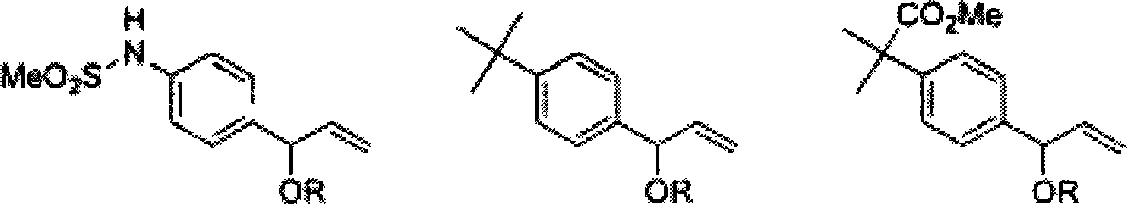
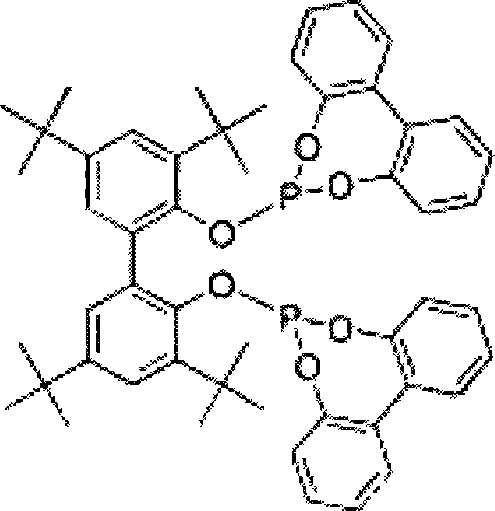
Hydroaminomethylation of olefins
A technology for aminomethylation and olefins, applied in the field of hydrogen aminomethylation of olefins, can solve the problems of increased processing costs, prolonged reaction time and the use of process equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1 - Preparation of dimethylaminomethylalkane mixture
[0026]
[0027] A Neodene(R) olefin blend (10 / 1112 / 13 / 12, 319 g, obtained from Shell Chemical) olefin substrate was charged to a 1-gal (4-L) reactor in THF (680 g). Dimethylamine (222 g) was added to this solution, and from [Rh(CO) 2 A solution of a complex prepared from (acac)] (3.7 g) and tris(2,4-di-tert-butylphenyl)phosphite (46.2 g, obtained from Aldrich Chemical) in THF (374 g). The final rhodium concentration was about 900 ppm by weight. This mixture was heated to 80°C and pressurized to 600 psi (4140 kPa) with syngas and stirred under these conditions for 7 hours. The reactor was cooled to 21°C overnight and the gas phase was vented. After stirring under nitrogen flow for about 1 hour to remove most of the excess dimethylamine, the reactor contents were decanted, THF stripped and distilled using a Kugelrohr apparatus to give a colorless mobile liquid (427 g, 99% yield).
Embodiment 2
[0028] The hydroaminomethylation of embodiment 2-oleic acid diethanolamide and diethanolamine
[0029]
[0030] Oleamide (13.49 g), diethanolamine (4.51 g) and THF solvent (20 mL) were added via syringe to the nitrogen purged reactor. The reactor was stirred under approximately 200 psi (1380 kPa) syngas to saturate the solution. After venting, the [Rh(CO) 2 (acac)] (5351 ppm by weight of Rh) and tris(2,4-di-tert-butylphenyl)phosphite ligand (5.00 moles of ligand / mole of Rh) in THF Aliquots of pre-prepared catalyst solutions A sample (10.4 g) was charged to the reactor. The reactor was sealed and pressurized with synthesis gas and heated to 80°C. The pressure was increased to 600 psi (4140 kPa) with additional syngas, and then fed at this pressure throughout the reaction as needed. After 4.5 hours, the reactor was cooled, vented and the reactor contents drained. The amber solution was extracted with cyclohexane, then toluene, and the supernatant was discarded. Acetonit...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Embodiment 3-hydroaminomethylation of terminally unsaturated isopolypropylene and dibenzylamine
[0032]
[0033] Vinylidene terminated polypropylene (5.43 g, obtained from Baker-Hughes Corporation) having a weight average molecular weight Mw of about 1800 g / mol was dissolved in toluene (70 mL). A portion of this solution (65 mL) was transferred to a 100 mL Parr reactor, whereupon dibenzylamine (2 mL, 9.8 mmols) was added and a solution containing the complex (20 mL of a stock solution prepared by dissolving [Rh( CO) 2 (acac)] (2.56 g), 2,4-di-tert-butylphenyl phosphite (32.09 g) to give a total solution mass of 200.73 g). The reactor was sealed and pressurized to 600 psi (4140 kPa) syngas and heated to 80°C for 130 minutes. After the reaction, the pressure was released and the reactor was opened while the temperature was still at 60°C, and the contents were drained into a glass beaker. The polymer product was precipitated by adding methanol (approximately 2 x vol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com