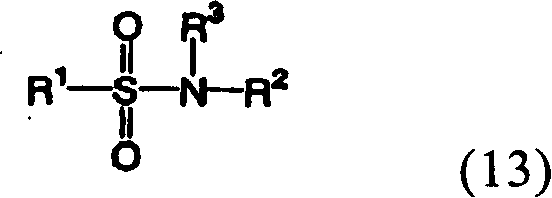
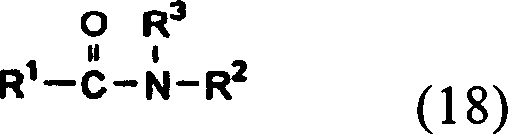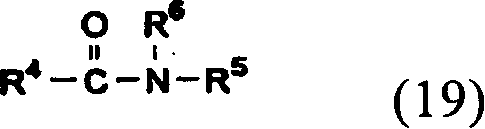Optical compensating polarizing plate, image display device and liquid crystal display device
A technology of optical compensation and optical compensation layer, applied in polarizing elements, optics, nonlinear optics, etc., can solve the problems of impossible to achieve the desired purpose, deterioration of polarizing plate performance, and phase difference changes.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0400] [Method for producing cellulose acylate film]
[0401] [Dissolution step]
[0402] Next, preparation of a cellulose acylate solution (dope) is explained. The cellulose acylate is dissolved by any method without limitation, ie, room temperature dissolution, cooling dissolution, heat dissolution or a combination thereof. Regarding the preparation of the cellulose acylate solution of the present invention, the concentration of the solution at the time of dissolution and filtration is preferably used as described in, for example, Japan Institute of Invention and Innovation Journal of Technical Disclosure No. 2001-1745 (2001.03.15, Japan Institute of Invention and Innovation), Methods on pages 22-25.
[0403] (transparency of dope)
[0404]It is preferable that the dope transparency of the cellulose acylate solution of the present invention is 85% or higher, more preferably 88% or higher, more preferably 90% or higher. In the present invention, it has been confirmed that...
Embodiment 1
[0486] (manufacturing transparent protective film)
[0487] In a stainless steel dissolving tank (4000L) with stirring blades, gradually add cellulose acetate powder (flakes) to the solvent mixture solution comprising the following ingredients, fully stir and disperse until the total amount reaches 2000kg. The optical anisotropy-reducing compound of the present invention and the wavelength dispersion regulator of the present invention (as listed in Table 1) were respectively added to obtain samples 101-106.
[0488] Cellulose triacetate (degree of substitution shown in Table 1) 17.0 parts by mass
[0489] Dichloromethane 70.5 parts by mass
[0490] Methanol 10.5 parts by mass
[0491] Provide optically isotropic compounds (as listed in Table 1) 2.0 parts by mass
[0492] Compounds for adjusting wavelength dispersion (as listed in Table 1) 0 or 8 parts by mass
[0493] The plane phase difference of the transparent protective film is |Re|≤10nm, and the thickness direction ph...
Embodiment 2
[0522] (manufacturing transparent protective film)
[0523] A solution of cellulose triacetate was prepared and sample 114 was made as in Example 1 but using the following composition.
[0524] Cellulose triacetate (powder, degree of substitution 2.86, viscosity-average degree of polymerization is 320, water content 0.4% by mass, viscosity in 6% by mass of dichloromethane solution is 305mPa·s, average particle size 1.5mm, and standard Deviation 0.5mm) 17.0 parts by mass
[0525] Dichloromethane 67.4 parts by mass
[0526] Methanol 12.7 parts by mass
[0527] Butanol 0.5 parts by mass
[0528] Triphenyl phosphate (TPP) 1.3 parts by mass
[0529] 0.7 parts by mass of biphenyl-diphenyl phosphate (BDP)
[0530] Provide optically isotropic compounds (as listed in Table 1) 2.0 parts by mass
[0531] Compounds (as listed in Table 1) for adjusting wavelength dispersion 0.8 parts by mass
[0532] (Structure of polarizing plate 7)
[0533] The above-mentioned transparent protect...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com