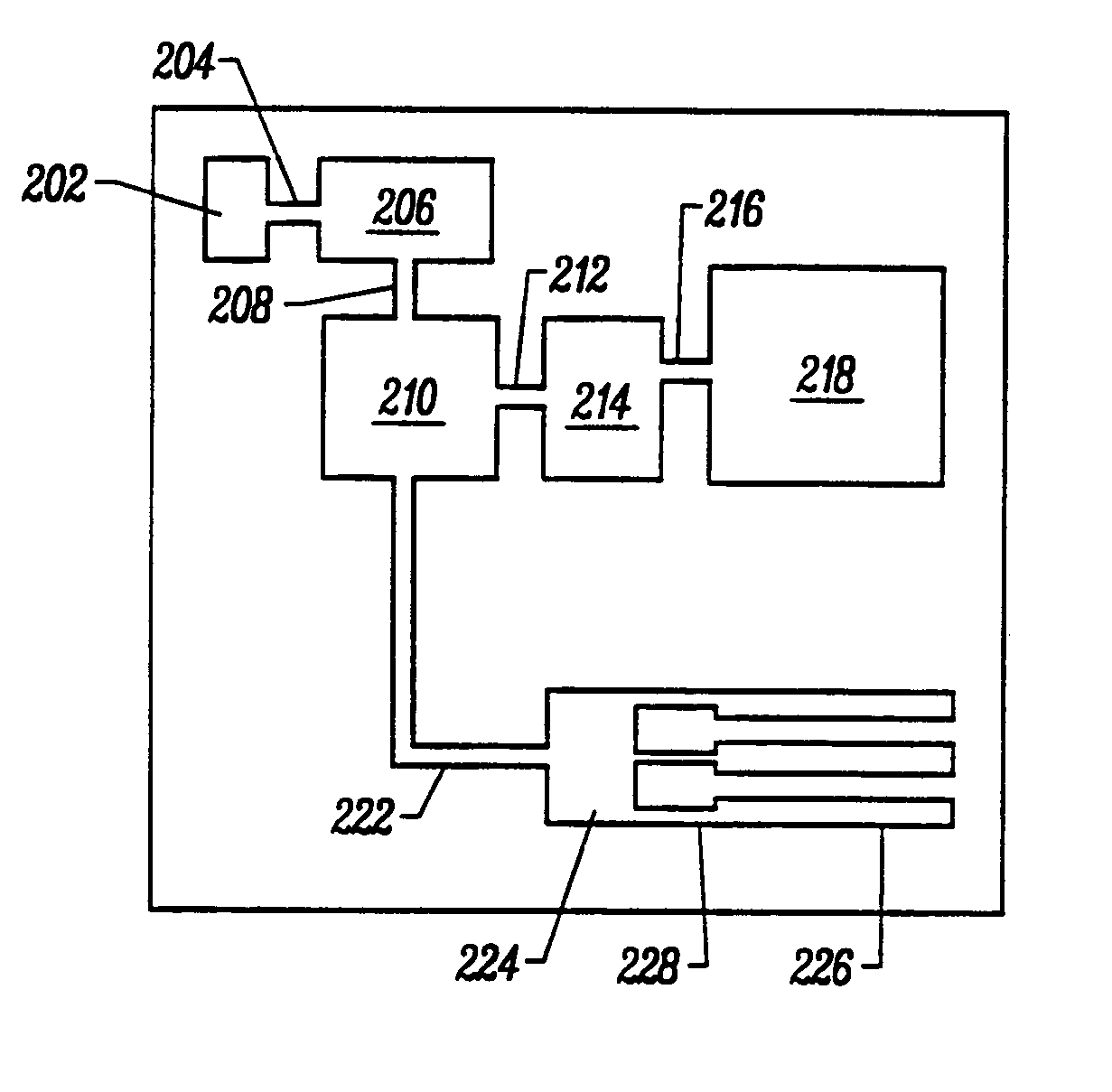
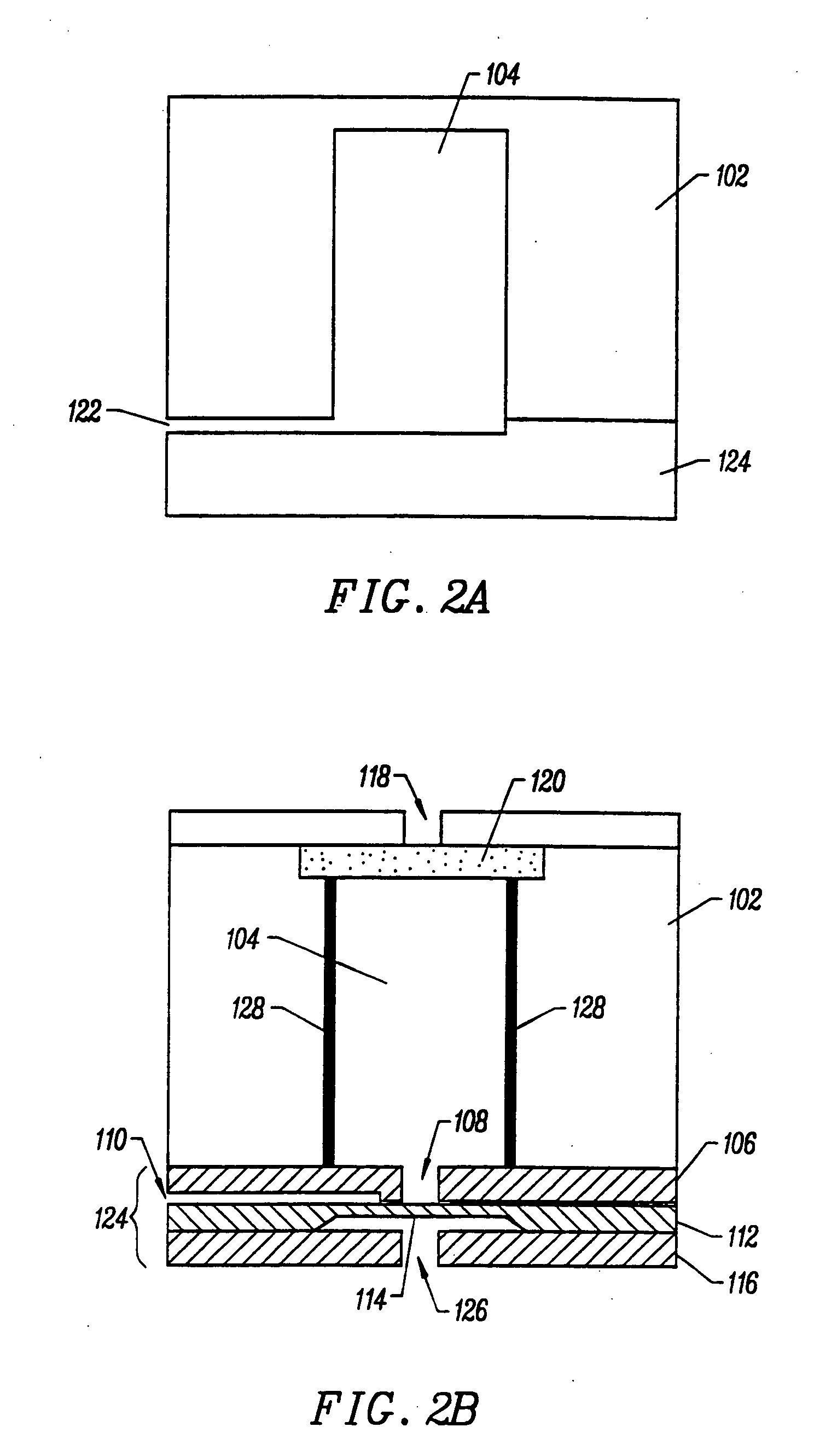
Integrated nucleic acid diagnostic device
a nucleic acid and diagnostic device technology, applied in the field of integrated nucleic acid diagnostic devices, can solve problems such as introducing a potential for error into the overall process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Extraction and Purification of Nucleic Acids
[0198] In separate experiments, HIV cloned DNA was spiked into either horse blood or a suspension of murine plasmacytoma fully differentiated B-cells derived from BALBc mice. Guanidine isothiocyanate was added to a concentration of 4 M, to lyse the material. In separate experiments, the lysate was passed through a cartridge containing glass wool (20 μl), a cartridge with soda glass walls (20 μl), and a glass tube. After 30 minutes at room temperature, the remaining lysate was washed away with several volumes of ethanol:water (1:1) and the captured DNA was eluted at 60° C. using 1×TBE. The yield of eluted DNA was measured using ethidum bromide staining on an agarose gel, and purity was tested by using the eluted material as a template for a PCR reaction. Elution yields ranged from 10% to 25% and PCR yields ranged from 90 to 100% as compared to controls using pure template.
example 2
RNA Preparation Reactions in Miniaturized System
[0199] A model miniature reactor system was designed to investigate the efficacy of miniaturized devices in carrying out prehybridization preparative reactions on target nucleic acids. In particular, a dual reaction chamber system for carrying out in vitro transcription and fragmentation was fabricated. The device employed a tube based structure using a polymer tubing as an in vitro transcription reactor coupled to a glass capillary fragmentation reactor. Reagents not introduced with the sample were provided as dried deposits on the internal surface of the connecting tubing. The experiment was designed to investigate the effects of reaction chamber materials and reaction volume in RNA preparative reaction chambers.
[0200] The sample including the target nucleic acid, DNA amplicons containing a 1 kb portion of the HIV gene flanked with promoter regions for the T3 and T7 RNA primers on the sense and antisense strands, respectively, RNA ...
example 3
PCR Amplification in Miniaturized System
[0203] The miniature polymeric reaction chamber similar to the one described in Example 2 was used for carrying out PCR amplification. In particular, the chamber was fabricated from a planar piece of poycarbonate 4 mm thick, and having a cavity measuring 500 μm deep machined into its surface. A second planar polycarbonate piece was welded over the cavity. This second piece was only 250 μm thick. Thermal control was supplied by applying a peltier heater against the thinner second wall of the cavity.
[0204] Amplification of a target nucleic acid was performed with Perkin-Elmer GeneAmp® PCR kit. The reaction chamber was cycled for 20 seconds at 94° C. (denaturing), 40 seconds at 65° C. (annealing) and 50 seconds at 72° C. (extension). A profile of the thermal cycling is shown in FIG. 9. Amplification of approximately 109 was shown after 35 cycles. FIG. 10C shows production of amplified product in the microchamber as compared to a control using a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com