Gypsum boards with glass fiber reinforcements having a titanate or zirconate coupling coating
a technology of glass fiber reinforcement and gypsum board, which is applied in the field of glass fibers, can solve the problems of difficult to predict or achieve fully satisfactory properties of glass fiber dispersed into a gypsum matrix, either as fibers or as finished products like non-woven mats, and achieve the effect of increasing flexural strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
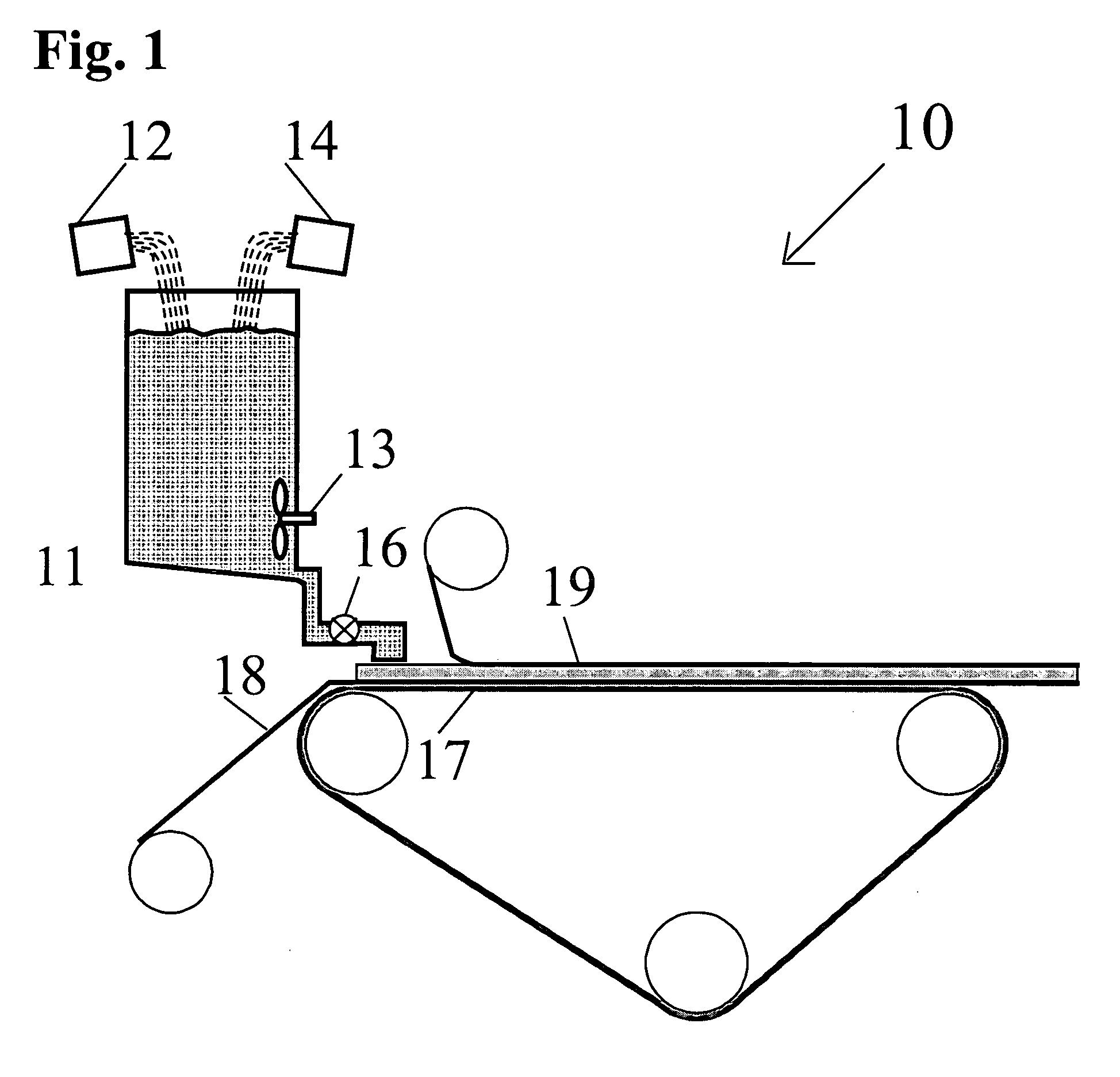
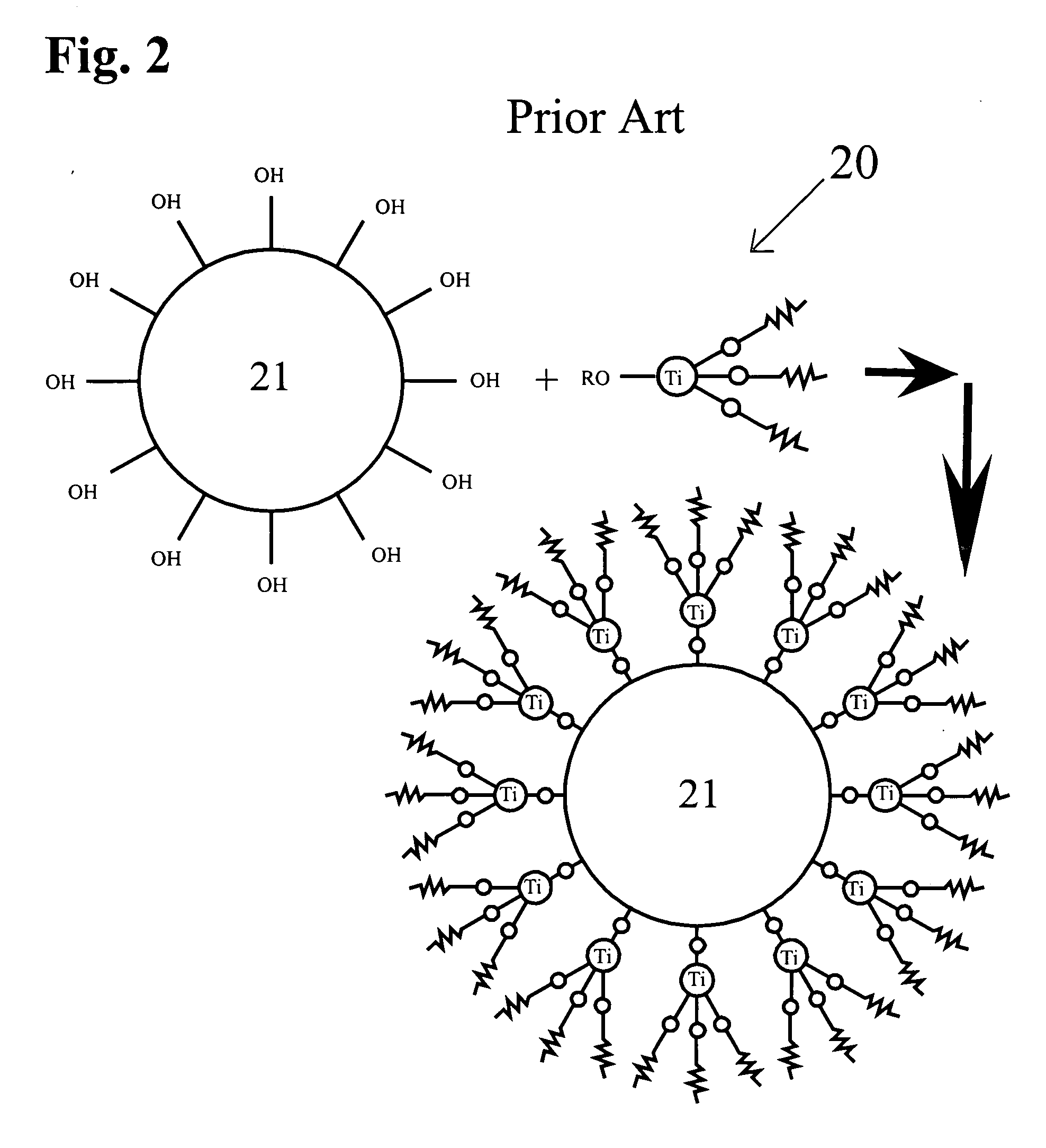
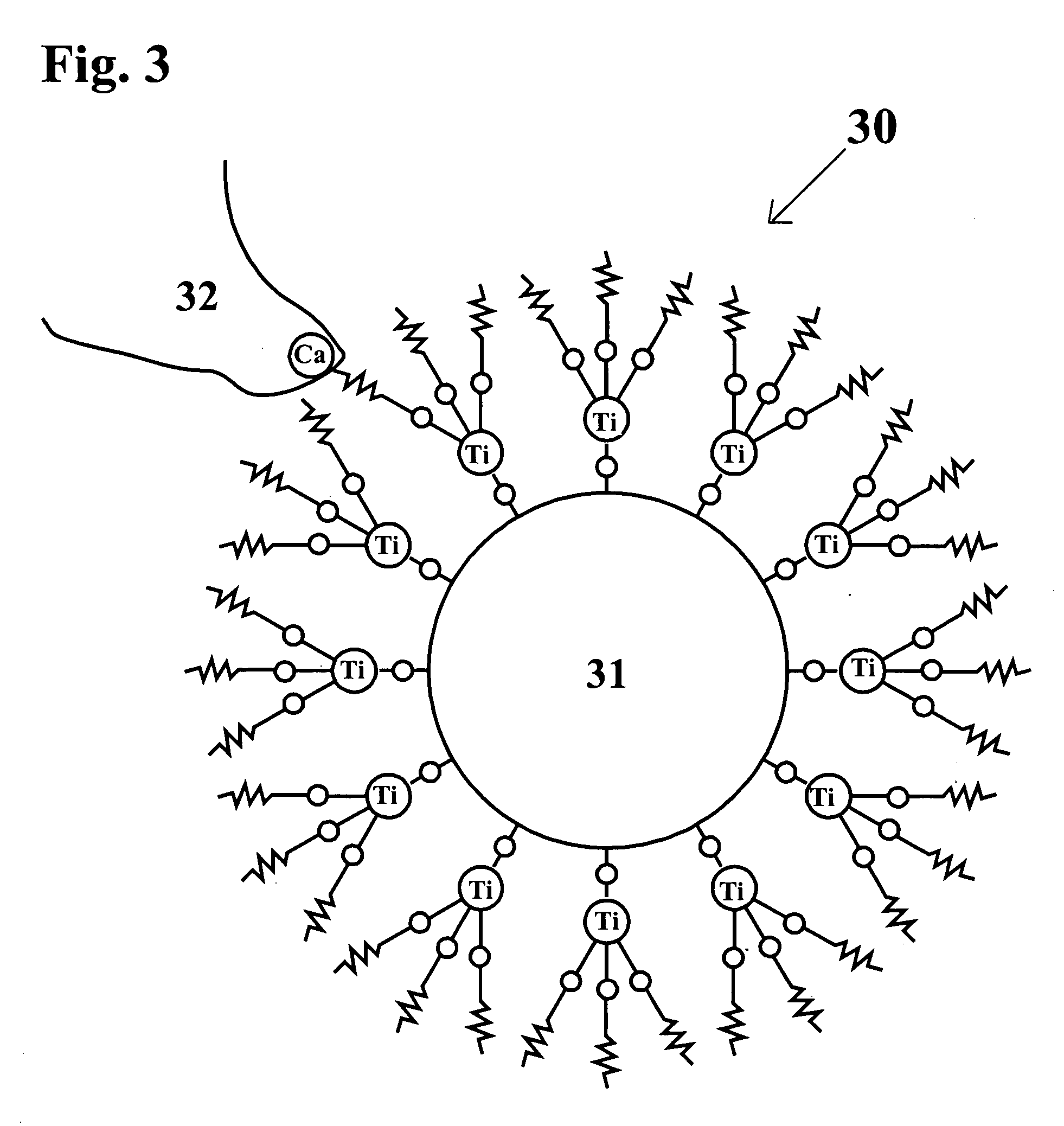
[0040] The present invention provides a gypsum board having glass fibers coated with a thin layer of titanium or zircinium coupling agent or sizing composition that chemically adheres to the glass fiber surface due to OH groups bonded to the Titanium IV or Zirconium IV ion. The titanium based coupling composition is selected from the group consisting of LICA 12, LICA 38, LICA 38J, and LICA 38ENP. The zirconium based coupling composition is a member selected from the group consisting of NZ 38 and NZ 38J. The amount of coupling agent needed is generally small. Specifically, the quantity of coupling agent is selected to be in the range of 0.01 to 3 weight percent of the glass fiber weight, providing a thin coating on the glass fibers external surface sufficient to provide a bond. A rotating roller covered with coupling agent solution may be used to deliver the titanium, or zirconium based, coupling composition to the glass fibers and produce a uniform coating. The coated glass fibers w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com