Adipose stromal stem cells for tissue and vascular modification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Isolation and Characterization of Stem Cells from Adipose Tissue
Isolation of Stem Cells From Adipose Tissue
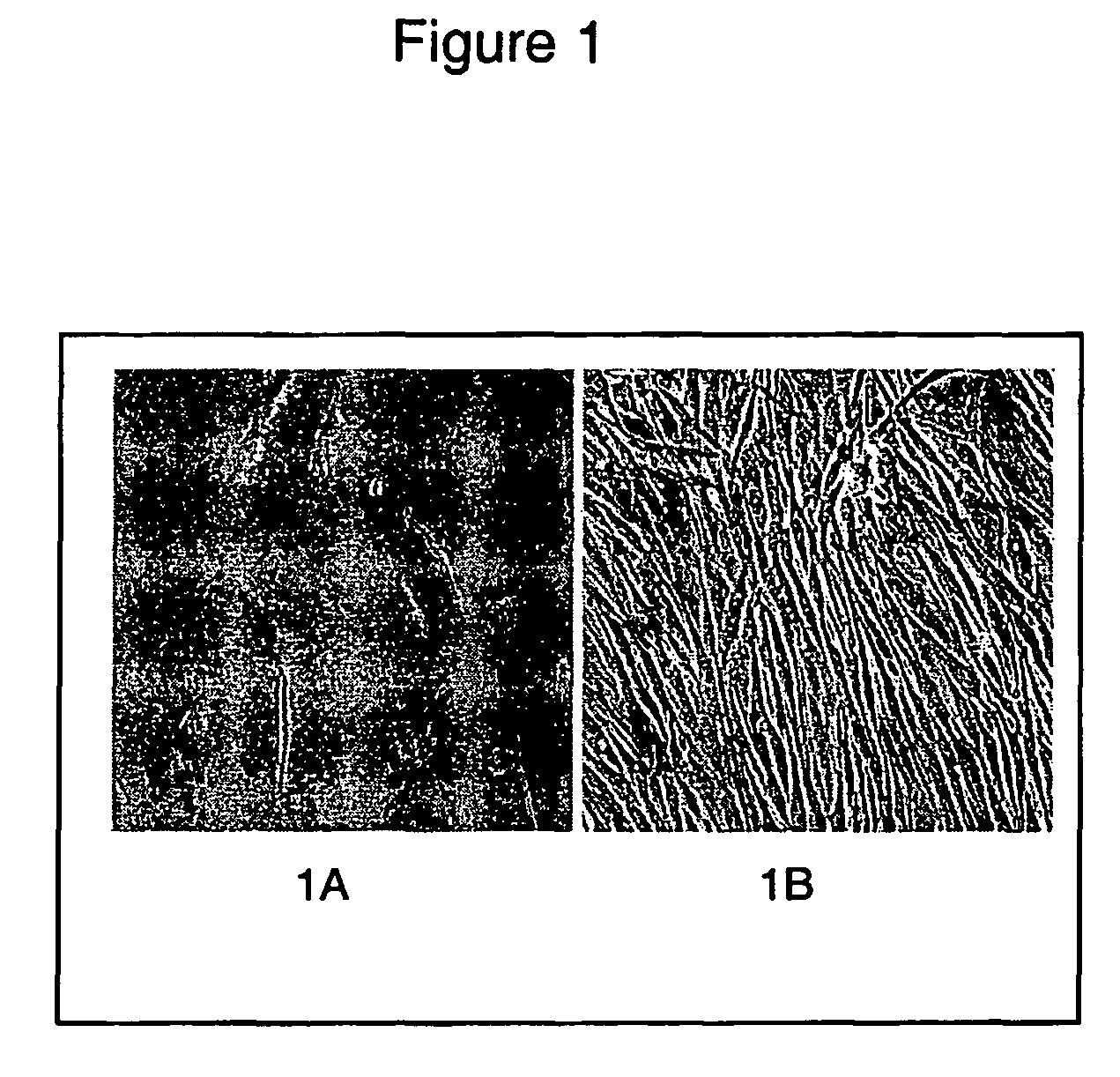
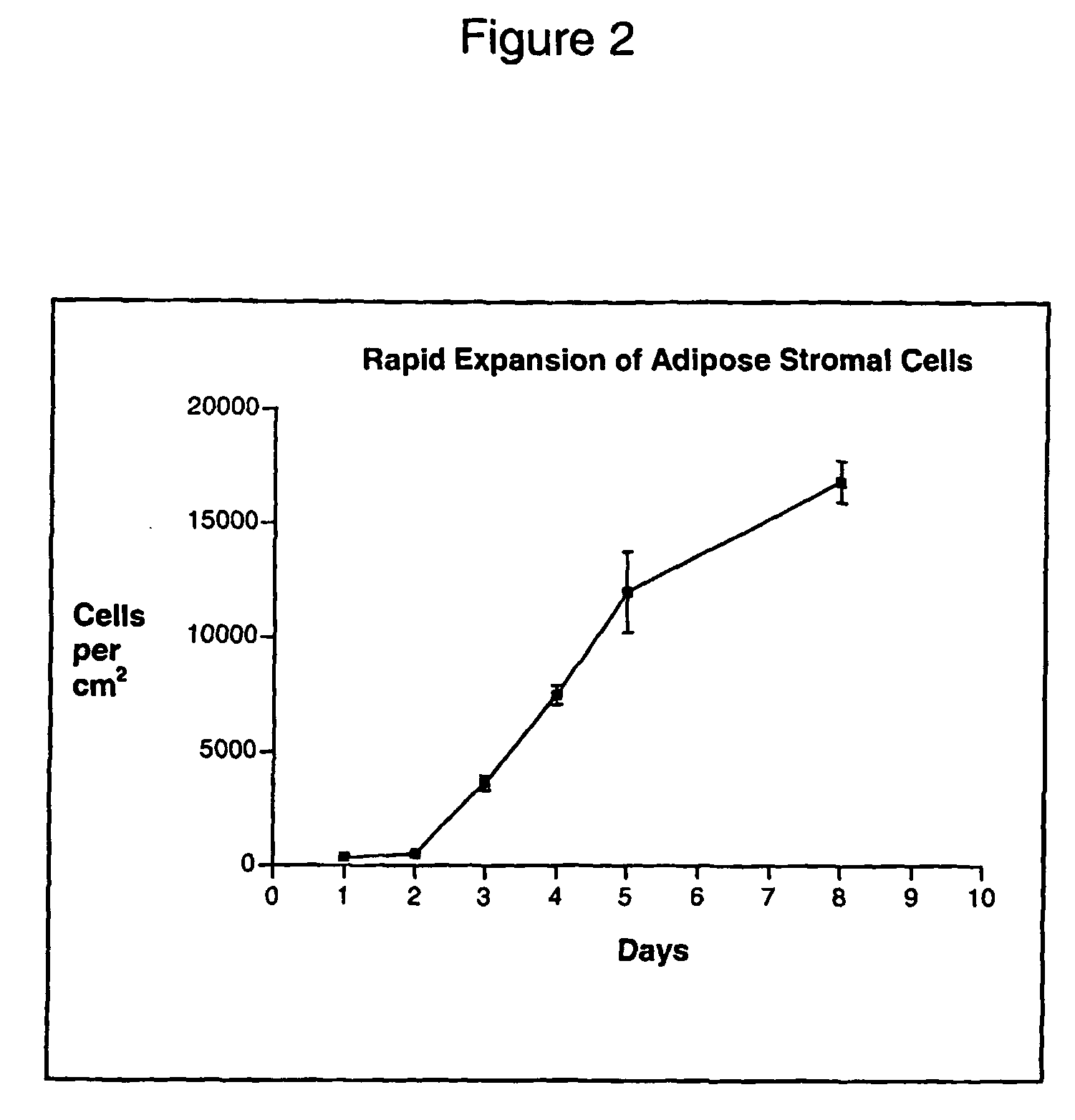
[0116] To isolate adipose stromal cells (ASCs,) subcutaneous adipose tissue (5-15 grams) was obtained from obese patients undergoing a gastroplasty procedure. The tissue was suspended in PBS and dissected into, smaller pieces using a scalpel. Collagenase (Worthington Biochemical) was then added to the suspension and placed in a shaker at 37° C. for approximately 90 minutes. The digested sample was filtered through a 750 micron Nitex filter and a 50 micron filter, and rinsed with Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Media (DMEM) with 10% Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS). The filtered suspension was centrifuged at 200 g for 5 minutes and the top layer consisting of adipocytes was discarded. After a second spin at 300 g for 5 minutes, any remaining adipocytes in the top layer were again discarded. The cell pellet was re-suspended in red cell lysis buffer and centrifuged at 300 g after 5-10 minute...
example ii
Differentiation of Adipose Derived Stromal Cells
ASCs Can Develop a Vascular Phenotype
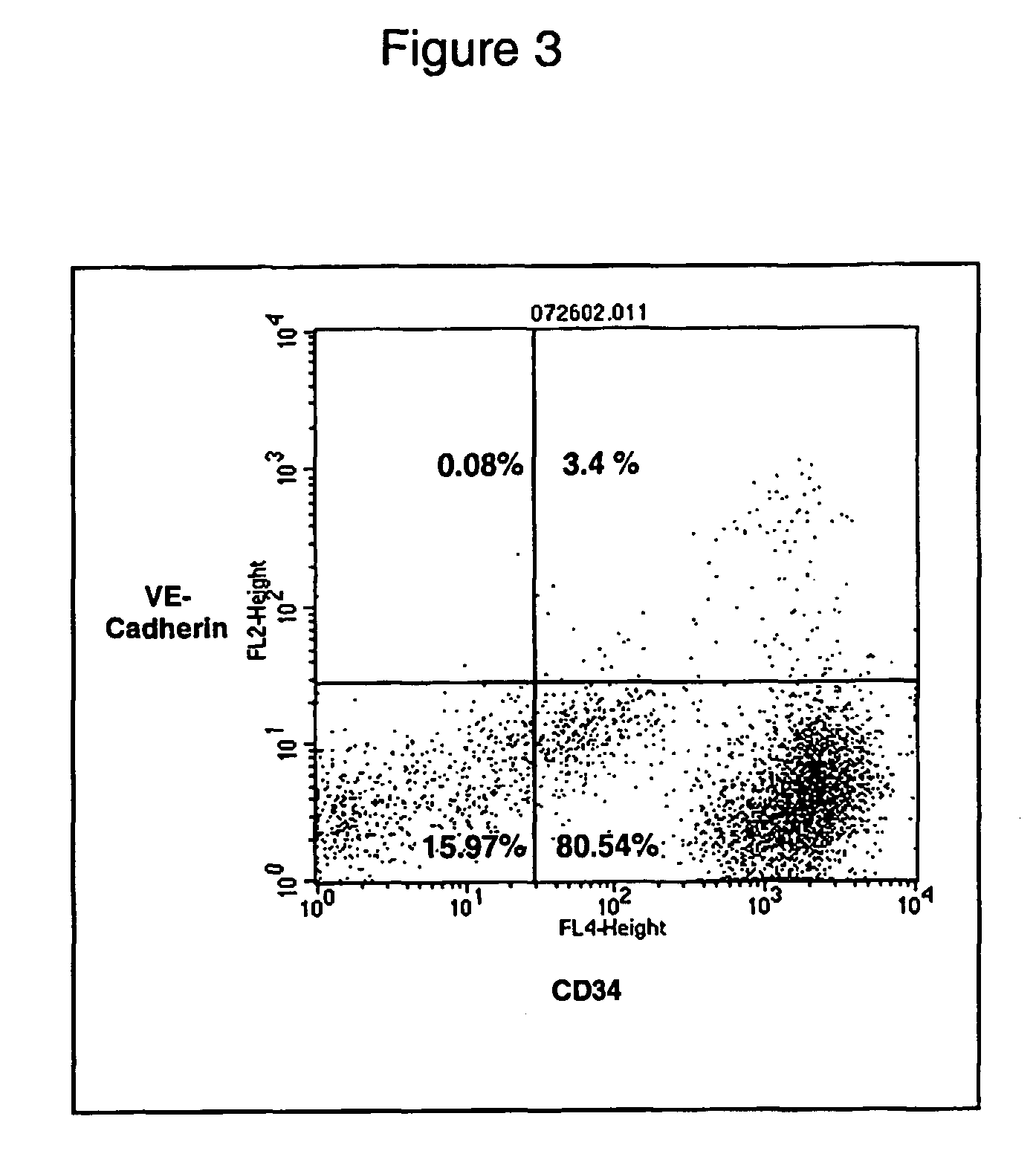
[0120] A major pathway by which ASCs can enhance angiogenesis is by differentiation of ASCs into a vascular cell phenotype. Since ASCs are already known to differentiate into a number of cell types like muscle, bone and neural cells, it was evaluated whether ASCs can develop phenotypes that correspond to either vascular endothelial cells or vascular smooth muscle cells. Plated adherent human ASCs were evaluated by flow cytometry for the expression of the stem cell marker CD34 and the endothelial marker VE-Cadherin, (FIG. 5). While the majority of cells are still CD34+ / VE-Cadherin, there has emerged a substantial proportion of cells that are CD34+ / VE-Cadherin+; this finding has been replicated consistently with samples from several donors. This is in contrast to freshly isolated ASCS, which express minimal VE-Cadherin (FIG. 3), prior to plating. The appearance of a CD34+ / VE-Cadherin+ cell populati...
example iii
Secretion of Growth Factors by Adipose Derived Stromal Cells
Secretion of Angiogenic Growth Factors by ASCs
[0124] Since stem and progenitor cells can secrete multiple growth factors (Majka M, et al. Blood. (2001)97:3075-85) and putative therapeutic utilities could in part be related to this endocrine function, the secretion of angiogenic growth factors by human subcutaneous ASCs was evaluated. Human subcutaneous adipose stromal cells were cultured in EGM-2-MV media to confluence, and then switched into growth-factor free basal media (EBM-2, Clonetics) for 72 hours. Cell supernatants were collected and subsequently assayed for angiogenic growth factors using ELISA and Multi-Analyte-Profiling kits (R&D Systems) for Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF), Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF) and Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF). The cell number was assessed at the end of the 72-hour period, and the secretion of growth factors is expressed in pg / 106 ASCs. The cell supernatan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com