Laser synthetic method for negative expansion coefficient material
A technology of negative thermal expansion coefficient and laser synthesis, which is applied in the field of laser application technology and material synthesis, can solve problems such as chemical ratio mismatch, achieve fast speed, avoid decomposition, and save the effect of waste liquid treatment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Embodiment 1, laser synthesis negative thermal expansion coefficient material ZrW 2 o 8 :
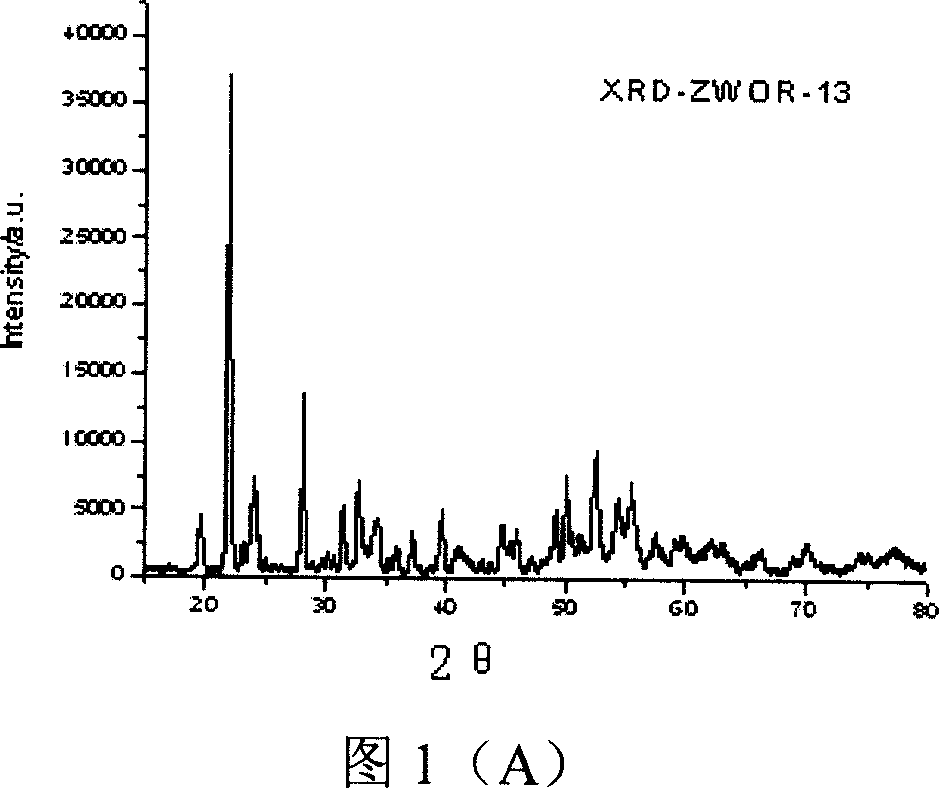
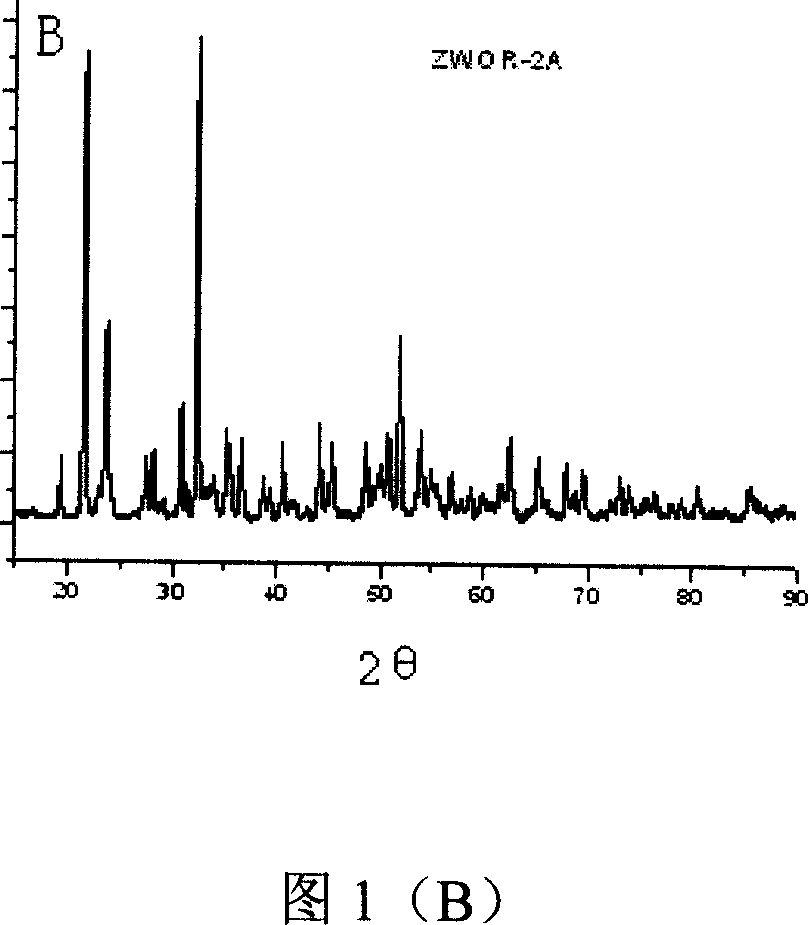
[0037] Weigh ZrO at a molar ratio of 1:2 2 with WO 3 , mixed and ground for 90 minutes, the mixture was compacted, and then laser synthesized. Laser synthesis process parameters are: laser wavelength 10.6μm, power density 1.03kW / cm 2 , beam scanning speed 6mm / s. The laser-synthesized material is a uniform green block, and the macroscopic appearance is flat and smooth. The corresponding X-ray diffraction and Raman spectra are shown in Figure 1 (A), (B), and Figure 2 (A), (B), (C).
[0038] XRD analysis by and 、 , "Search-Match" and other XRD database comparisons are completed (the same below). X-ray Diffraction Phase Analysis Shows Laser Synthesized ZrW 2 o 8 Mainly γ phase (Figure 1A), and the γ phase ZrW with space group P212121 and ICSD card number 56566 2 o 8 The XRD matches perfectly. After annealing at 200 °C, ZrW 2 o 8 From γ phase to α phase, and the ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2: Laser synthesis of negative thermal expansion coefficient material ZrW 2 o 8 :
[0042] Weigh ZrO at a molar ratio of 1:2 2 with WO 3 , mixed and ground for 90 minutes, the mixture was compacted, and then laser synthesized. Laser synthesis process parameters are: laser wavelength 10.6μm, power density 0.2kW / cm 2 , beam scanning speed 0.2mm / s. The laser-synthesized material is a uniform green block, and the macroscopic appearance is flat and smooth. The corresponding Raman spectrum is shown in Figure 2(B).
Embodiment 3
[0043] Embodiment 3: Laser synthesis of negative thermal expansion coefficient material ZrW 2 o 8 :
[0044] Weigh ZrO at a molar ratio of 1:2 2 with WO 3 , mixed and ground for 90 minutes, the mixture was compacted, and then laser synthesized. Laser synthesis process parameters are: laser wavelength 10.6μm, power density 1.5kW / cm 2 , beam scanning speed 12mm / s. The laser-synthesized material is a uniform green block, and the macroscopic appearance is flat and smooth. The corresponding X-ray diffraction and Raman spectra are shown in Figure 2(C).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com