Bearing component and method
a technology of bearing components and components, applied in the direction of shafts, bearings, rotary machine parts, etc., can solve the problems of high hardness and brittleness of white layers, cracks may develop in white layers between, and flaking can occur, so as to improve rolling contact fatigue performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
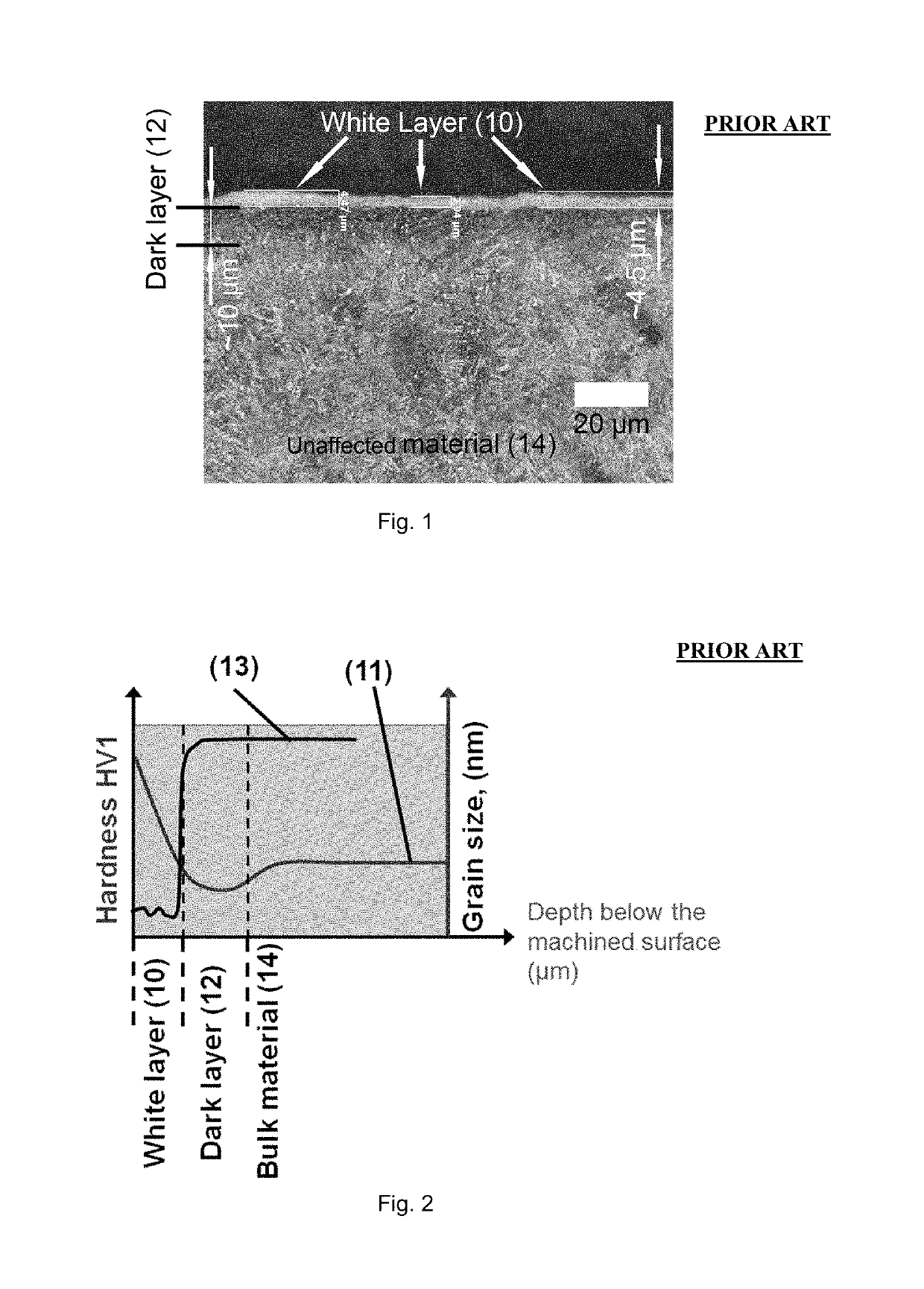
[0034]FIG. 1 shows a cross sectional view of a typical subsurface microstructure of an as-machined workpiece subjected to a hard machining process according to the prior art. The workpiece comprises a white layer 10, an underlying dark layer 12 directly adjacent to the white layer 10 and underlying unaffected material 14 directly adjacent to the dark layer 12.
[0035]The white layer 10 comprises evenly distributed carbides. The underlying dark layer 12, which is thicker than the white layer 12, also contains evenly distributed carbides. The unaffected material 14, which is unaffected by the hard machining process, comprises martensitic / bainitic needles having a length of about 2-3 μm and a width of about 0.5 μm. The martensitic / bainitic unaffected material also comprises evenly distributed carbides.
[0036]FIG. 2 shows the hardness profile 11 and the grain size 13 of an as-machined workpiece according to the prior art with depth below the as-machined surface, i.e. the uppermost surface ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| grain size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Vickers hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Vickers hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com