Dual voltage electrical body nano positioning and voltage electrical driver, its control method and controller
A piezoelectric driver, nano-positioning technology, applied in piezoelectric devices/electrostrictive devices, generators/motors, piezoelectric effect/electrostrictive or magnetostrictive motors, etc. Temperature zone, small volume, easy integration and other issues, to achieve the effect of simple structure, large working temperature zone, and easy integration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Example 1: Basic dual piezoelectric linear nanopositioning piezoelectric actuator
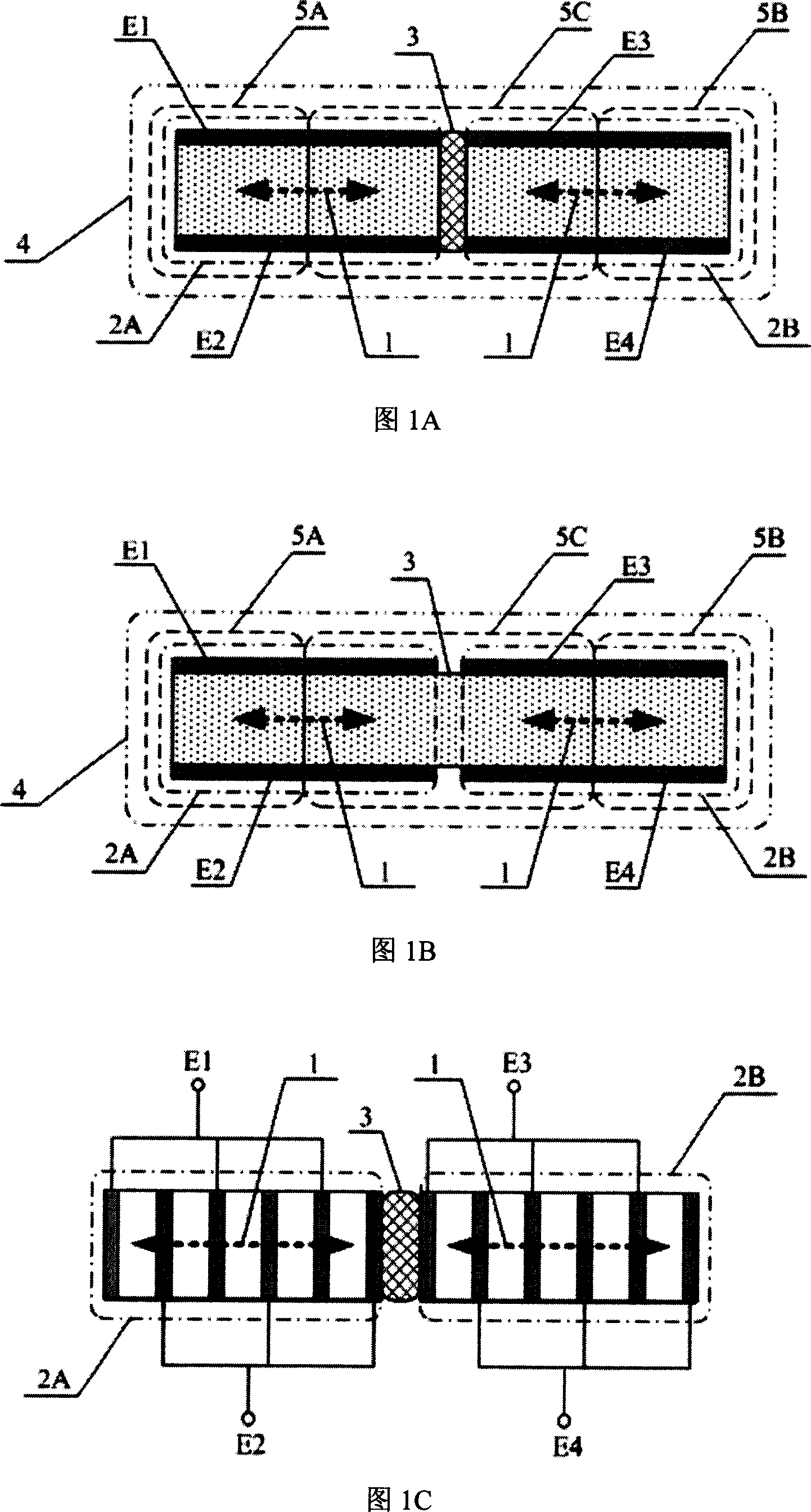
[0066] Referring to Fig. 1A, the left and right piezoelectric actuators are fixedly connected to the connecting body 3 in a mechanically in series manner along the deformation direction 1 to form independently controllable two-connected bodies 4; or as shown in Fig. 1B: The electrodes of a piezoelectric actuator are divided into two to form two components respectively called the left piezoelectric actuator 2A and the right piezoelectric actuator 2B, which deform along the original deformation direction 1 and are integrated with the connecting body 3 The piezoelectric actuator constitutes a dijoint 4. The deformation refers to piezoelectric deformation.
[0067] As shown in Figures 1A and 1B, the left piezoelectric actuator 2A and the right piezoelectric actuator 2B are bounded by their respective mid-sections along their deformation directions, dividing the two conjoined bodies into thr...
Embodiment 2
[0087] Embodiment 2: force body type driver
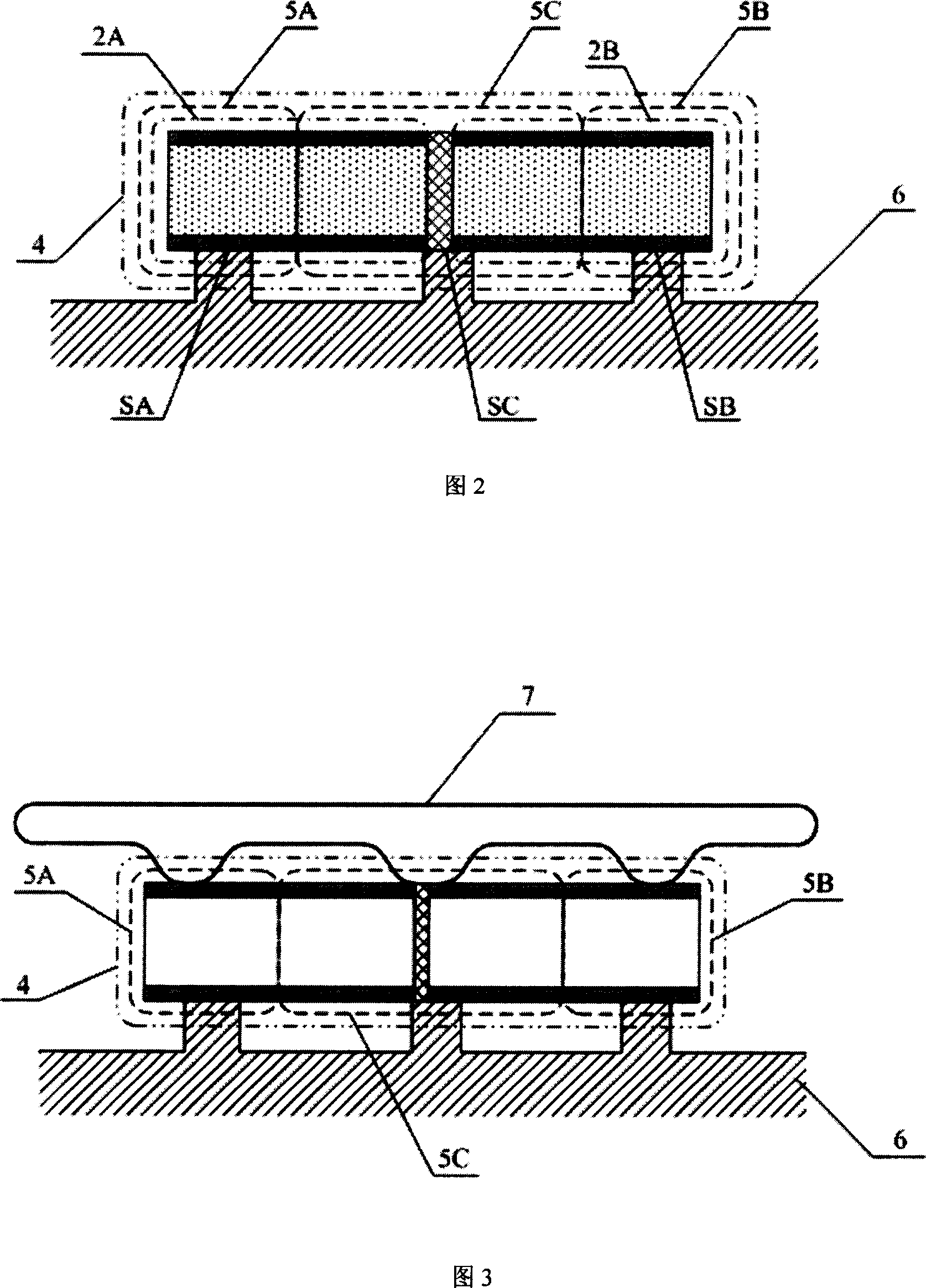
[0088] If the gravity of the dijoint itself is used as its pressure on the base body to generate friction and then generate driving force, this driving force is often relatively small and cannot meet many practical needs, especially when it is required to drive in the vertical direction. In this embodiment, by adding a force applying body, the left area, the middle area and / or the right area of the dijoined body are pressed against the substrate with the force applying body, which makes the dijoined body generate greater pressure on the base body to produce more Greater friction, and thus greater thrust.
[0089] As shown in Fig. 3, the two conjoined body 4 is placed on the base body 6 and acts on the left area, the middle area and / or the right area of the two conjoined body 4 with a force applying body 7, and the force applying body 7 uses elasticity, gravity and / or Or the electromagnetic force presses the dyad 4 onto the sub...
Embodiment 3
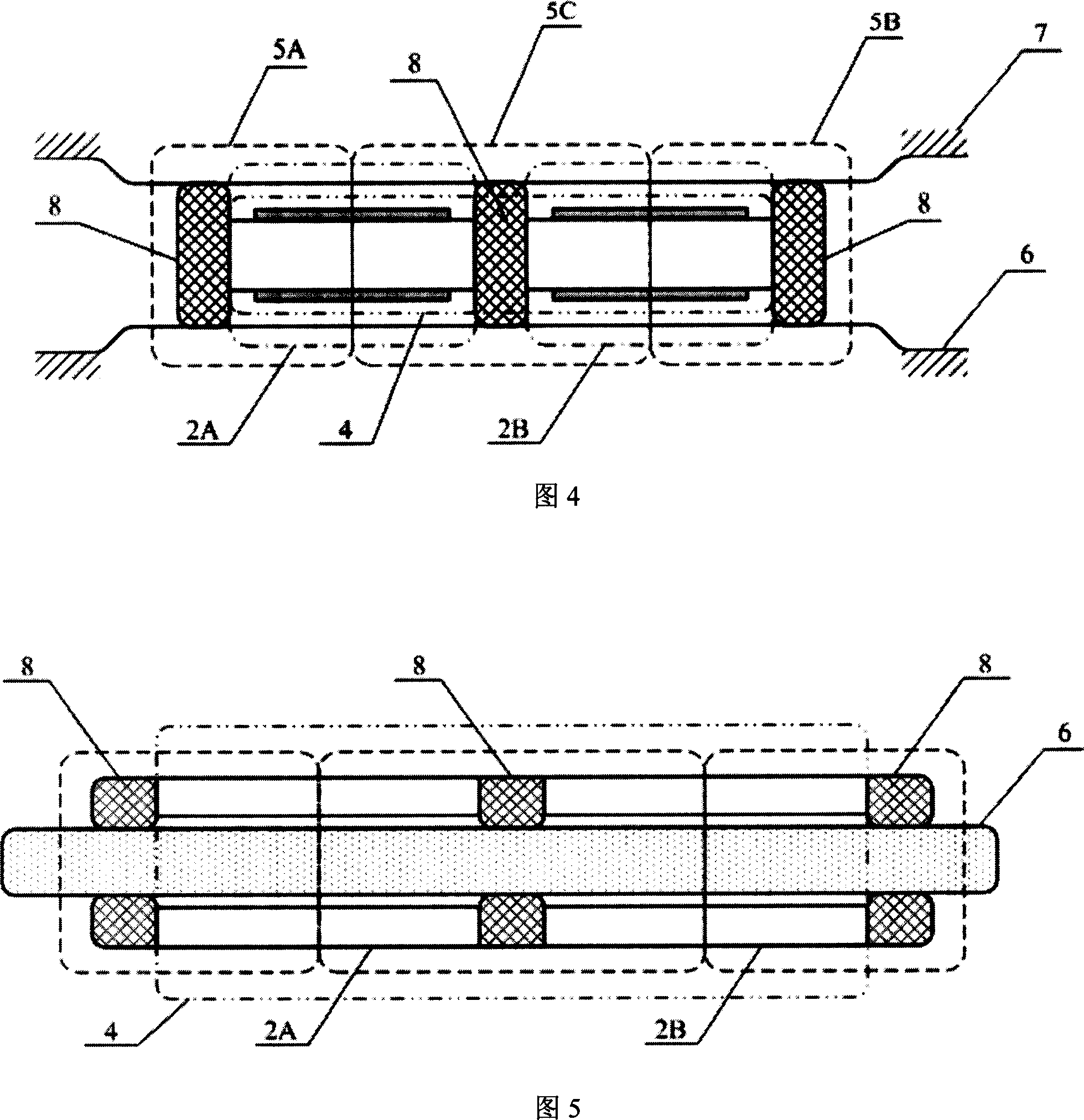
[0090] Embodiment 3: Forced Pad Driver
[0091] As shown in Figure 4, the present embodiment is on the basis of the above-mentioned embodiment on the left area 5A, the middle area 5C and / or the right area 5B of the two conjoined body 4, and the force-bearing pad 8 is fixed with the base body 6 with the force-bearing pad 8. The effect of pressure is to protect the two conjoined body 4 or the base body 6, change the pressure between each zone and the base body 6, change the acting area of the pressure, and change the coefficient of static friction. In a word, the maximum friction between the two conjoined body 4 and the base body 6 can be adjusted static friction. The pressure between the force pad 8 and the base body 6 comes from the original pressure of the area where it is located and the base body, and also can come from its own force on the base body, including its gravity, electromagnetic force, elastic clamping force, and can also come from external force. The pressure...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com