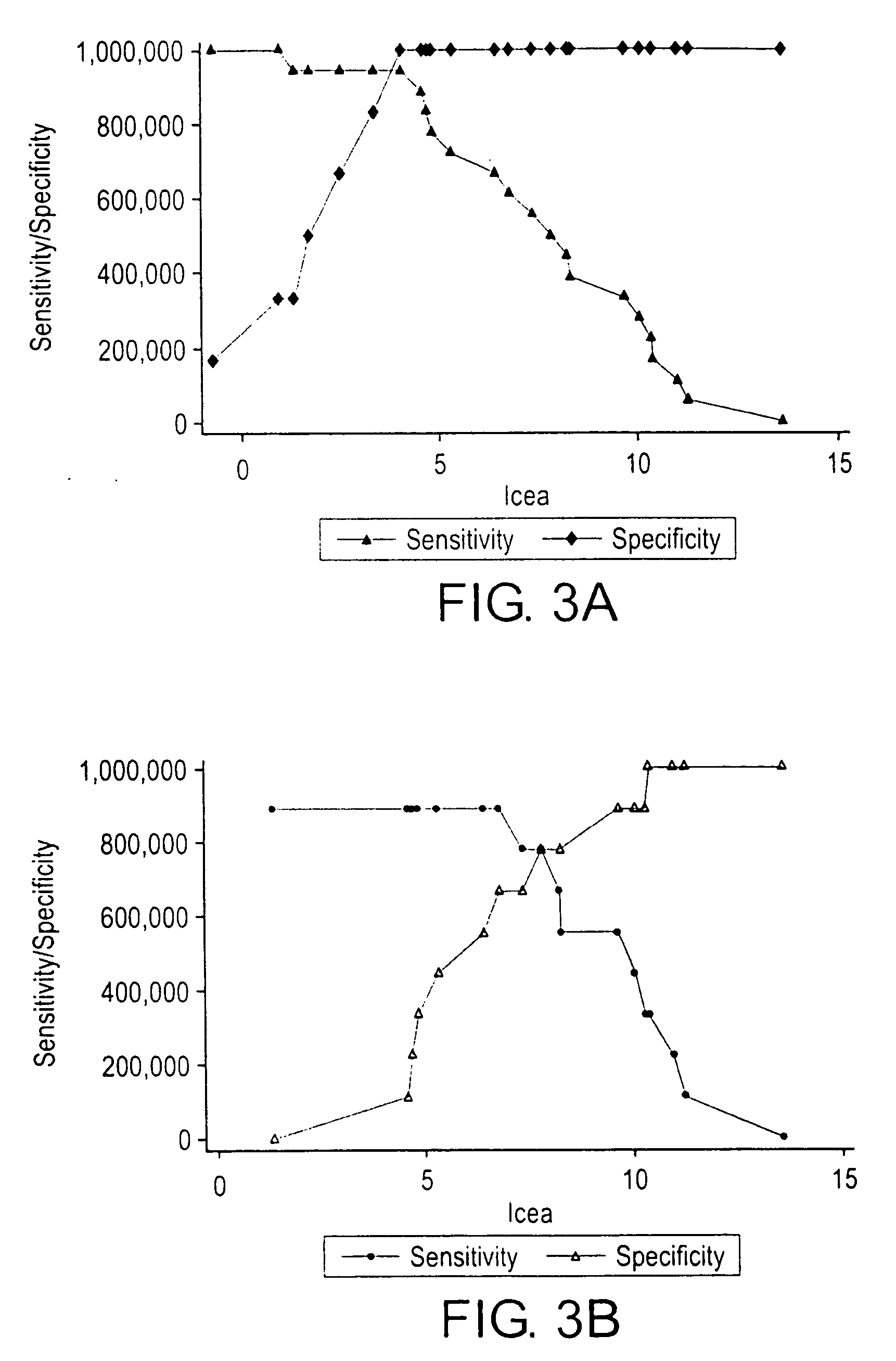
Topographic genotyping for determining the diagnosis, malignant potential, and biologic behavior of pancreatic cysts and related conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0187] A study was undertaken spanning 19 months from November of 2002 to May of 2004. All patients presenting to Presbyterian University Hospital with a pancreatic cyst were eligible for inclusion. EUS was performed with a Pentax CLA echo-endoscope. Pancreatic cyst aspiration was performed according to clinical need (Wilson Cook N1 (22 gauge or 25 gauge needles)) and fluid sent for cytological evaluation and CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen) tumor marker analysis. Intravenous (IV) antibiotics (Levofloxacin, 500 mg) were administered at the time of cyst aspiration.
[0188] Cyst aspirate cytology exams were performed in a routine fashion, familiar to the skilled artisan in the medical profession. The primary tissue and fluid targets were from the head of the pancreas. Cytopathologic criteria for malignancy included nuclear enlargement, pleomorphism (minimum of 3 to 4 fold variation in nuclear size), elevated N / C ratio, nuclear membrane irregularity, and coarse chromatin (Solcia, et al., ...
example 2
[0209] An interesting observation, consistently displayed by most metastatic neoplasms, is the preservation of the time course of mutation acquisition in metastatic deposits of tumor (FIG. 6, Table 8). In this representative example, a pancreatic carcinoma was associated with an isolated recurrence of cancer in the lip after a two year latency interval. The possibility of new primary occurrence was considered in view of the unusual location for metastatic spread (i.e., to the lip). No other tumor deposits were noted in the patient. The pancreatic and lip neoplasms were each microdissected at two sites within each specimen. Tissue microdissection was designed to capture purified representative cellular samples of each tumor deposit in pancreas and in lip. Tissue microdissection was performed manually using a scalpel under stereomicroscopic observation (Olympus SZ-PT). The neoplasms were found to be highly concordant with respect to the specific markers and alleles affected by mutatio...
example 3
[0213] Additional experiments were performed to validate the approach of calculating the mutation acquisition pattern from the ratio of allele peak heights on electropherograms. These involved 17 cases of bile duct cancer and pancreatic cancer with cytologic and surgical specimens previously studied for microdissection based genotyping (Table 9). The methodology is similar, it involves obtaining and analyzing multiple cells clusters from different parts of the tumor (cytology and surgical pathology) for k-ras point mutation and microsatellite loss analysis. The LOH analysis utilized fluorescent capillary electrophoresis. Allelic imbalance analysis is based on the use of fluorescent labeled primers (HEX, TET, FAM, and TAMRA) during PCR amplification. The primer labeled molecules are then separated by capillary electrophoresis according to manufacturer's recommendations (Applied Biosystems, ABI 3100; Mountainview, Calif.). The temporal sequence for each patient was calculated as discu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com