System for detecting symptoms, determining staging and gauging drug efficacy in cases of Alzheimer's disease
a technology for alzheimer's disease and symptoms, applied in the field of functional magnetic resonance imaging, can solve the problems of reducing the prevalence of alzheimer's disease by 50%, affecting the accuracy of diagnosis, so as to achieve accurate diagnosis, efficient, consistent and reliable manner
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
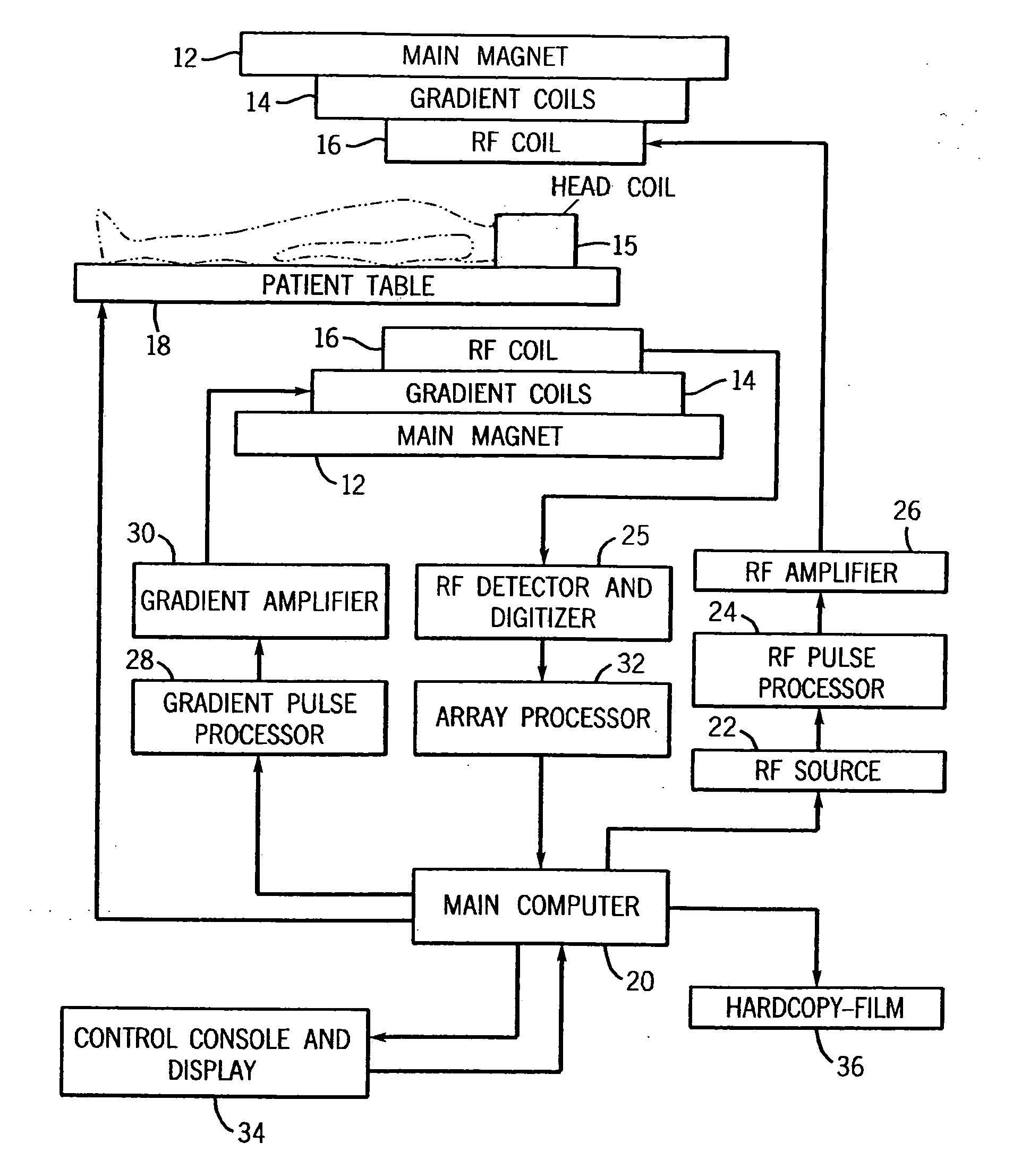
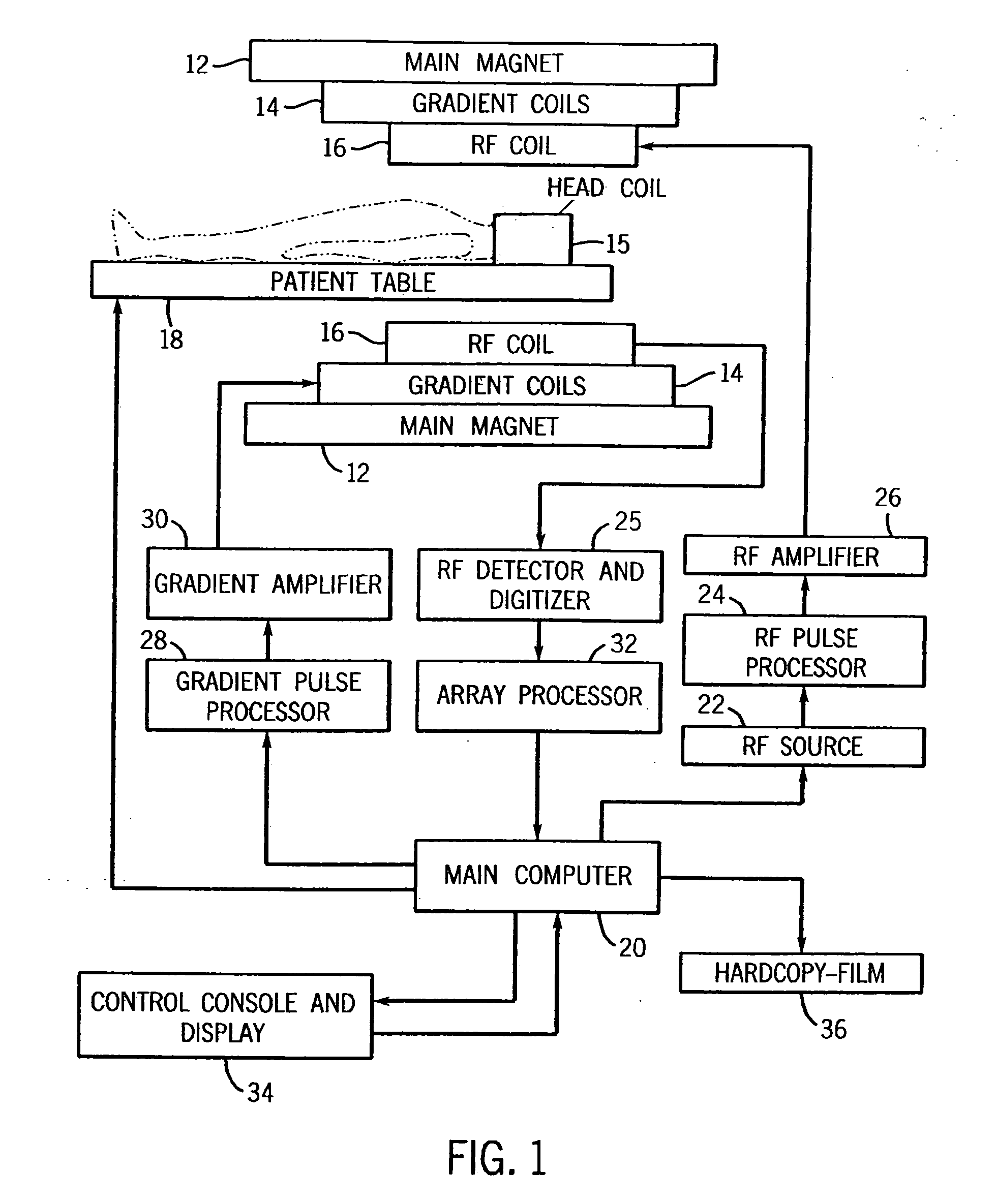
[0018] Referring now to FIG. 1, the basic components of a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machine 10 are shown. The main magnet 12 produces a strong B. field for the imaging procedure. Within the magnet 12 are the gradient coils 14 for producing a gradient in the Bo field in the X, Y, and Z directions as necessary to provide frequency discrimination. A head coil 15 is also used to improve accuracy and resolution for studies involving the brain. Within the gradient coils 14 is a radio frequency (RF) coil 16 for producing RF pulses and the B1 transverse magnetic field necessary to rotate magnetic spins by 90° or 180°. The RF coil 16 also detects the return signals from the spins within the body and supplies these signals to the RF detector and digitizer 25. The patient is positioned within the main magnet by a computer controlled patient table 18. The scan room is surrounded by an RF shield, which prevents the high power RF pulses from radiating out through the hospital and prevents ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com