Methods and apparatus for anchoring an occluding member
a technology of occlusion member and anchoring device, which is applied in the direction of catheters, applications, other blood circulation devices, etc., can solve the problems of undesirable use of external cross-clamps, and achieve the effects of optimizing inflation pressure, high friction, and high friction portions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
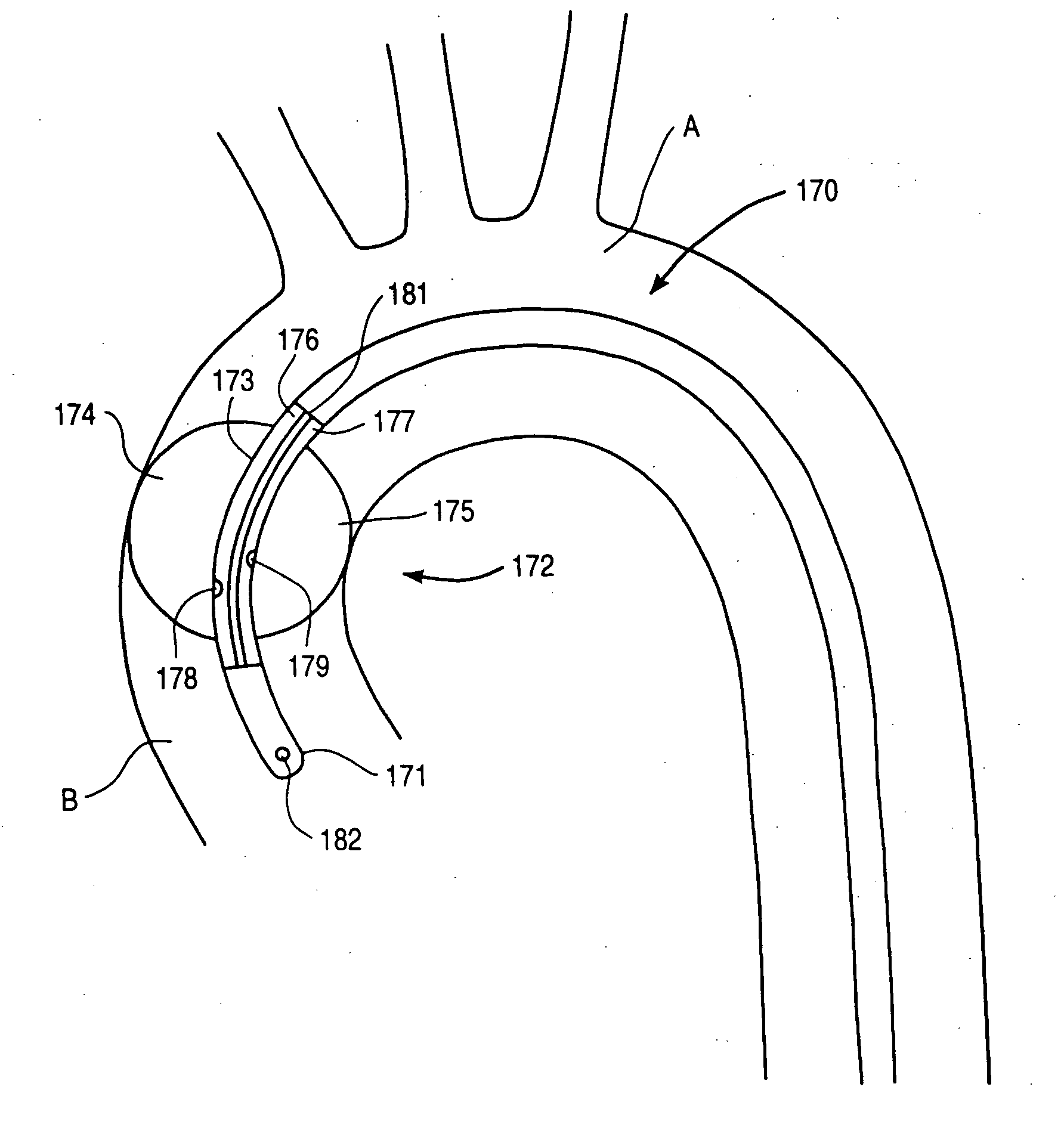
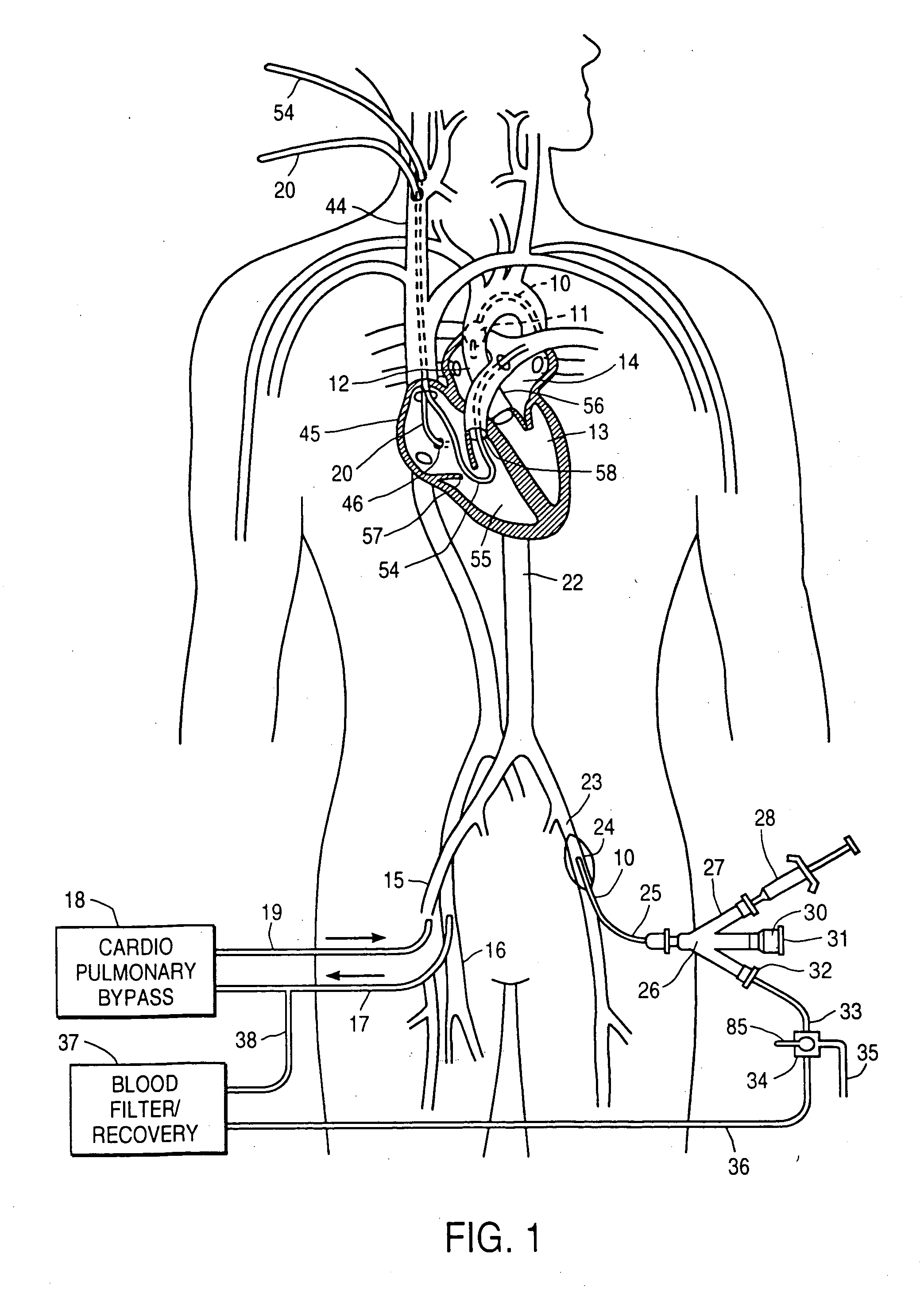
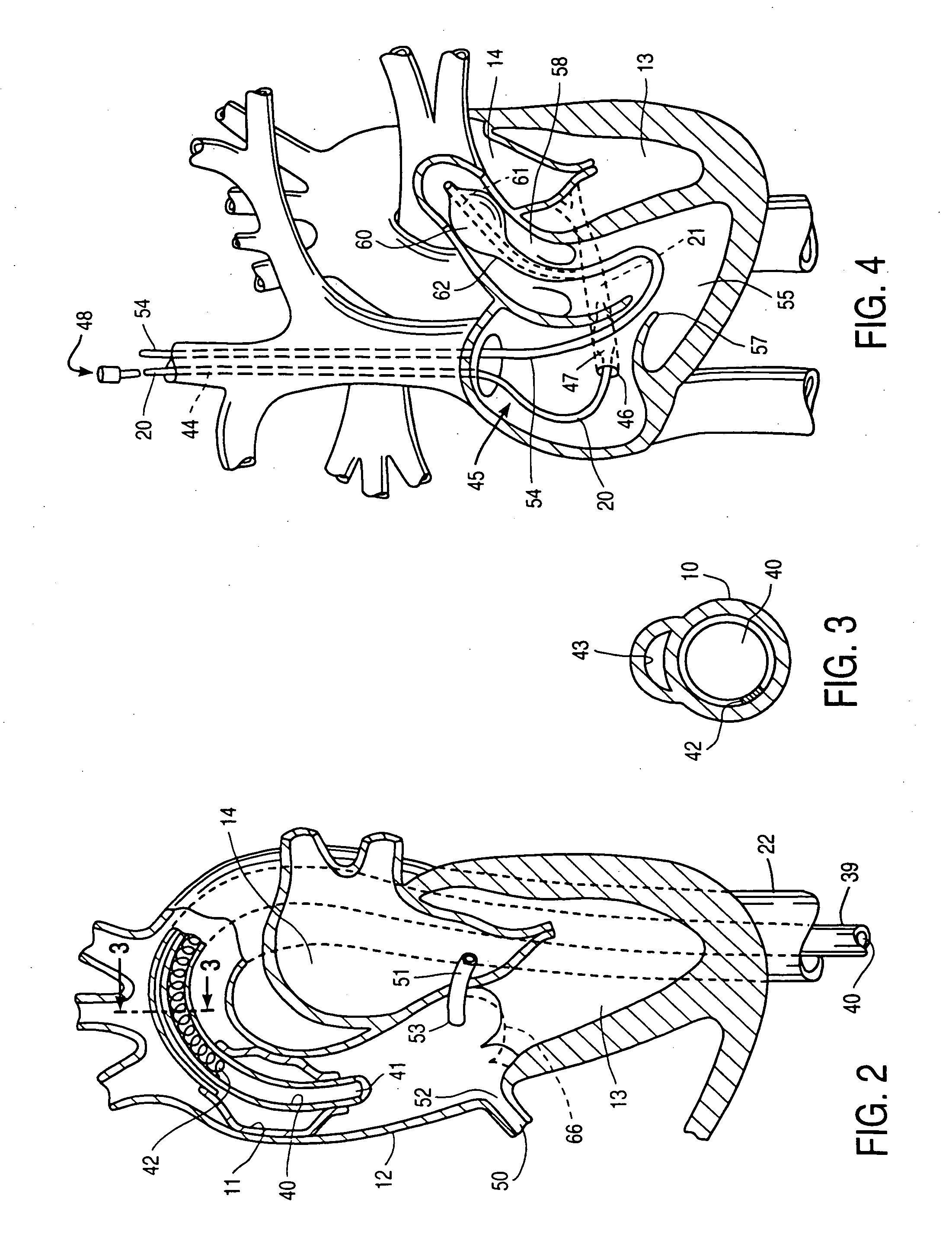
[0091] The invention provides a cardiac access system including an endovascular device for partitioning the ascending aorta, as well as a system for selectively arresting the heart, which are useful in performing a variety of cardiovascular, pulmonary, neurosurgical, and other procedures. The procedures with which the invention will find use include repair or replacement of aortic, mitral, and other heart valves, repair of septal defects, pulmonary thrombectomy, electrophysiological mapping and ablation, coronary artery bypass grafting, angioplasty, atherectomy, treatment of aneurysms, myocardial drilling and revascularization, as well as neurovascular and neurosurgical procedures. The invention is especially useful in conjunction with minimally-invasive cardiac procedures, in that it allows the heart to be arrested and the patient to be placed on cardiopulmonary bypass using only endovascular devices, obviating the need for a thoracotomy or other large incision. Moreover, even in c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Force | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com