Linear optical amplifier using coupled waveguide induced feedback
A technology for optical amplifiers and feedback layers, applied in the field of semiconductor optical amplifiers, can solve problems such as high operating current, gain compression or saturation affecting data transmission, and increasing optical mode size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
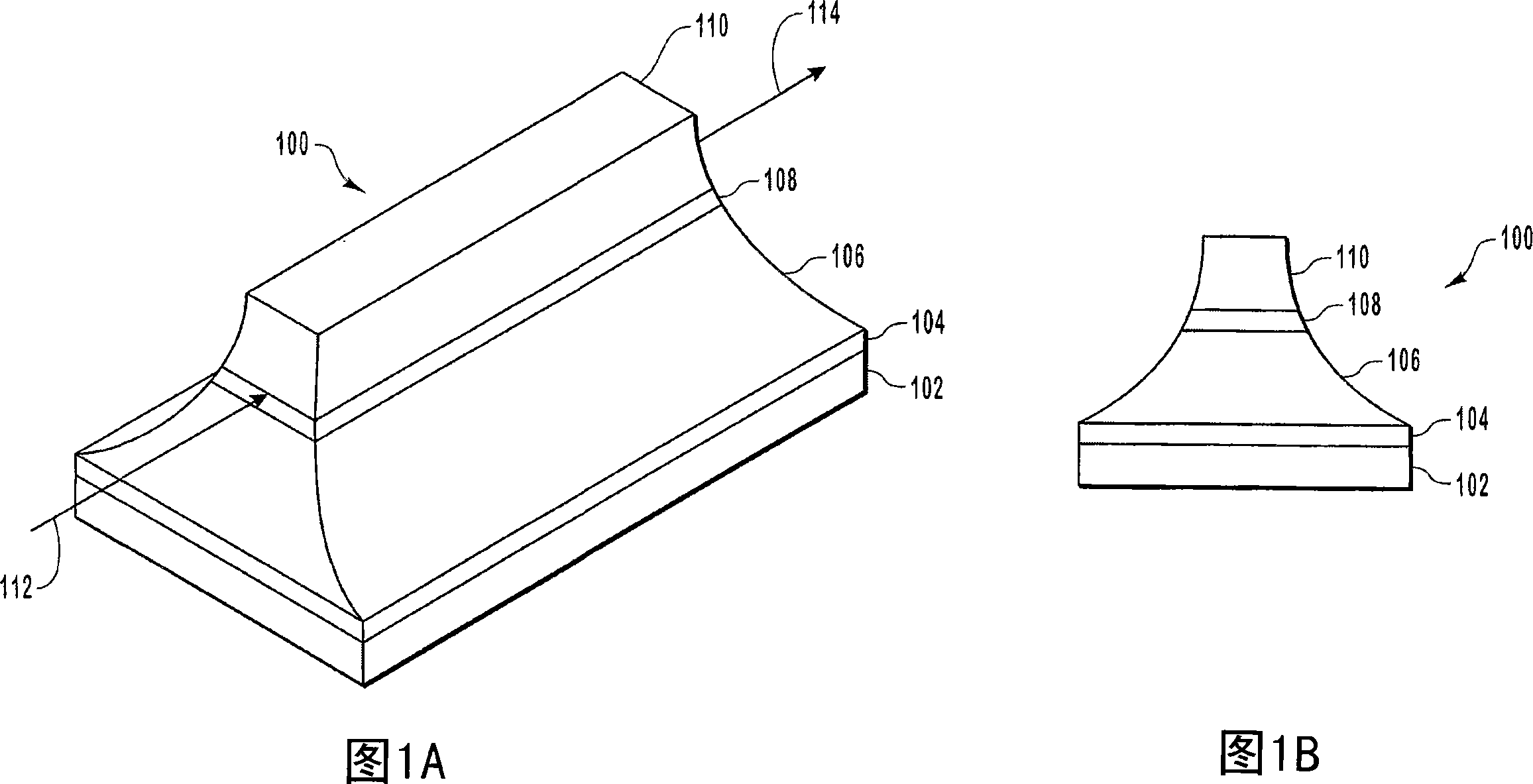
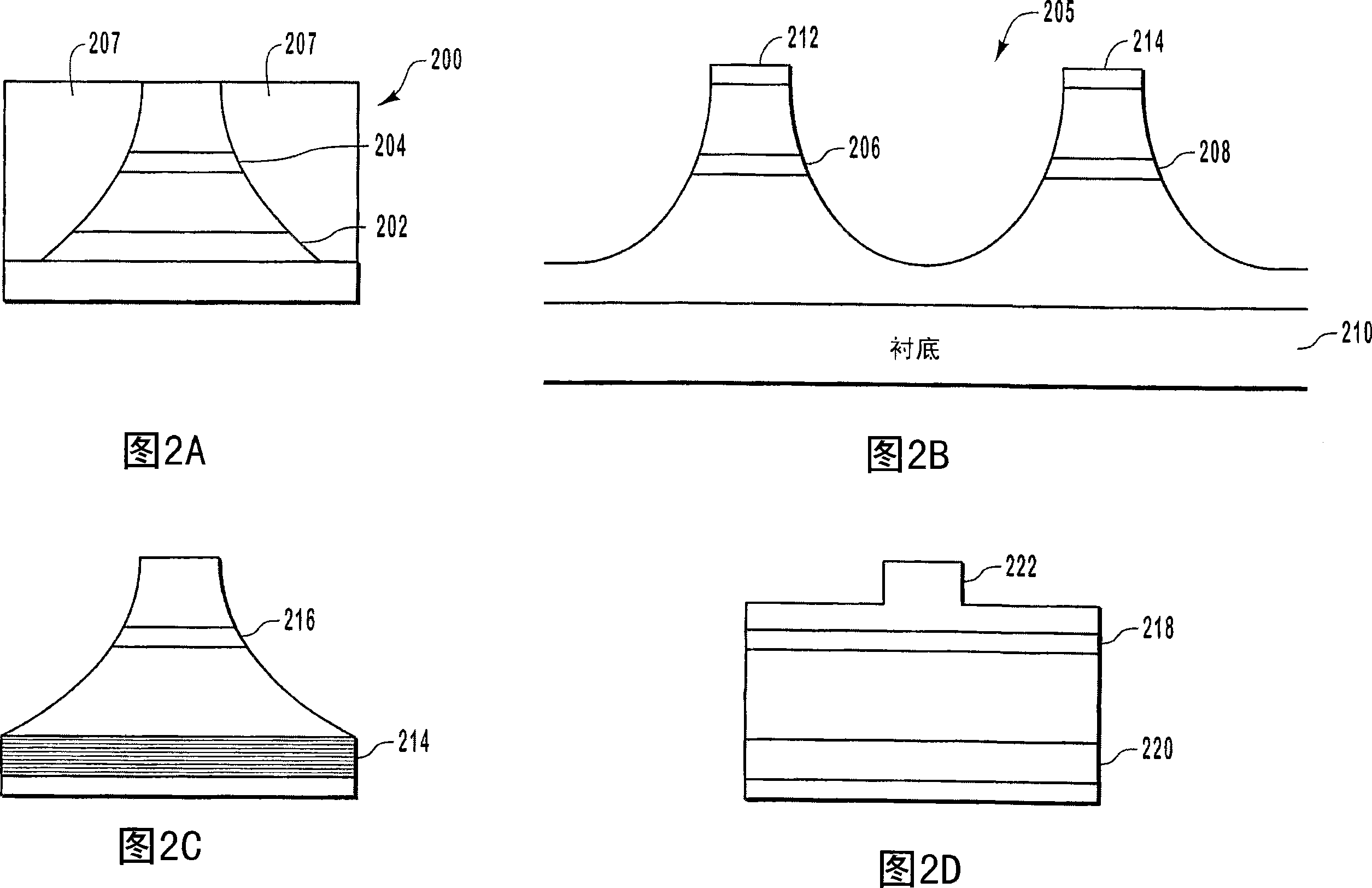
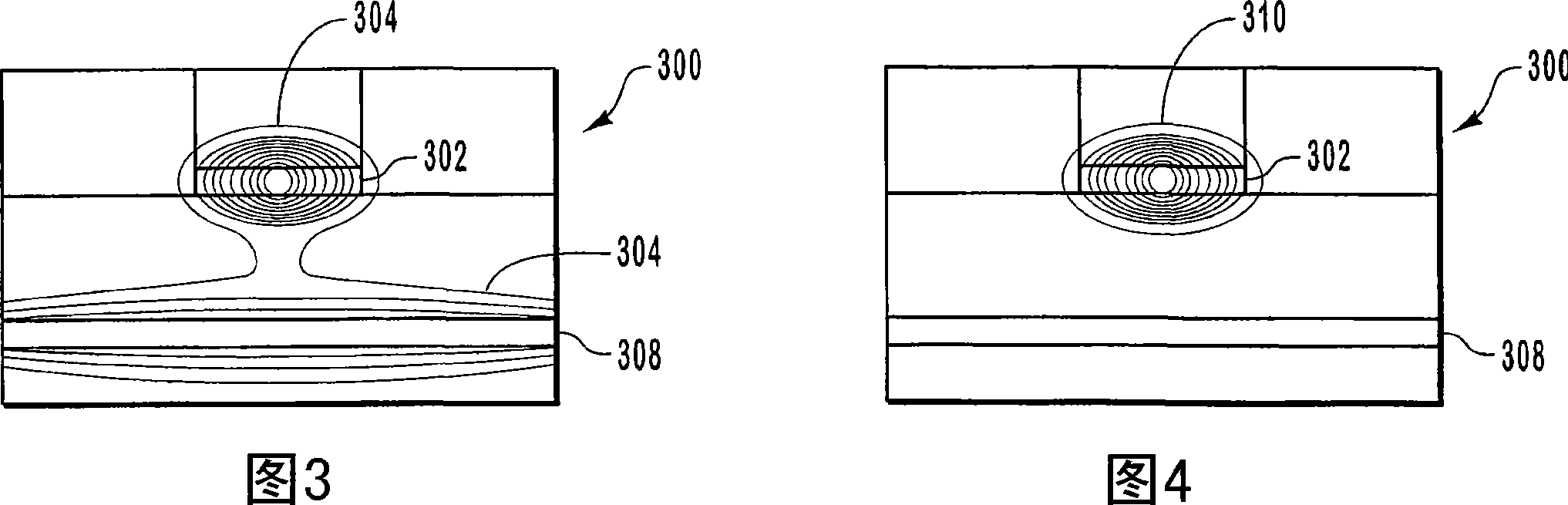
[0028] A semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA) amplifies an optical signal without converting the incident optical signal to an electrical signal. SOAs utilize stimulated emission to amplify incident light signals. However, as mentioned above, SOAs often suffer from gain compression as the output optical power increases. However, gain compression is often accompanied by undesired results such as intersymbol interference and crosstalk.
[0029] Embodiments of the present invention relate to extending the operating linear range of SOA. Expanding the linear range enables the SOA to linearly amplify optical signals over a wider range of optical power. The linear range of operation of the SOA is extended by providing optical feedback that linearizes the gain of the SOA as the optical output power increases. Another advantage of some embodiments of the present invention is the ability to increase the gain (gain expansion) as the optical output power increases, as opposed to gain ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com