Method for diagnosing diseases based on levels of anti-glycan antibodies
a technology of antibodies and glycans, applied in the field of diagnosis of diseases by detecting levels of antibodies to glycans, can solve the problems of reducing affecting the diagnostic accuracy of ibd and ibs, so as to facilitate earlier and more appropriate therapeutic intervention, reduce uncertainty for patients and their families, and high serological testing. the a technology of glycan antibody detection and diagnosis of diseases, a technology of glycan antibody detection and diagnosis of diseases, a technology of glycan and glycan and anti-glycan and glycan and anti-glycan and applied in the field of a method, which is applied in the field of a method of glycan and glycan and glycan and glycan level a technology of a technology of a technology of a technology of a technology of a glycan antibody detection and diagnosis method, applied in the field of a technology of a technology of a method, which is applied in the field of a method,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Comparative Antiglycan Antibody Levels in the Serum of Crohn's Disease Patients and Patients with Other Digestive Diseases
[0110] An anti-glycan antibody profile for IgG, IgA and IgM in the serum of the patients was obtained using GlycoChip® arrays (Glycominds, Ltd., Lod, Israel, Cat No. 9100). The arrays were constructed using procedures described in Schwarz et. al. Glycobiology, 13: 749-54, 2003. Anti-glycan antibody profiles of 45 CD patients and 27 patients with other digestive diseases were compared.
[0111] All serum samples were tested using GlycoChip® plates (Glycominds Ltd., Lod, Israel, Cat No. 9100), which was an array of mono and oligosaccharides covalently attached to a reduced volume 384-well micro titer plate. The mono and oligosaccharides displayed on the array are listed in Table 1. A translation of the LinearCode™ syntax used to describe glycan structure to IUPAC nomenclature can be found in Table 1.
[0112] The sera from patients volunteers who had signed an informe...
example 2
Comparative Antiglycan Antibody Levels in the Serum of Crohn's Disease (CD) Colitis Patients and Ulcerative Colitis (UC) Patients
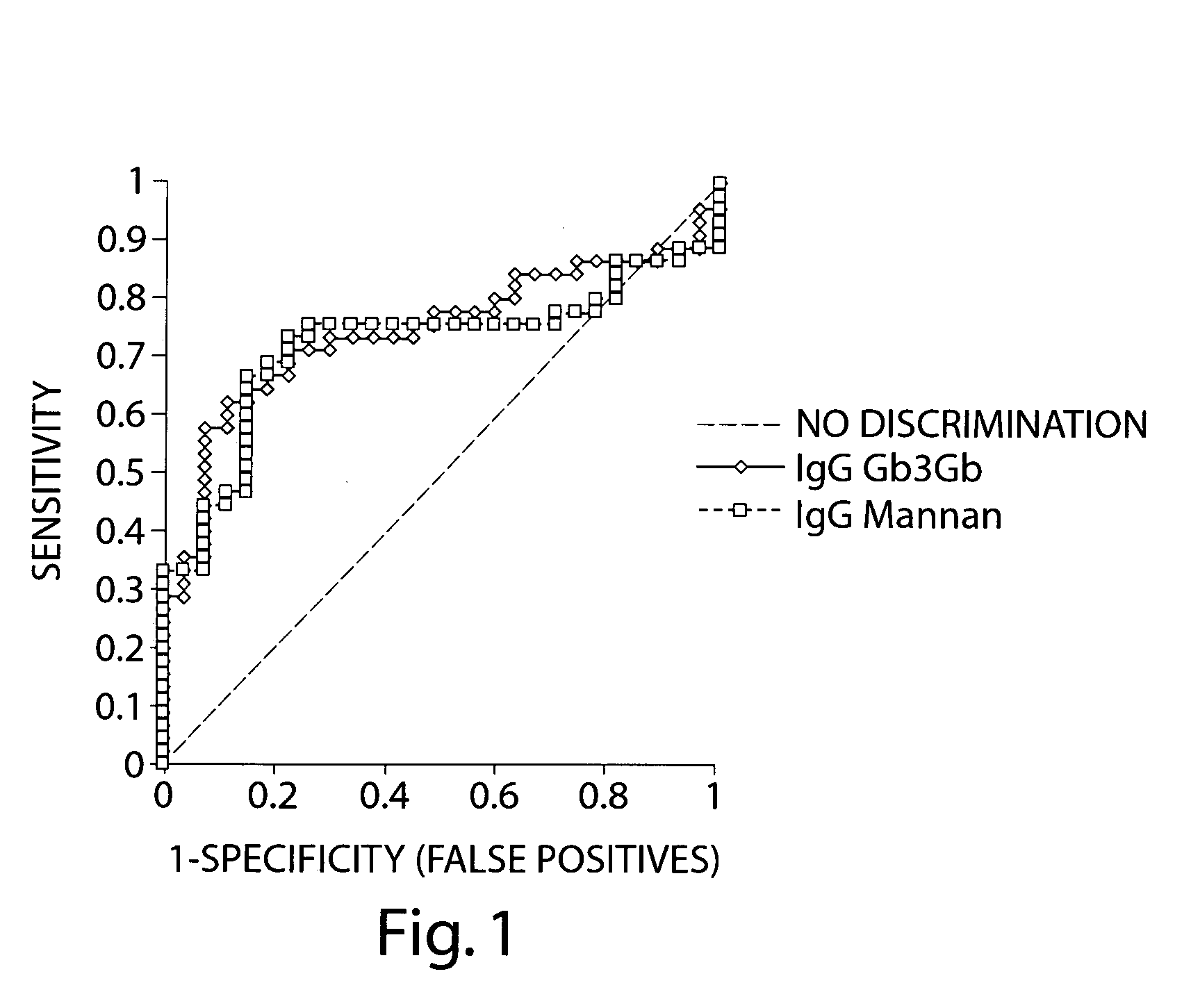
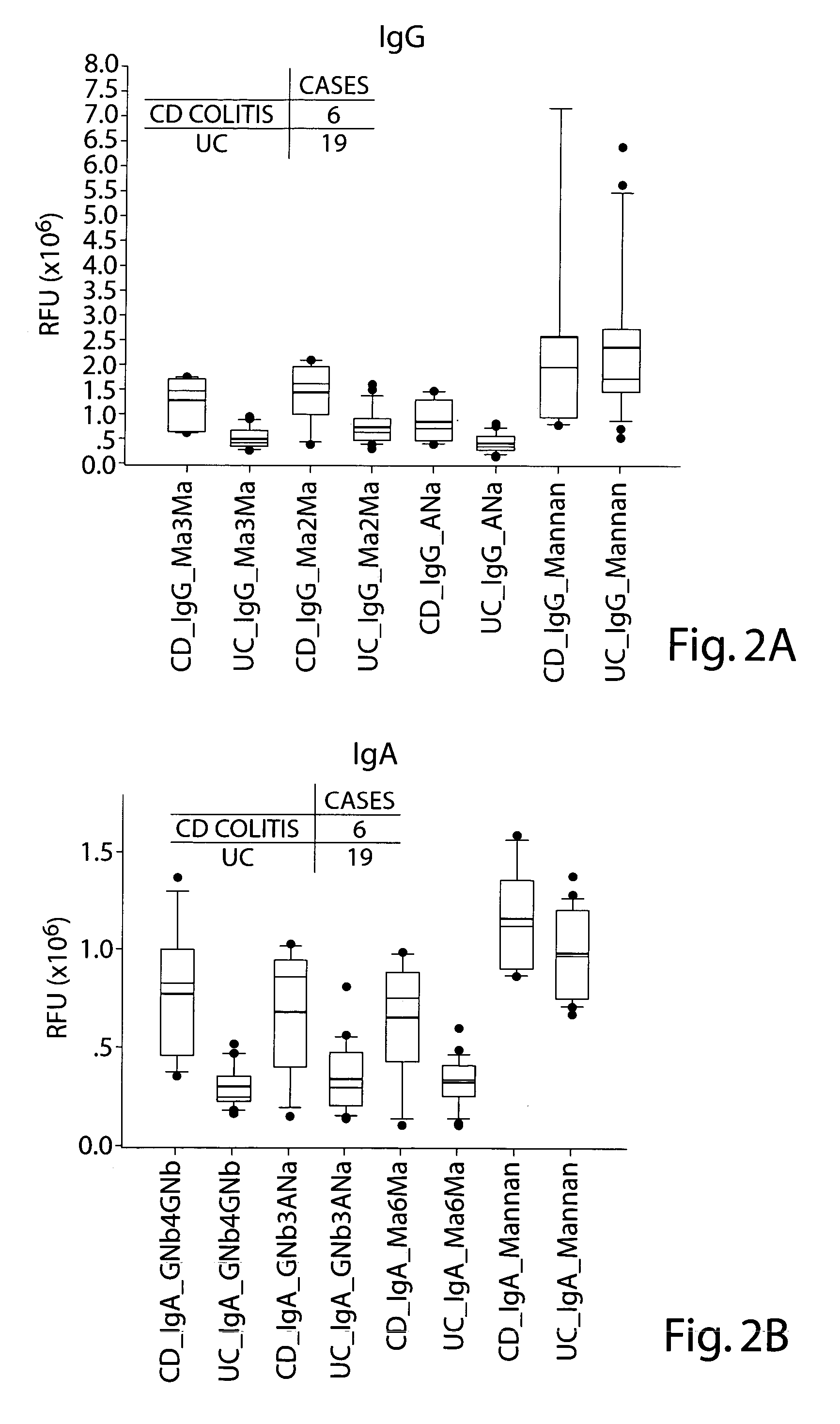
[0119] An anti-glycan antibody profile for IgG and IgA in the serum of the patients was obtained using GlycoChip® arrays (Glycominds, Ltd., Lod, Israel, Cat No. 9100). The arrays were constructed using procedures described in Schwarz et. al., Glycobiology 13: 749-54, 2003. Anti-glycan antibody profiles of 6 CD colitis patients and 19 UC patients were compared. All serum samples were collected and tested as described in Example 1.
[0120] Tables 7 and 8 show the levels of IgG and IgA type antiglycan antibodies that were detected at significantly different levels between the CD Colitis population and the UC population. The values presented for IgG and IgA are absolute values. Comparison of the average and median values of anti-carbohydrate antibodies in the CD Colitis patients and UC patients populations reveals a significant elevation in most of the anti gl...
example 3
Comparative Antiglycan Antibody Levels in the Serum of Crohn's Disease (CD) Patients, Ulcerative Colitis (UC) Patients, and Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Patients
[0121] The levels of antiglycan antibodies in serum from CD, UC, and IBS patients were compared.
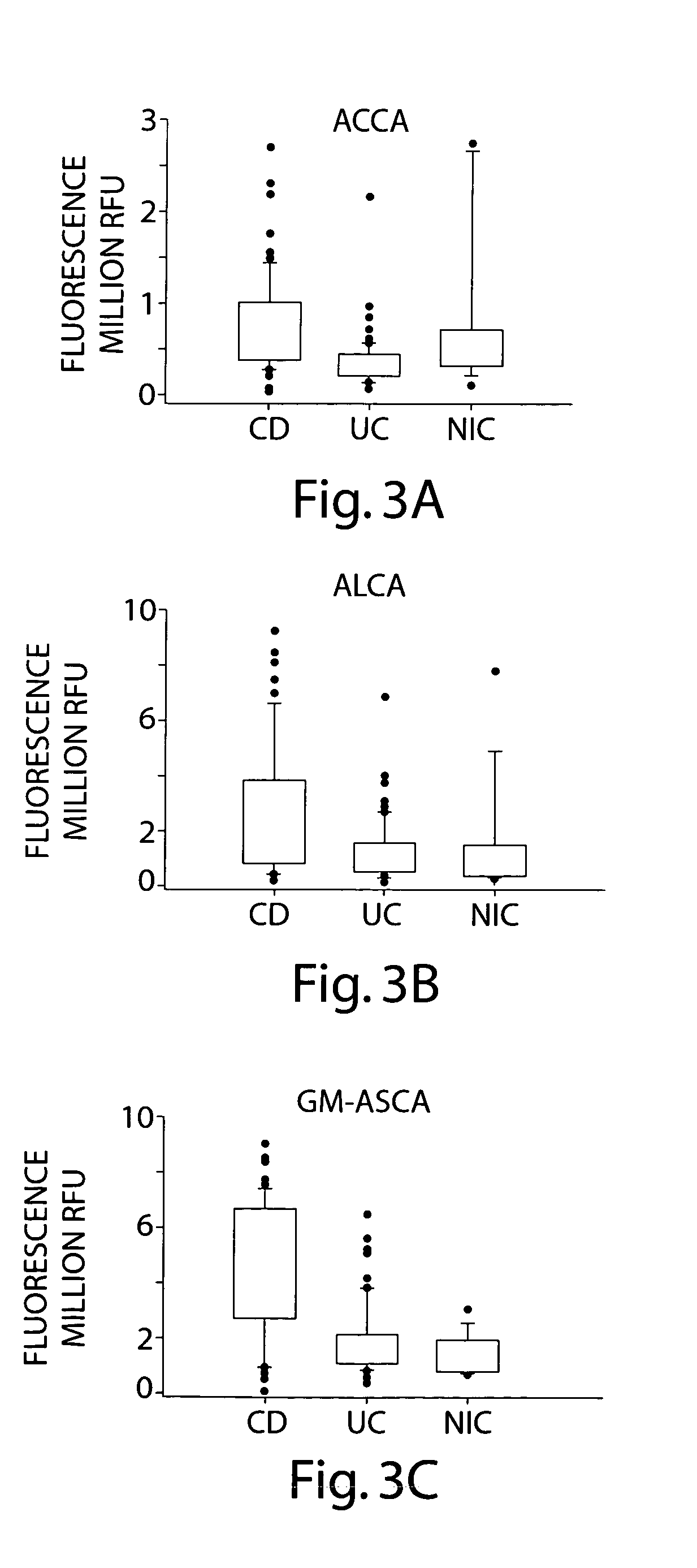
[0122] An anti-glycan antibody profile for IgG, and IgA in the serum of the patients was obtained using GlycoChip® arrays (Glycominds, Ltd., Lod, Israel, Cat No. 9100). The arrays were constructed using procedures described in Schwarz et. al. Glycobiology 13:749-54, 2003. The levels of the following Anti-glycan antibody were measured: Anti Laminarobioside (Glc(β,1-3)Glc(β)) Carbohydrate Antibodies (ALCA); Anti Chitobioside (GlcNAc(β,1-4)GlcNAc(β)) Carbohydrate Antibodies (ACCA); and Anti mannan (Anti Saccromyces Cervicia Antigen (ASCA)). Those antibodies were measured in the serum 70 CD patients, 56 UC patients and 19 patients with Non-IBD digestive diseases Controls (NIC) were also compared. All serum samples were collected a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| gastrointestinal disorder | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com