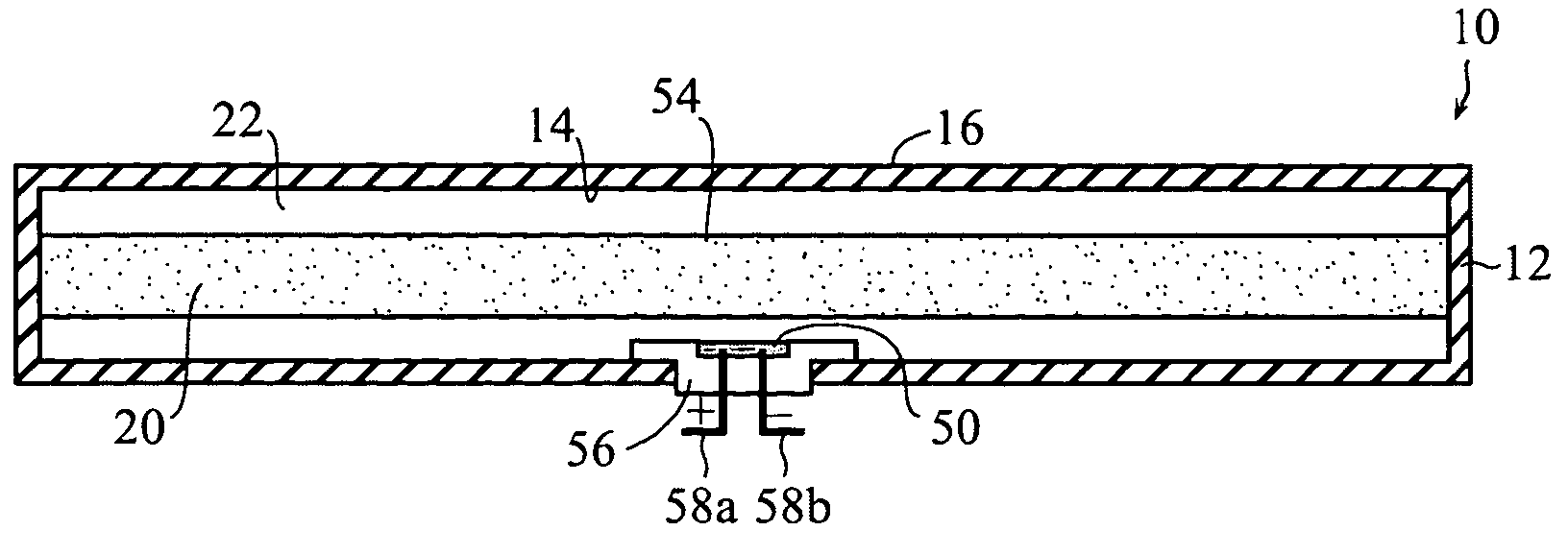
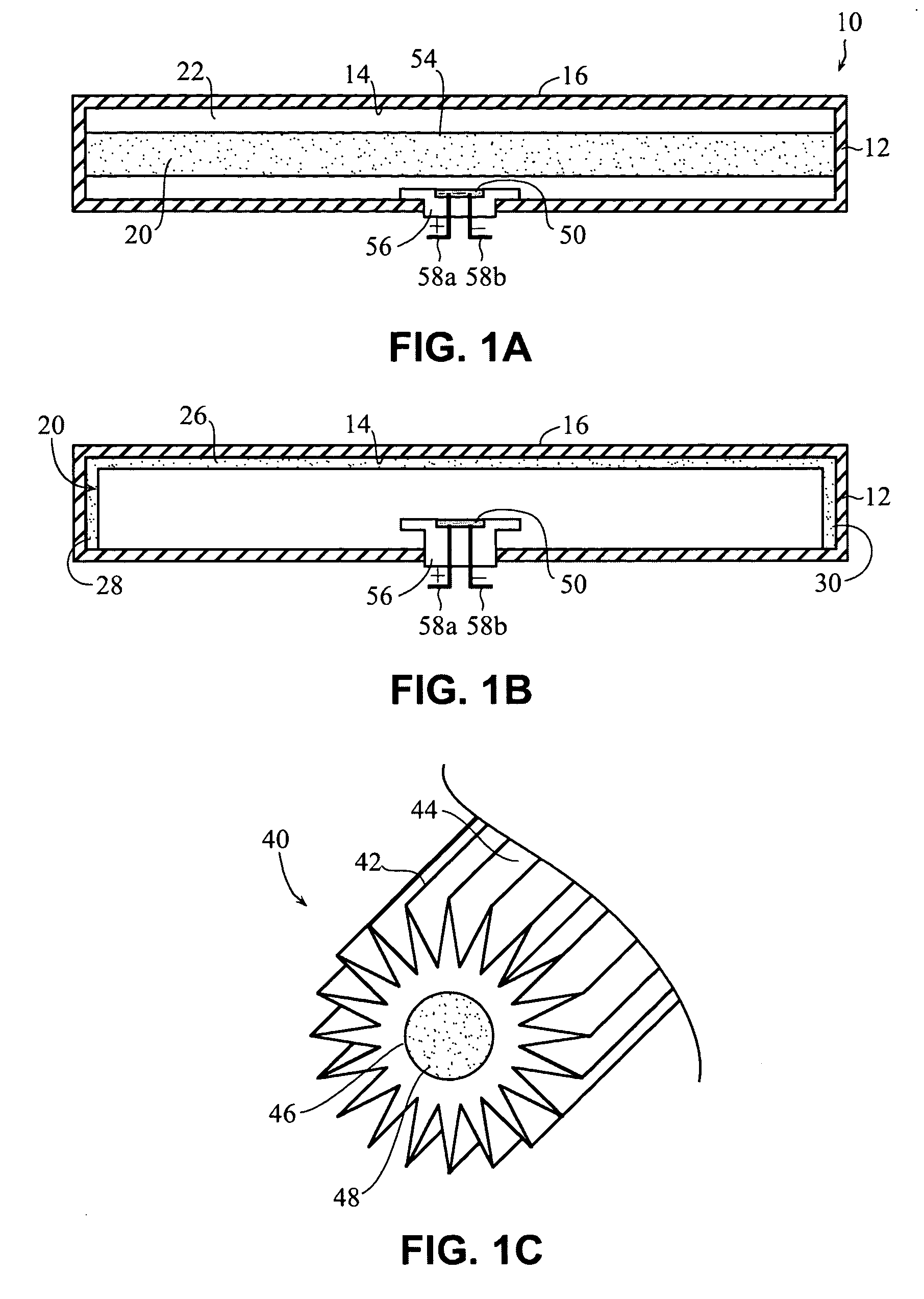
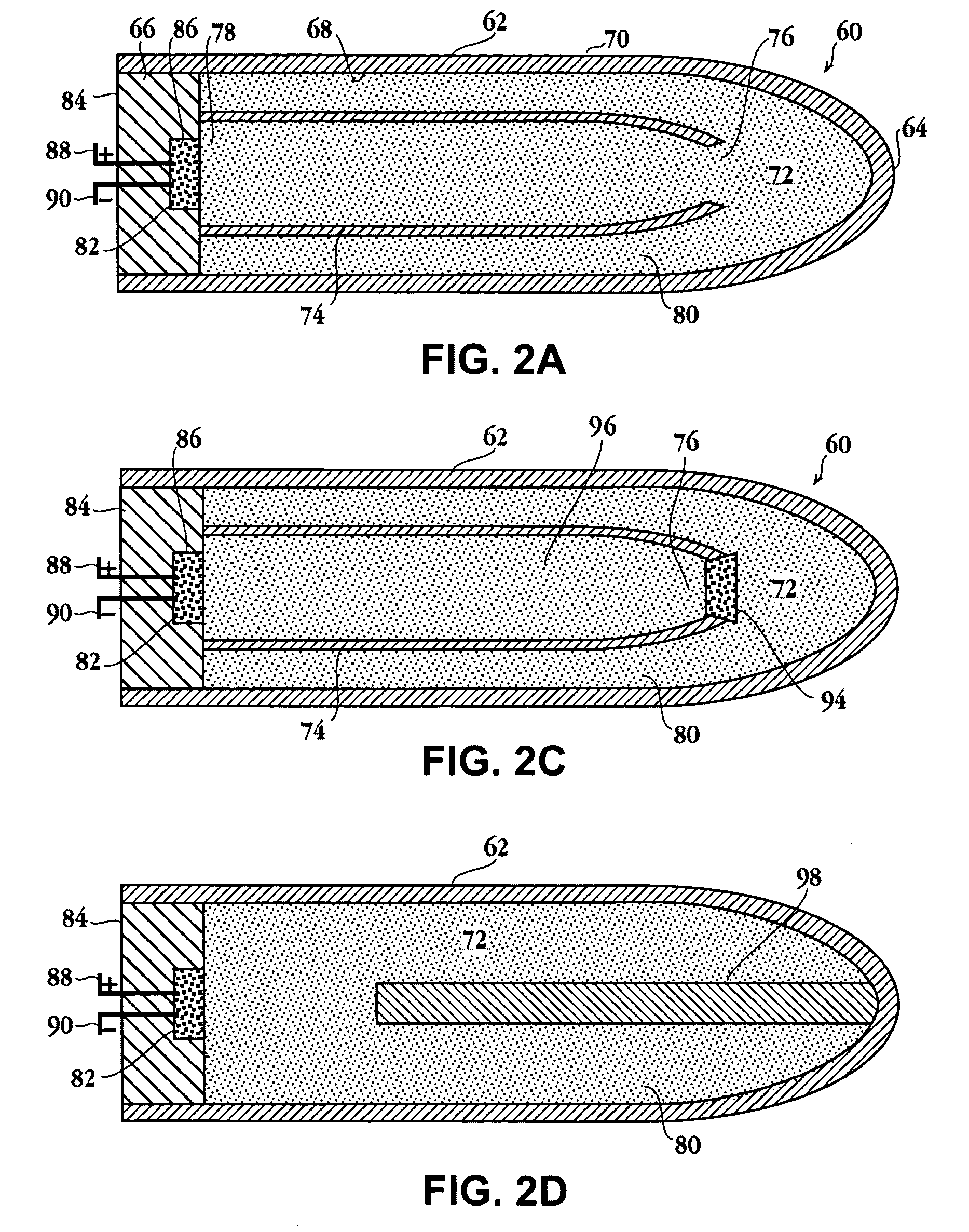
Self-contained heating unit and drug-supply unit employing same
a self-contained heating and drug supply technology, applied in the direction of heat inorganic powder coating, food heating containers, indirect carbon-dioxide mitigation, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, bulky ohmic heating, and substantial delay of seconds or minutes between the time heating is initiated and the maximum temperatur
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Solid Fuel with Laponite
The following procedure was used to prepare solid fuel coatings comprising 76.16% Zr: 19.04% MoO3: 4.8% Laponite® RDS.
To prepare wet Zirconium (Zr), the as-obtained suspension of Zr in DI water (Chemetall, Germany) was agitated on a roto-mixer for 30 minutes. Ten to 40 mL of the wet Zr was dispensed into a 50 mL centrifuge tube and centrifuged (Sorvall 6200RT) for 30 minutes at 3,200 rpm. The DI water was removed to leave a wet Zr pellet.
To prepare a 15% Laponite® RDS solution, 85 grams of DI water was added to a beaker. While stirring, 15 grams of Laponite® RDS (Southern Clay Products, Gonzalez, Tex.) was added, and the suspension stirred for 30 minutes.
The reactant slurry was prepared by first removing the wet Zr pellet as previously prepared from the centrifuge tube and placed in a beaker. Upon weighing the wet Zr pellet, the weight of dry Zr was determined from the following equation: Dry Zr (g)=0.8234 (Wet Zr (g))−0.1059.
The amou...
example 2
Measurement of Internal Pressure
Thin film heating units were used to measure the peak internal pressure and the peak temperature of the exterior surface of the substrate following ignition of the solid fuel.
The thin film heating units were substantially as described in Example 9 below and as illustrated in FIGS. 10A and 10B. Two, 2×2 square inch, 0.004 inch thick 304 stainless steel foils formed the substrates. A solid fuel comprising 76.16 wt % Zr, 19.04% MoO3, 4.8% Laponite® RDS and water was coated onto the interior surface of the stainless steel substrates. The thickness of the solid fuel layer was 0.0018±0.0003 inches. The layer of solid fuel covered an area of 1.69 in2 and after drying, the weight of the solid fuel disposed on the interior surface of each substrate was 0.165 to 0.190 grams. The spacer comprised a 0.24 inch thick section of polycarbonate (Makrolon). The ignition assembly comprised a FR-4 printed circuit board having a 0.03 inch diameter opening at the end t...
example 3
Thermal Images of Heating Unit
A solid fuel consisting of a mixture of zirconium (40.6 wt %), MoO3 (21.9 wt %), and KClO3 (1.9 wt %), nitrocellulose (0.6 wt %), and diatomaceous earth (35 wt %) was prepared. The solid fuel was placed in a 0.030-inch gap between a stainless steel substrate (0.015 inch wall thickness) and a stainless steel backing member (0.015 inch wall thickness). The diameter of the substrate was {fraction (9 / 16)} inch. The fuel was ignited, and thermal images of the heating unit were taken as a function of time after ignition. The results are shown in FIGS. 4A-4F.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com