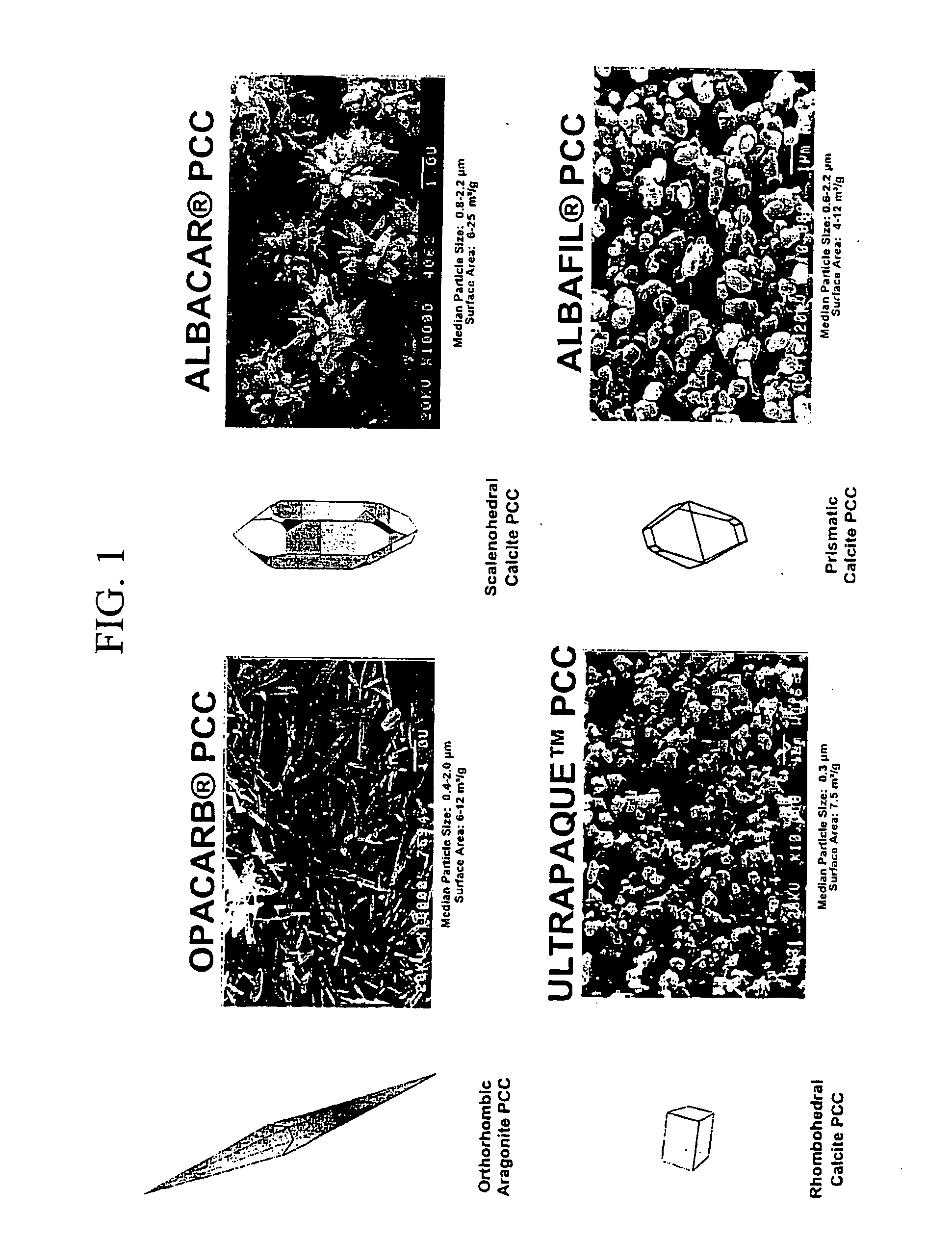
Filler for the manufacture of base paper and method for the manufacture of base paper
a technology of base paper and filler, which is applied in the field of filler for the manufacture of base paper, can solve the problems of not being able to use calcium carbonate, paper is subjected to a force that tends to crack paper, and pcc pigments have not achieved particular success, etc., to achieve good internal strength and density, improve light scattering and opacity, and low base weight
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0039] Laboratory Tests with Different Fillers
[0040] In a series of tests, laboratory sheets were produced on a Formette Dynamique sheet mould. The fibre pulps, broke and different fillers described below were used at test points. A standard amount of retention agents and starch was also used.
[0041] The following fibre pulps were used in the tests:
[0042] Nordic bleached chemical softwood pulp, which was refined to an SR number of 24 on an Escher Wyss laboratory refiner;
[0043] bleached CTMP containing 85% aspen and 15% spruce, which was refined to a CSF value of 48 ml on a Voith Sulzer laboratory refiner (consistency 4.2%, specific edge load 0.3 J / m, specific energy consumption 90 kWh / t). The fibre distribution of the pulp and its most important paper technical values measured from laboratory sheet were:
[0044] length-weighted fibre length: 0.69 mm
[0045] McNett classification +28 mesh: 3.3%
[0046] McNett classification {fraction (28 / 48)} mesh: 39.4%
[0047] McNett classification {fractio...
example 2
[0060] Manufacture of Base Paper on a Pilot Paper Machine as Well as its Coating and Calendaring
[0061] The following fibre pulps were used in tests:
[0062] mill-ground Nordic bleached chemical softwood pulp,
[0063] bleached CTMP containing 85% aspen and 15% spruce, which was after-refined on a pilot-scale refiner with a low specific edge load while the specific energy consumption was 140 kWh / t. Before the after-refining, the CSF of the pulp was 115 ml. After the after-refining, the most important properties of the pulp and laboratory sheets were:
[0064] CSF 59 ml
[0065] length-weighted fibre length 0.73 mm
[0066] McNett classification +16 mesh: 0.0%
[0067] McNett classification {fraction (16 / 30)} mesh: 5.4%
[0068] McNett classification {fraction (30 / 50)} mesh: 31.3%
[0069] McNett classification {fraction (50 / 200)} mesh: 34.1%
[0070] McNett classification -200 mesh: 29.1%
[0071] brightness 78.6
[0072] tensile index 46.7 Nm / g
[0073] tear index 3.9 mNm.sup.2 / g
[0074] density 570 kg / m.sup.3 (bulk 1....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
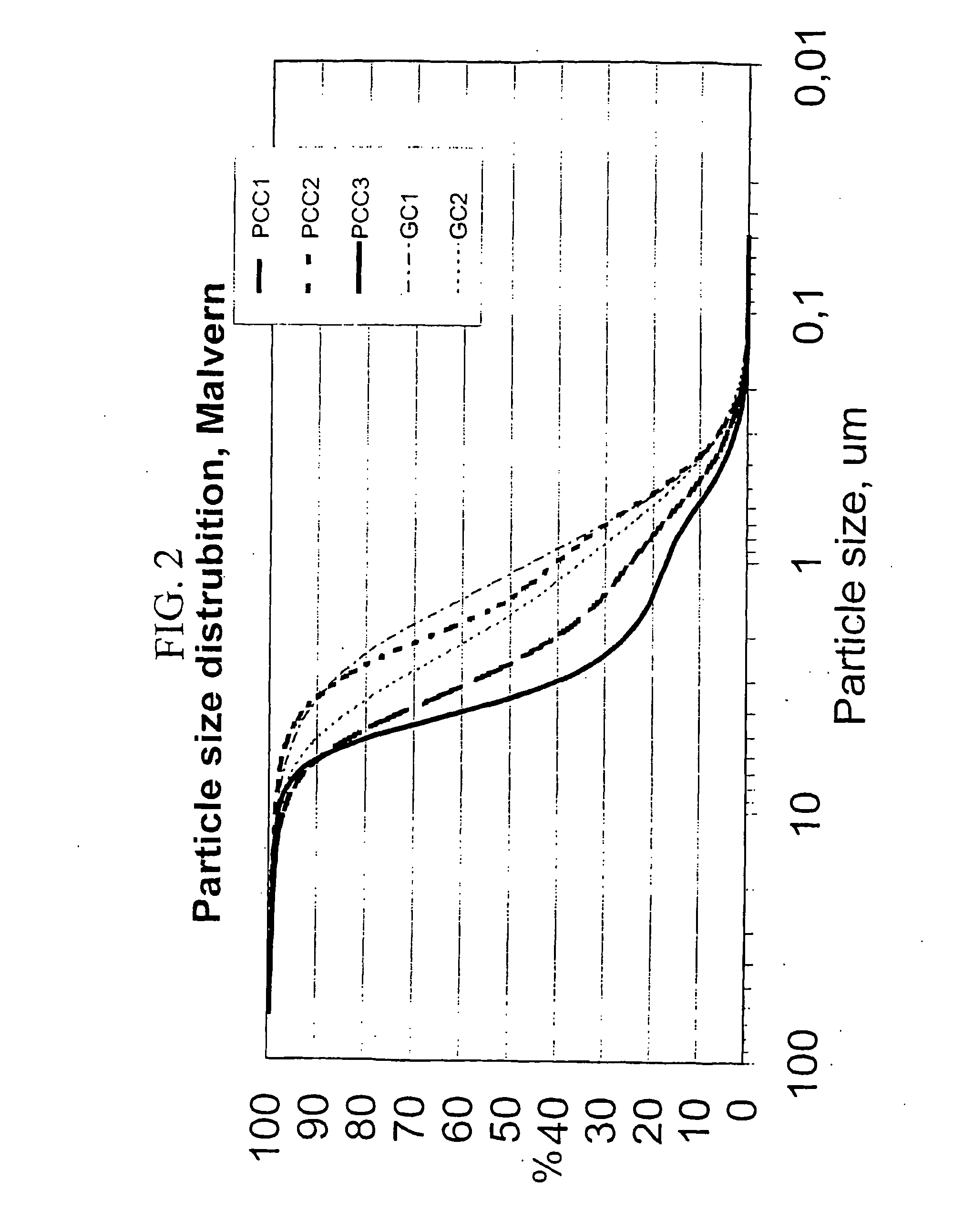
| particle size distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com