Methods and pharmaceutical compositions for treating celiac disease and gluten intolerance
a technology for applied in the field of methods and pharmaceutical compositions for treating celiac disease and gluten intolerance, can solve the problems of high sodium dose and undesirable for certain patients, and achieve the effect of preventing signs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0130]Buffers composed of acetate and citric acid or citrate and citric acid at pH 5.4 over a range of 0.75-3 g of total buffer were prepared. These buffers were added into a gluten-free vegetable korma test meal and titrated by adding 2 ml of 100 mM HCl followed by a pH measurement. FIG. 1 shows that addition of buffer can enhance the buffering capacity in a dose dependent manner relative to the unbuffered meal. The data indicate that the buffering capacity of acetate is about twice as much as citrate, and a 3 g citrate buffer can double the amount of HCl necessary to get the meal pH below 3.0 compared to the meal without buffer added. This example demonstrates that ALV003 dose forms containing at least 0.75 g and up to 3 g of citrate buffer at about pH 5.4 provide a significantly longer duration for the enzymes to degrade gluten effectively by maintaining the pH above 3.5 until after 2 or more millimoles of hydrochloric acid were added. Similar superior results may be achieved in ...
example 2
[0131]A series of citrate buffers at either pH 5.4 or 5.2 ranging from 1-3 g of total buffer were prepared and added to a vegetable korma test meal (FIG. 2). The meal was titrated by adding 2 ml of 100 mM HCl followed by a pH measurement. These citrate buffers were compared to a formulation used in a previous clinical trial and a formulation without buffer added. The 2 g citrate buffers at either pH 5.4 or 5.2 were able to buffer the meal similarly to the clinical trial formulation and increased the amount of HCl necessary to reduce the pH to 3.0 by approximately 50% compared to the unbuffered meal. This example demonstrates that ALV003 dose forms containing at least 2 g of citrate buffer at pH 5.2-5.4 provide a substantially longer period of time at a favorable pH for the enzymes to effectively degrade gluten by maintaining the pH above 3.5 until 2 or more millimoles of hydrochloric acid were added. Similar superior results may be achieved in accordance with the invention using sim...
example 3
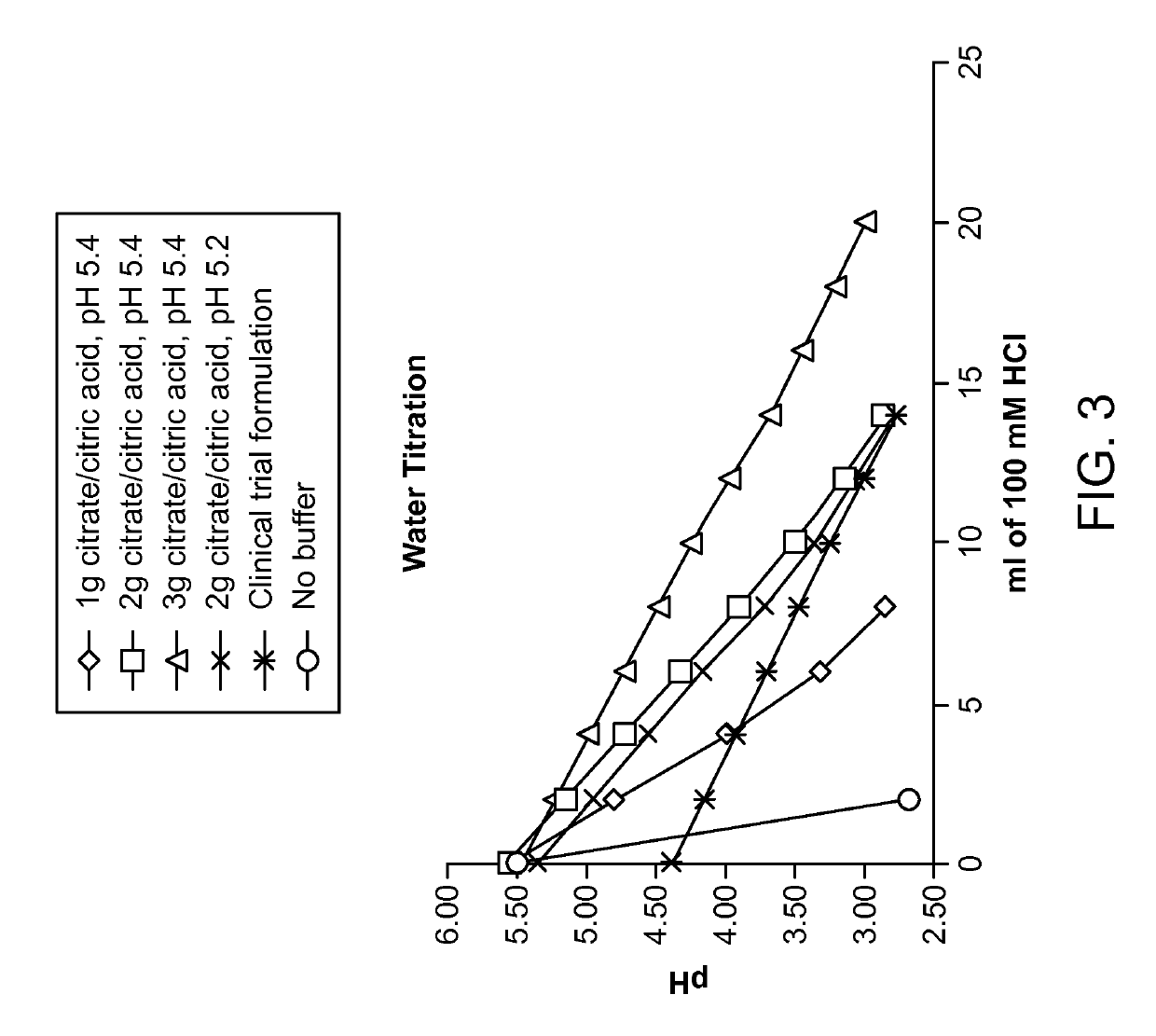
[0132]A series of citrate buffers at either pH 5.4 or 5.2 ranging from 1-3 g of total buffer were prepared and added to a water test meal to simulate a worst-case scenario of a low buffering meal (FIG. 3). The water meal was titrated by adding 2 ml of 100 mM HCl followed by a pH measurement. These citrate buffers were compared to a formulation used in a previous clinical trial and a formulation without buffer added. Addition of buffers significantly enhanced the buffering capacity relative to water without buffer. This example demonstrates that ALV003 dose forms containing at least 1 g and up to 3 g of citrate buffer at pH 5.4 provide superior results by maintaining the pH above about 4 until about 0.5 millimoles or more of hydrochloric acid were added. Similar superior results may be achieved in accordance with the invention using similar amounts of citrate buffer at pH ranging from 5 to 5.5. As discussed above, the citrate buffer may be divided into the various solid dose forms of...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| RH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com