Energy management head restraint insert
a head restraint and energy management technology, applied in the field of head restraints in motor vehicles, can solve the problems of increasing neck force, soft foam, and insufficient structure of head restraints, and achieve the effect of reducing neck injuries
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
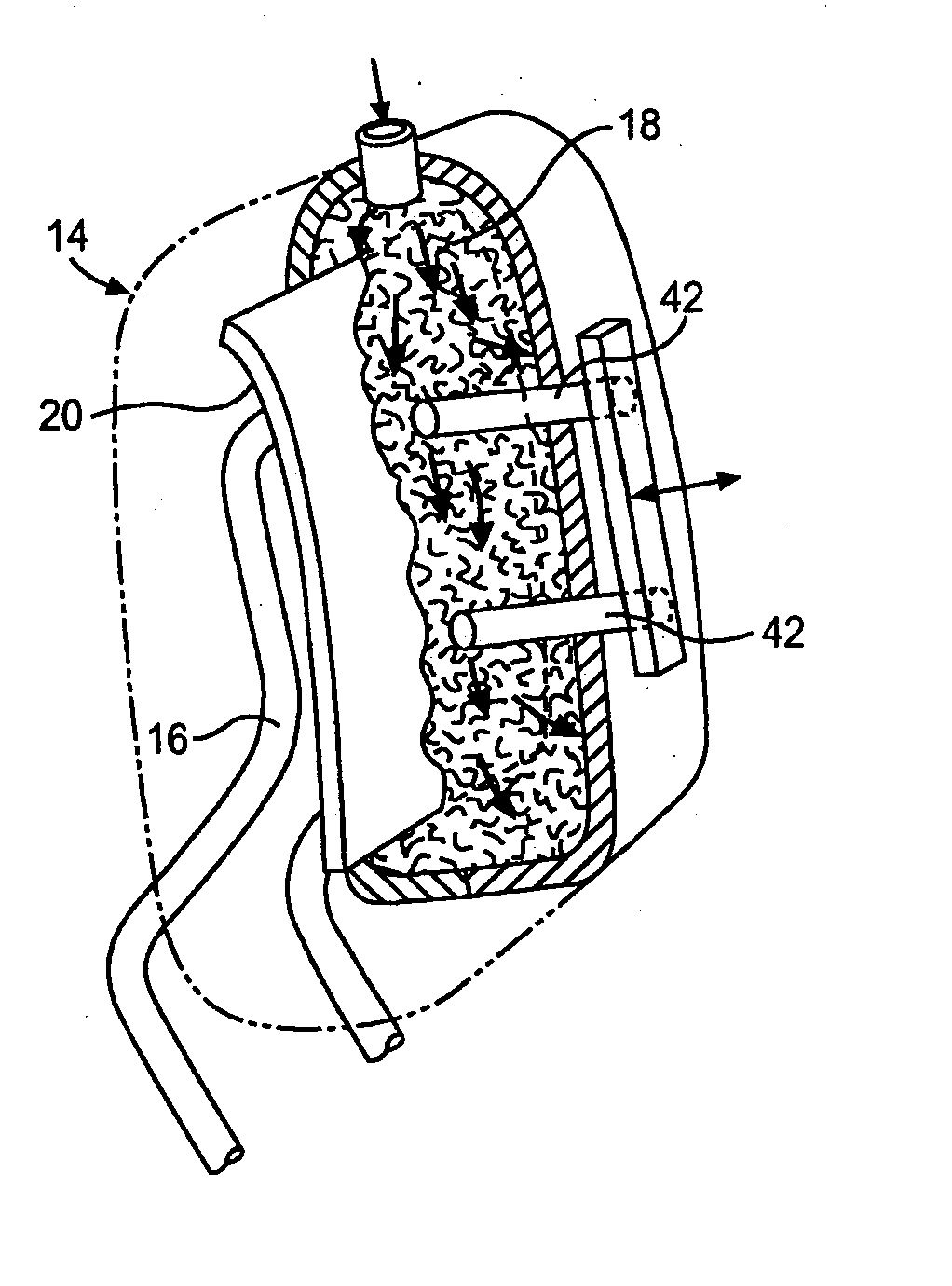
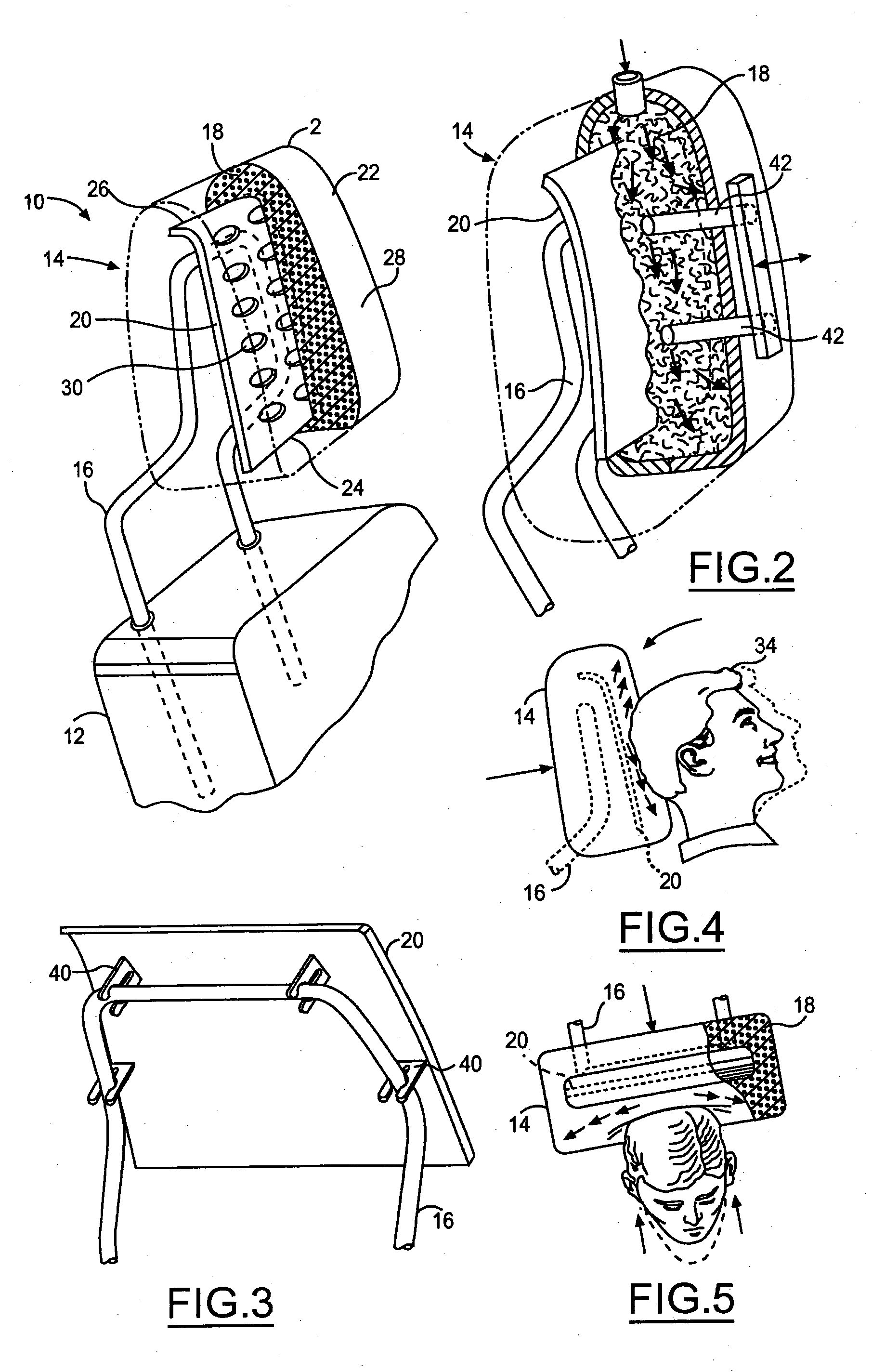
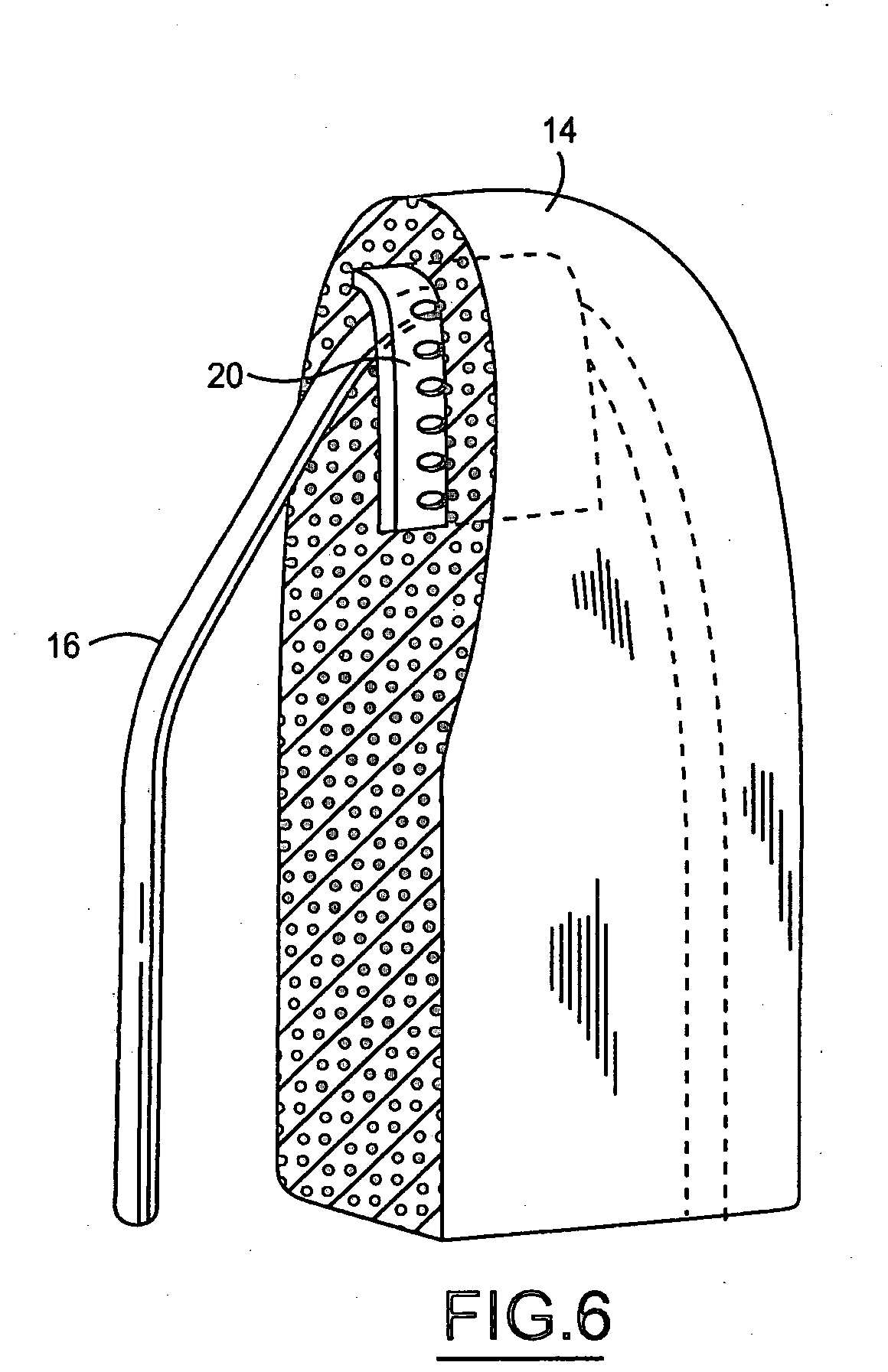
[0017] With reference to FIG. 1, this invention comprises a post 4, foam 6, an insert 8, and trim cover 14 creating head restraint 2. This insert 8 that is the object of this invention will be sized to fit any variety of head restraints. Generally, head restraints use an M or U shaped post but the insert 8 can be designed to fit any shaped post.
[0018] The insert 8 is molded into the foam 6 on the front side of the post 4 at some nominal distance below the surface of the head restraint 2. The insert 8 needs to be buried within the foam 6 so that the head restraint 2 still is comfortable for occupants. This insert 8 also needs to cover a majority of the front surface area and top of the head restraint 2. The insert 8 could also be formed to fit a variety of head restraint contour designs. Additionally, the insert 8 can comprise of plastic, metal, or a composite material. The versatility of the designs for this insert 8 allow it to be used in most if not all head restraints.
[0019] Th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com