Lipid encapsulated interfering RNA
a technology of interfering rna and lipids, which is applied in the direction of aerosol delivery, drug compositions, metabolic disorders, etc., can solve the problems of immune response, safety concerns, and potential undesired immune responses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
SNALP Formulations Encapsulating siRNA
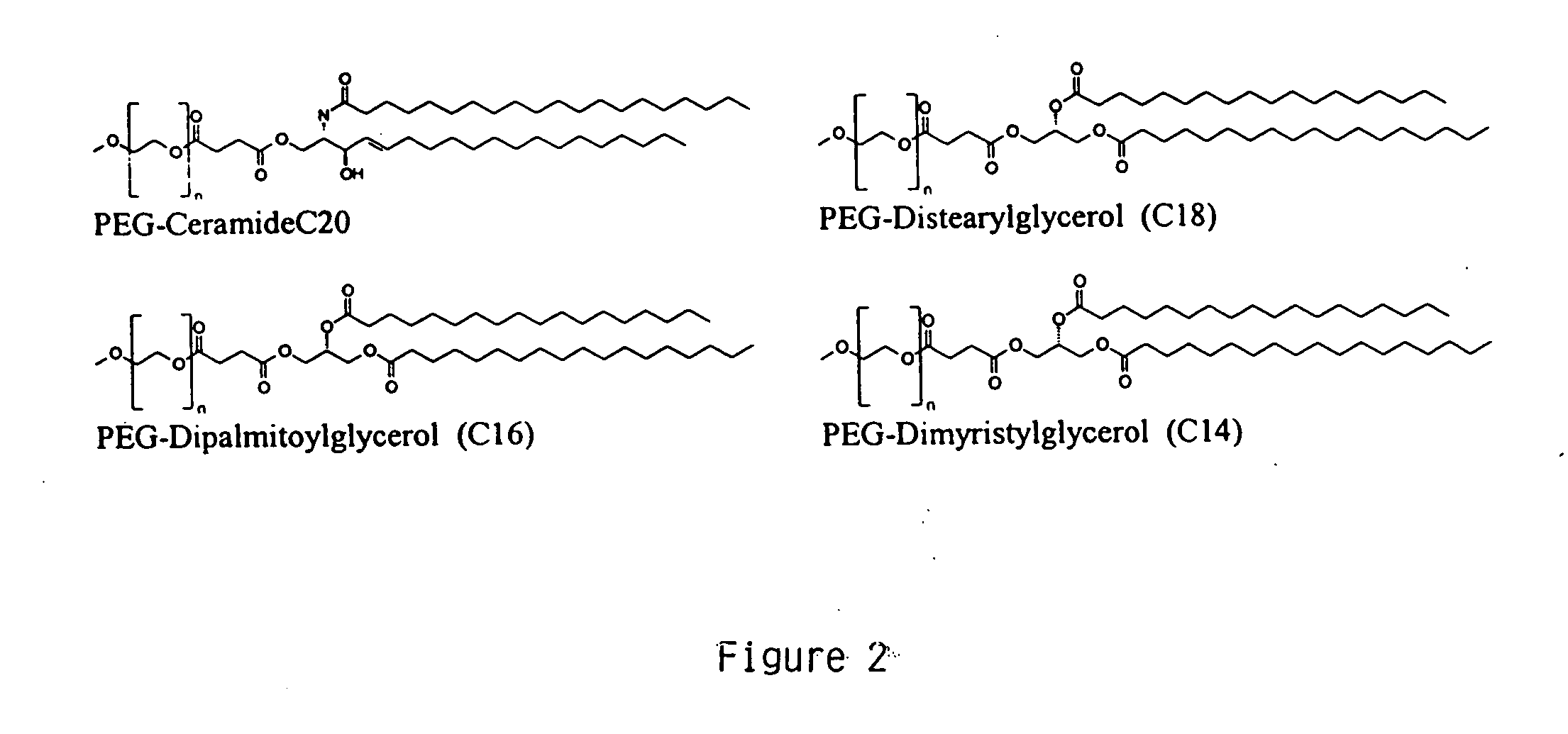
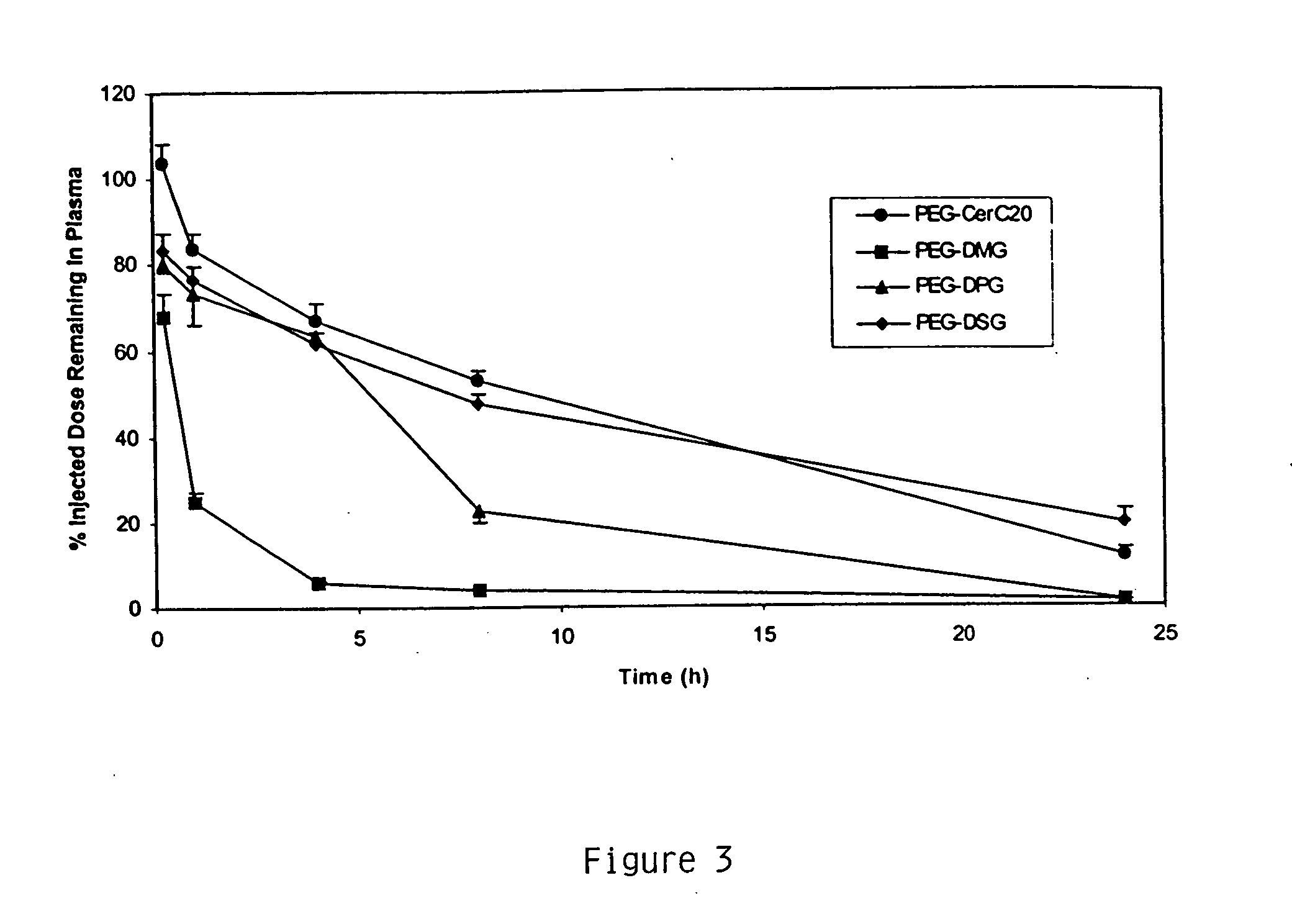
This example demonstrates encapsulating siRNA in SNALP formulated with either short- or long-chain PEG-DAG and produced by continuously mixing organic lipid and aqueous buffer solutions. PEG-DAG lipids employed were PEG-dimyristylglycerol (C14) (PEG-DMG) and PEG-distearylglycerol (C18) (PEG-DSG). Anti-α-galactosidase (β-gal) siRNA encapsulated in DSPC:Cholesterol:DODMA:PEG-DMG / PEG-DSG SNALP by this method resulted in ≧90% encapsulation (Ribogreen Assay) and ˜120 nm particle size (Malvern sizer). The preparations had the following characteristics:
4 ml prep: anti-B-gal siRNA in DSPC:Chol:DODMA:PEG-DMG liposomes
Initial mix=94% encapsulation Post dilution mix=98% encapsulation Post incubation mix=97% encapsulation Post overnight dialysis=96% encapsulation Particle size=109.7 nm Polydispersity=0.14
8 ml prep: anti-B-gal siRNA in DSPC:Chol:DODMA:PEG-DMG liposomes Post dilution & incubated mix=89% Post overnight dialysis=91% Particle siz...
example 2
Downregulation of Intracellular Expression in Cells by Delivering In Vitro an SNALP Formulation Encapsulating siRNA
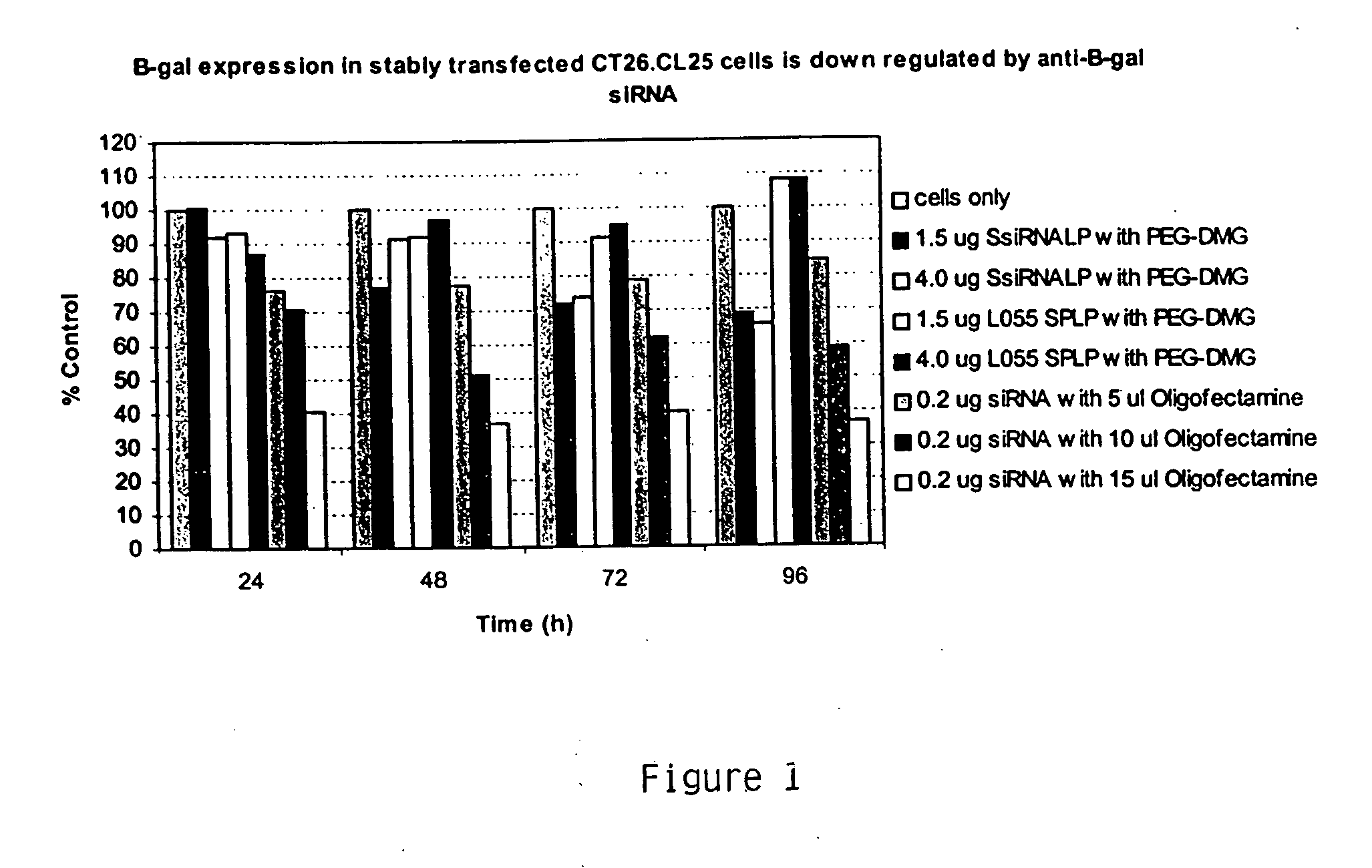
This example demonstrates downregulation of β-Gal expression in CT26.CL25 cells delivered in vitro DSPC:Cholesterol:DODMA:PEG-DMG liposomes encapsulating anti-β-Gal siRNA. The results are depicted in FIG. 1.
In vitro delivery of 0.2 μg Oligofectamine-encapsulated anti-β-Gal siRNA decreased β-Gal activity by about 60% in comparison to unexposed control cells. Encapsulating 1.5 μg anti-β-Gal siRNA in DSPC:Cholesterol:DODMA:PEG-DMG liposomes decreased β-Gal activity by about 30% in comparison to unexposed control cells.
example 3
Assays for Serum Stability
Lipid / therapeutic nucleic acid particles formulated according to the above noted techniques can be assayed for serum stability by a variety of methods.
For instance, in a typical DNase 1 digestion, 1 μg of DNA encapsulated in the particle of interest is incubated in a total volume of 100 μL of 5 mM HEPES, 150 mM NaCl, 10.0 mM MgCl2 pH 7.4. DNase treated samples are treated with either 100 or 10 U of DNase I (Gibco-BRL). 1.0% Triton X-100 can be added in control experiments to ensure that lipid formulations are not directly inactivating the enzyme. Samples are incubated at 37° C. for 30 min after which time the DNA is isolated by addition of 500 μL of DNAZOL followed by 1.0 mL of ethanol. The samples are centrifuged for 30 min at 15,000 rpm in a tabletop microfuge. The supernatant is decanted and the resulting DNA pellet is washed twice with 80% ethanol and dried. This DNA is resuspended in 30 μL of TE buffer. 20 μL of this sample is loaded on a 1.0% agar...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| median diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com