System and method for removing organic compounds from waste water by oxidation
a technology of organic compounds and waste water, applied in the direction of water/sewage treatment by oxidation, water treatment parameter control, treatment control/steering, etc., can solve the problems of increasing water consumption in multiples, difficult to develop new water resources, and science parks in the taiwan area face a severe pressure on water shortage and water restriction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
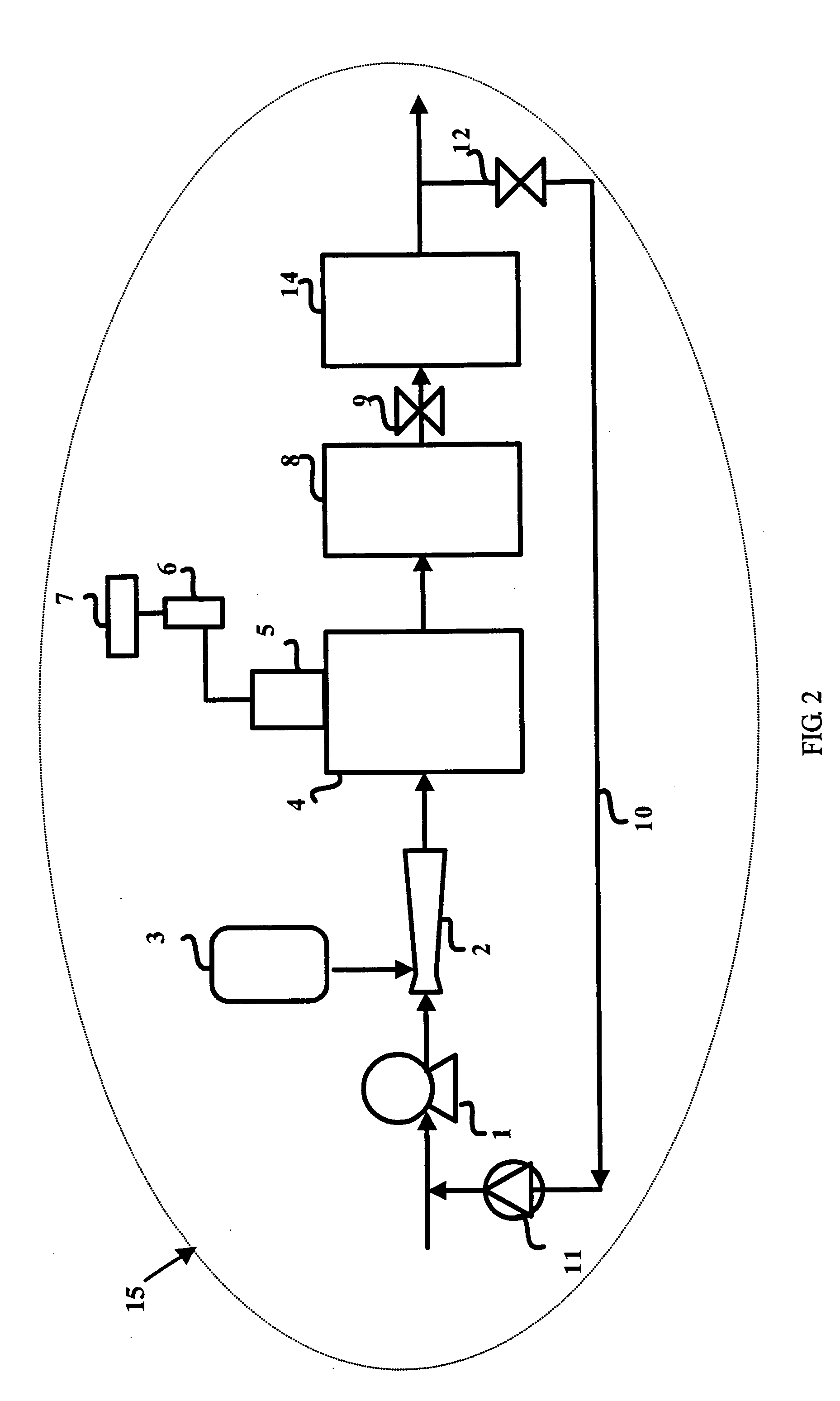
[0025] A module as shown in FIG. 1 was used to carry out an organic oxidation removal experiment in a waste water containing a TOC of IPA of about 18600 ppb.
[0026] The ozone concentration in the ozone / waste water mixture in the ozone injector was maintained at 20 ppm, and the pressure differential was 2.8 kg / cm2. The residence time in the ozone dissolution tank was 41 seconds. The flow ratio of the recycled water to the discharged water was controlled at 4:1. The TOC value in the discharge water was reduced to 12250 ppb, with a removal rate of 34%. The discharge water was again treated by repeating the abovementioned procedure, and the TOC value thereof was reduced from 12250 ppb to 7840 ppb, with a removal rate of 36%. A further treatment on the discharge water of 7840 ppb by repeating the abovementioned procedure successfully reduced the TOC value to 4468 ppb, with a removal rate of 43%. Thus, when the waste water was repeated treated by the abovementioned procedure, the TOC valu...
example 2
[0027] The experimental steps of Example 1 were repeated, with the influent being changed to a waste water containing a TOC of NMP of about 10053 ppb. The TOC of the influent was first reduced to about 6700 ppb, with a removal rate of 33%, and then to about 3820 ppb, with a removal rate of 43%. Thus, when the waste water was repeated treated by the abovementioned procedure, the TOC value thereof could be reduced below a desired concentration. The UV / ozone oxidation removal modules could be connected in series continuously or discontinuously, i.e. a purification element that was not the UV / ozone oxidation removal module could be inserted between two adjacent modules.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| residence time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| TOC recovery threshold | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| residence time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com