Polypeptides of Alicyclobacillus sp.
a technology of alicyclobacillus and polypeptides, which is applied in the field of functional polypeptides, can solve the problems of not being able to identify functional enzymes, limited to the availability of enzyme assays, and large majority of sequences obtained encode non-secreted proteins
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Identifying Functional Polypeptides Secreted by Alicyclobacillus sp. DSM 15716
Genomic Library Construction
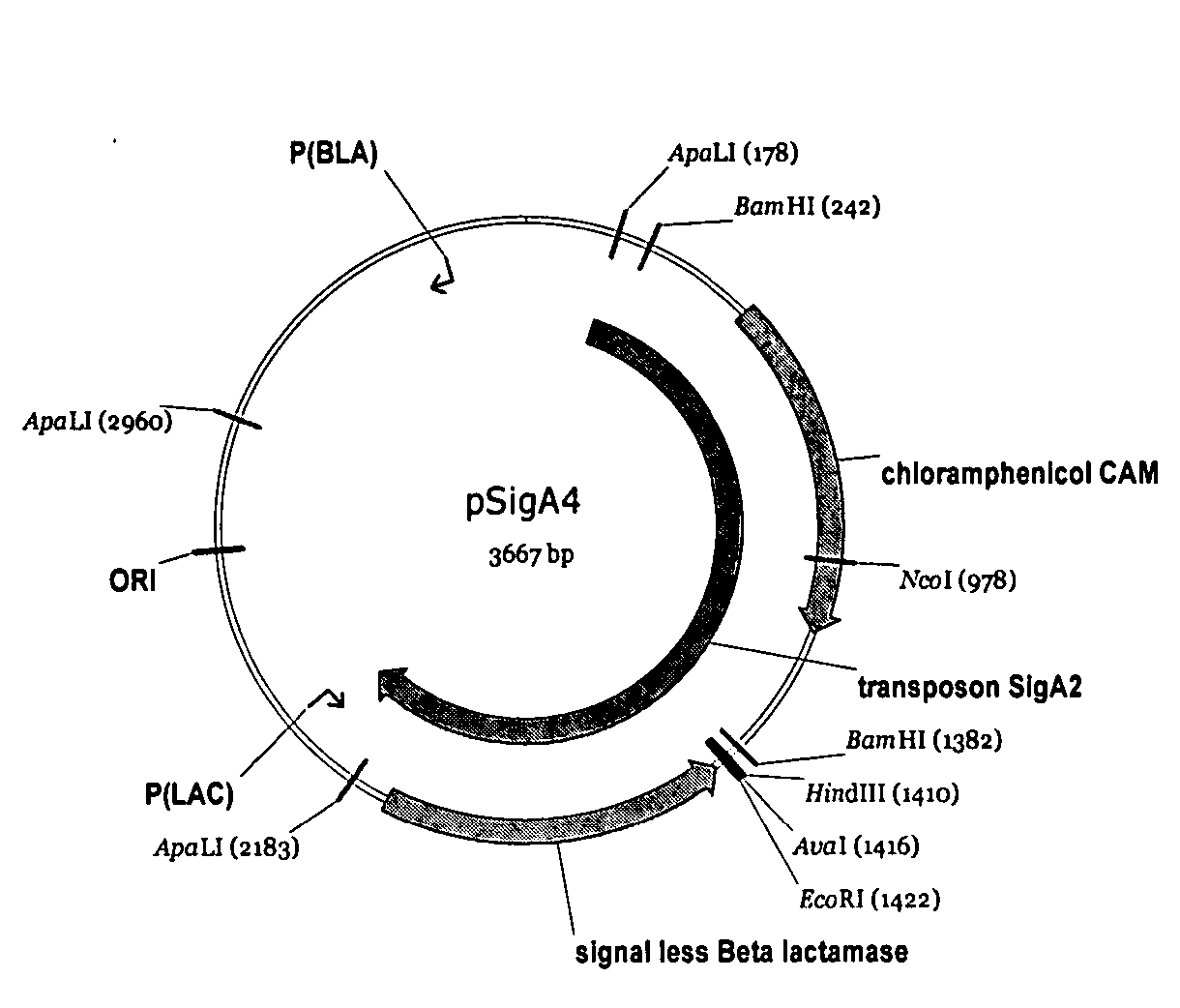
[0252] Chromosomal DNA from Alicyclobacillus sp. DSM 15716 was prepared by using standard molecular biology techniques (Ausuble et al. 1995 “Current protocols in molecular biology” Publ: John Wiley and sons). The prepared DNA was partially cleaved with Sau3A and separated on an agarose gel. Fragments of 3 to 8 kilobases were eluted and precipitated and resuspended in a suitable buffer.
[0253] A genomic library was made by using the Stratagene ZAP Express™ predigested Vector kit and Stratagene ZAP Express™ predigested Gigapack® cloning kit (Bam HI predigested) (Stratagene Inc., USA) following the instructions / recommendations from the vendor. The resulting lambdaZAP library comprised 38000 pfu of which 10000 were collected for mass excision. The resulting 70000 E. coli colonies were pooled and plasmids were prepared by using the Qiagen Spin Mini prep kit (Qiagen, Germany). The ...
example 2
Determining Function by Homology
[0266] The function of the polypeptides SEQ ID NO: 26 to SEQ ID NO: 50 were annotated by sequences comparison with genes or polypeptides of known function. The polypeptides of the invention were compared to a list of closest related sequences from public and inhouse databases of contig's. The contigs, from which SEQ ID NO: 26 to SEQ ID NO: 50 were derived, were subsequently compared to sequences available in standard public DNA and protein sequences databases by using the program BLASTX 2.0a19 MP-WashU [14 Jul. 1998]. A careful analysis of sequence alignments of SEQ ID NO: 26 to SEQ ID NO: 40 to their closest related sequences with known function from other databases made it possible to predict the function of these polypeptides on the basis of the degree of amino acid identity. Even when the overall amino acid identity was below 40%, which usually makes it difficult to make a good prediction, we were able to predict the function of SEQ ID NO: 26 to ...
example 3
Preparing Polypeptides of SEQ ID NO: 26 to SEQ ID NO: 50
[0267] To prepare the polypeptides of SEQ ID NO: 26 to SEQ ID NO: 50, the genes comprised in SEQ ID NO: 1 to SEQ ID NO: 25 encoding these polypeptides are expressed by fusing the DNA encoding the open reading frame to DNA a promoter, ribosome-binding site and terminator suitable for genes expression in an appropriate host strain, for example Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus licheniformis or Bacillus clausii or a derivative of Alicyclobacillus sp. The promoter can either be an inducible promotor or a constitutive promoter. Any signal sequences of SEQ ID NO: 26 to SEQ ID NO: 50 can be exchanged with a suitable signal peptide of another bacterium. The expression construct can either be part of a plasmid or of a linear DNA. It can be integrated into the chromosome of the host strain by recombination or it can be present in the host cell on a plasmid. Then the transformed cells carrying the gene of interest are grown i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com