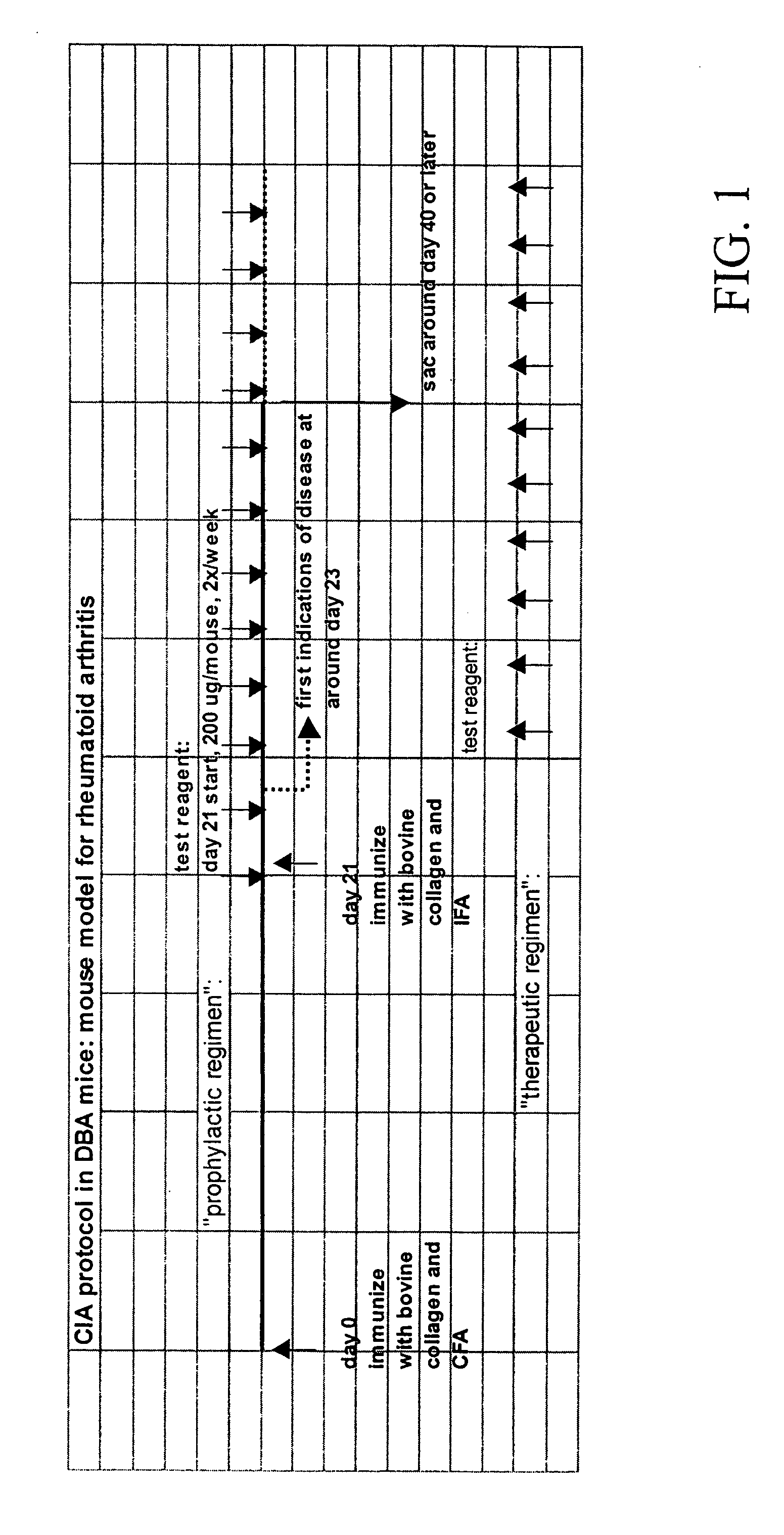
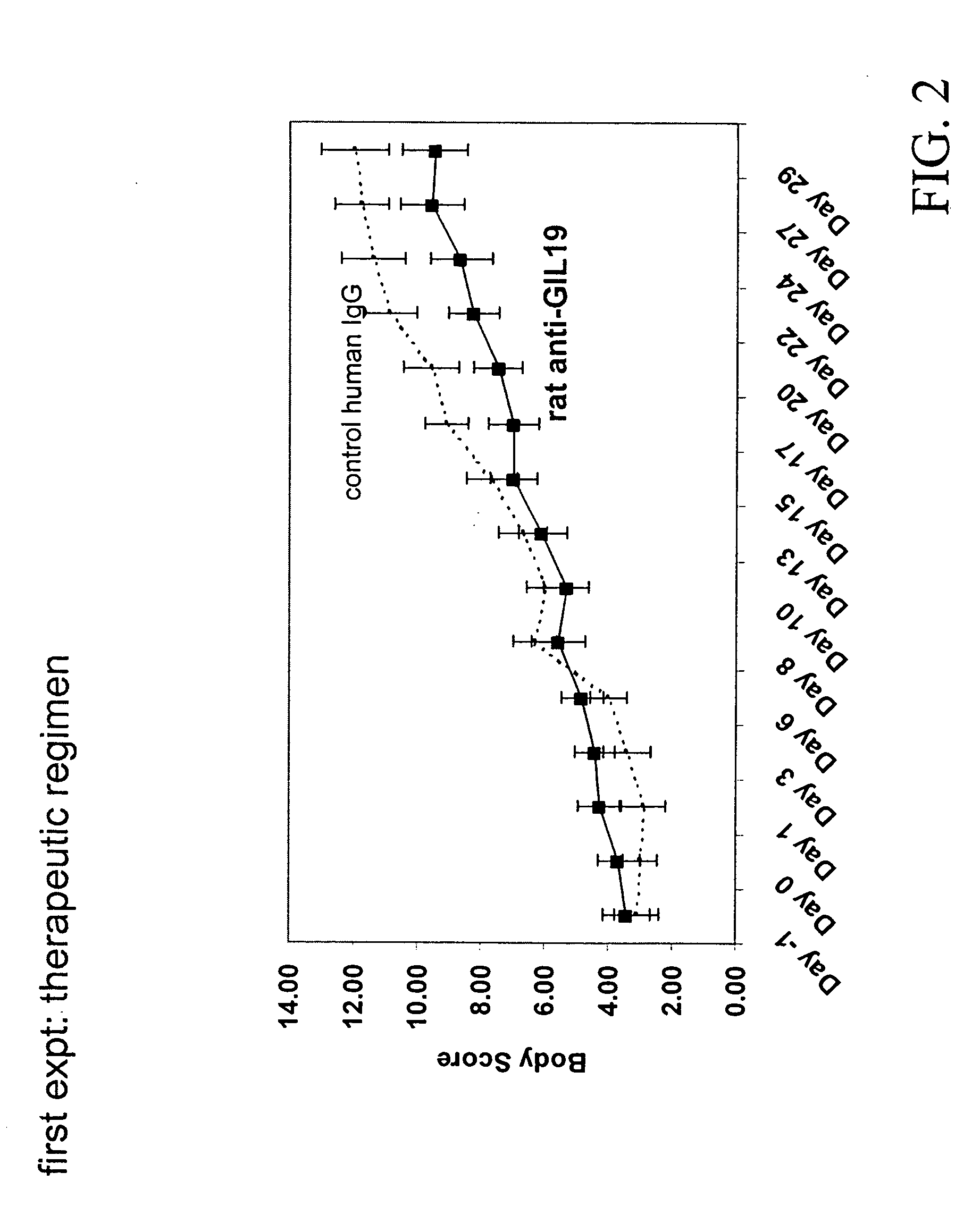
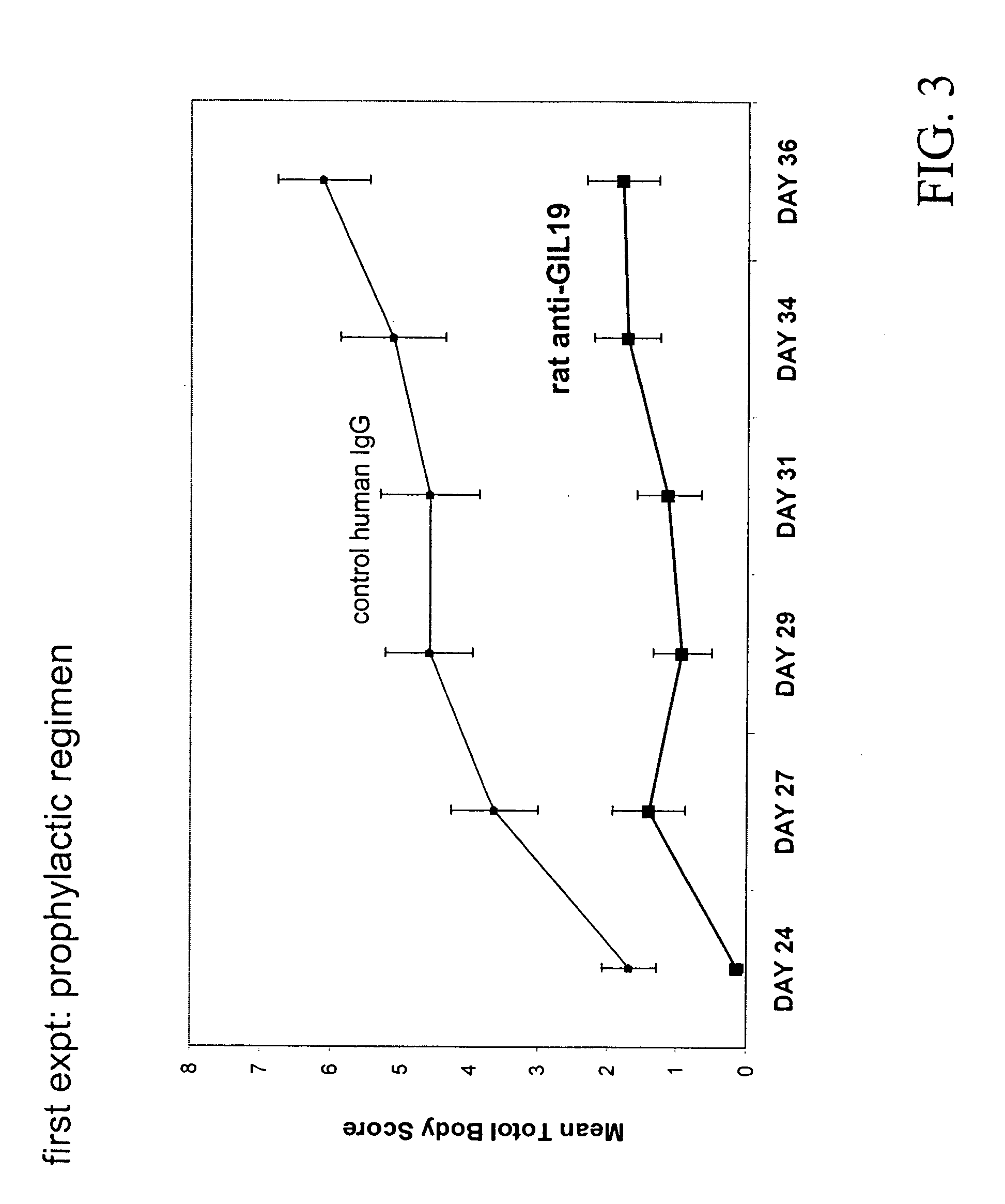
Composition and method for trating inflammatory disorders
a technology of inflammatory disorders and composition, applied in the field of cytokine polypeptides and polynucleotides, can solve the problems of cartilage destruction and bone erosion, and achieve the effect of enhancing the immune response of the subject and enhancing the immune respons
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Identification and Characterization of Clone “IL-22”
[0220] A polynucleotide of the present invention has been identified as clone “IL-22”. Clone IL-22 was isolated according to the following method. A murine EST was identified from a murine cDNA library made from splenocytes activated with both ConA and bone marrow derived dendritic cells. The EST was identified using methods which are selective for cDNAs encoding secreted proteins (see U.S. Pat. No. 5,536,637). The murine EST sequence was used to isolate a full-length murine clone from the same cDNA library. Analysis of the sequence of the murine clone revealed a significant homology to interleukin-10 (IL-10).
[0221] In order to isolate a human homolog of the murine clone, PCR primers were constructed based upon the region of the murine sequence which showed homology to IL-10. Use of such primers for amplification in a cDNA library derived from PHA / PMA-stimulated human PBMCs produced a PCR product of significant size. Analysis of t...
example 2
Characterization of IL-22 Protein
[0224] Cell lines which stably express and secrete full length IL-22 protein were created by transfecting CHO cells with IL-22 cDNA in appropriate expression vectors. Transiently transfected COS cells using appropriate IL-22 expression vectors have been used to make IL-22 protein for analysis. Transfections were accomplished using the commercially available Lipofectamine reagent (Gibco). Interestingly, COS cells which express IL-22 were observed to non-uniformly detach, forming holes in the cell culture monolayer. Media conditioned by transfected COS cells was used to demonstrate cytokine-like activity of IL-22 protein. Western blot analysis of cell lysates showed that Stat-3 becomes phosphorylated (activated) in a kidney mesangial tissue-derived cell line exhibiting macrophage-like qualities (MES-13; see, Dumoutier et al (2000) J. of Immunology 164:1814-1819) upon exposure of that cell to media conditioned by IL-22-expressing cells. In addition pho...
example 3
Establishment of IL-22 Recombinant Adenovirus Vector and In Vivo Administration
[0228] The Adori 1-2 murine IL-22 (mIL-22) vector was derived by digesting pED6dpc-2mIL-22 with EcoRI and NotI, and ligating the 1.1 kb mIL-22 cDNA fragment with EcoRI and NotI digested adenovirus vector Adori 1-2. Adori 1-1 green fluorescent protein (GFP) construct was derived by digesting pEGFP-N1 (CLONTECH Laboratories, Inc., Palo Alto, Calif.) with EcoR1 and Not1 and inserting the EGFP into the EcoR1 and Not1 site of Adori 1-1. Both constructs were verified by extensive restriction digestion analysis and sequencing of the cDNA inserts within the plasmids. Expression of the mIL-22 cDNA and EGFP are driven from cytomegalovirus (CMV) immediate early promoter and enhancer.
[0229] Ad5 E1a deleted (dl327) recombinant adenovirus was generated by homologous recombination in a human kidney embryonic kidney cell line 293. Recombinant adenovirus virus was isolated and subsequently amplified on 293 cells. The vi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com