Composition for the treatment of digestive pathologies
A therapeutic, digestive disorder technology, applied in the composition of paracellular permeability, hyperalgesia and other abdominal pain, bowel dysfunction, irritable bowel syndrome, which can solve unrecognized problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
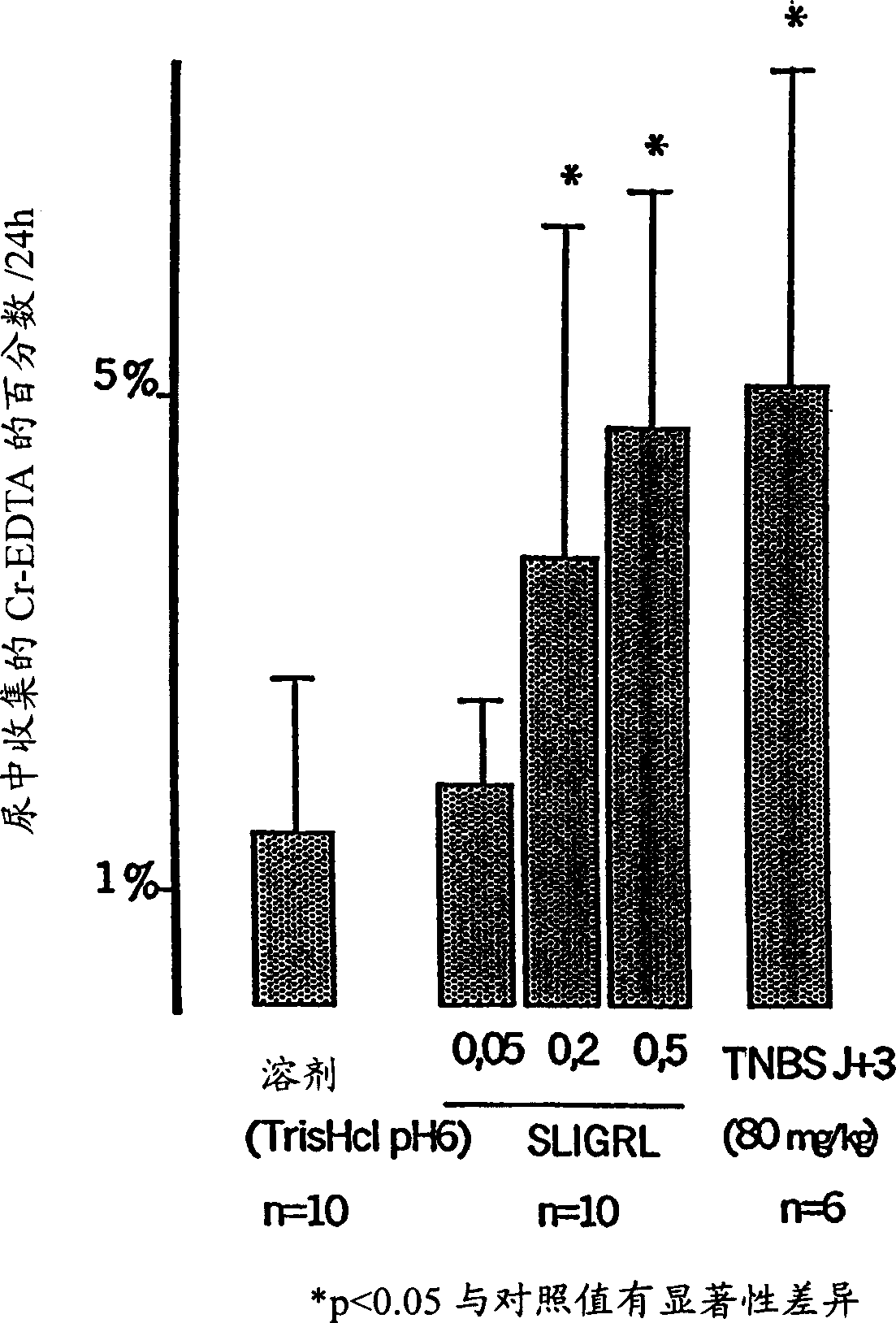
[0045] Example 1: Reduction of rectal hyperalgesia by tight junction blockers.
[0046] The intestinal epithelium contains structures connecting epithelial cells that ensure the controlled passage of immune cells into the intestinal submucosa. This example shows that some molecules known to increase the paracellular permeability of the intestine, such as SLIGRL, promote the accumulation of immune cells (mast cells, enterochromaffin cells) in the submucosa of the intestine, and by blocking Intracolonic treatment of the agent can prevent (eg, inhibit, reduce) this effect.
[0047] Six groups of 8 male Wistar rats (200-250 g) each were used in this study. The animals were equipped with an indwelling intracolic catheter in the proximal colon (3 cm from the cecum-colon junction). In these experiments, four groups of rats received 10 hours of 51 Cr-EDTA (0.5μC / h) was infused into the colon. Animals were placed in different cages and urine was collected for 24 hours. Measurement...
Embodiment 2
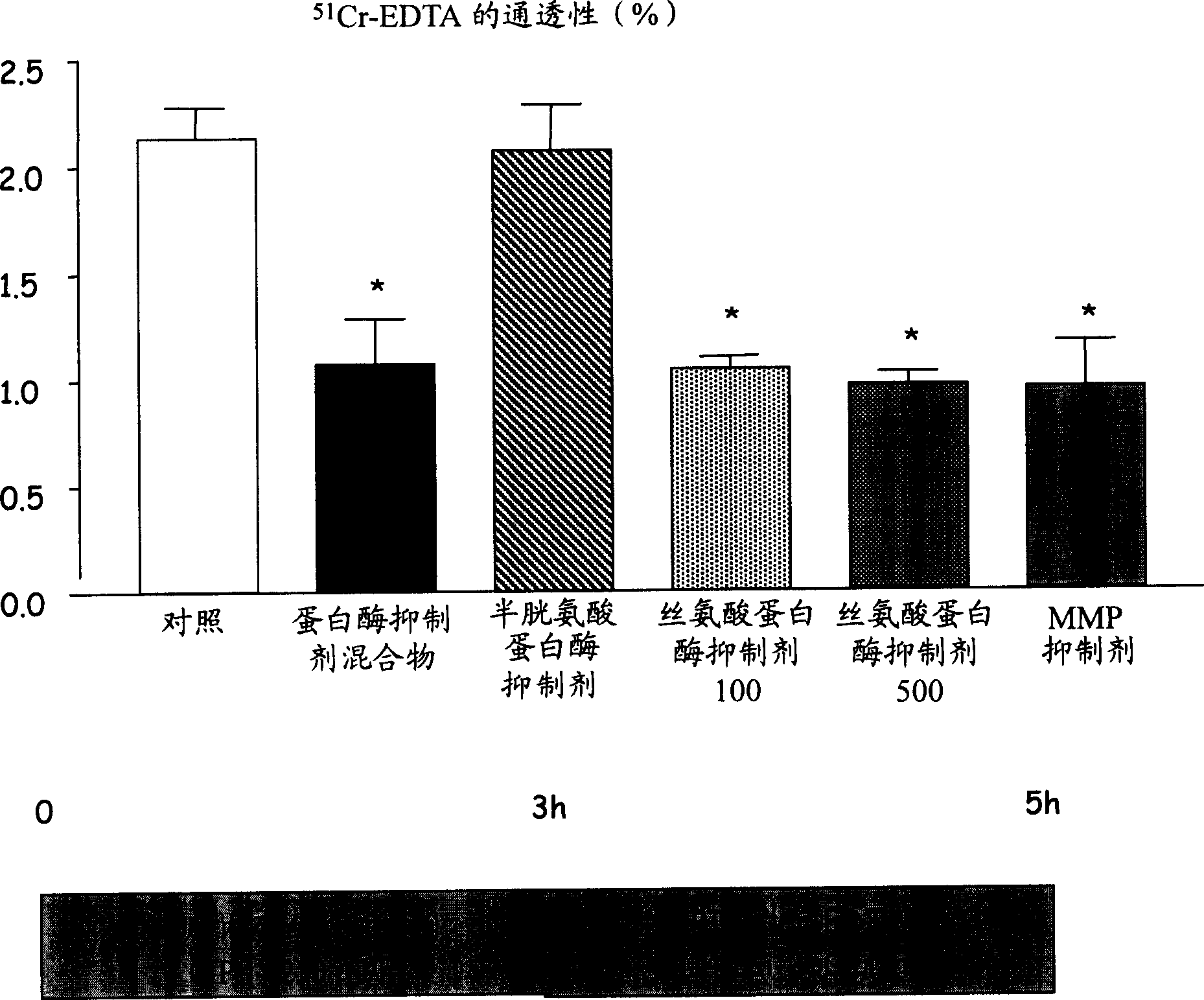
[0048] Example 2: Paracellular permeability in mouse colon. Effect of different bacterial protease inhibitors.
[0049] Six groups of 10 male Swiss mice (25-30 g) each were used for this study. Animals received 5 hours of intracolonic infusion (250 μl / h) of different protease inhibitor solutions through a catheter inserted into the rectum and fixed at the base of the tail; 51 Cr-EDTA was added to the infusion solution ( figure 2 ). At t=5 hours, the animals were sacrificed, the colons were removed, and the total radioactivity remaining in vivo was taken as an index of paracellular permeability. Paracellular permeability was improved after infusion of protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche ref.: 1,873,580, EDTA-free), serine protease inhibitors (aprotinin, Sigma A 1153) and nonspecific matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors (garlardin, Sigma: M5939.) After significantly lower ( figure 2 ).
Embodiment 3
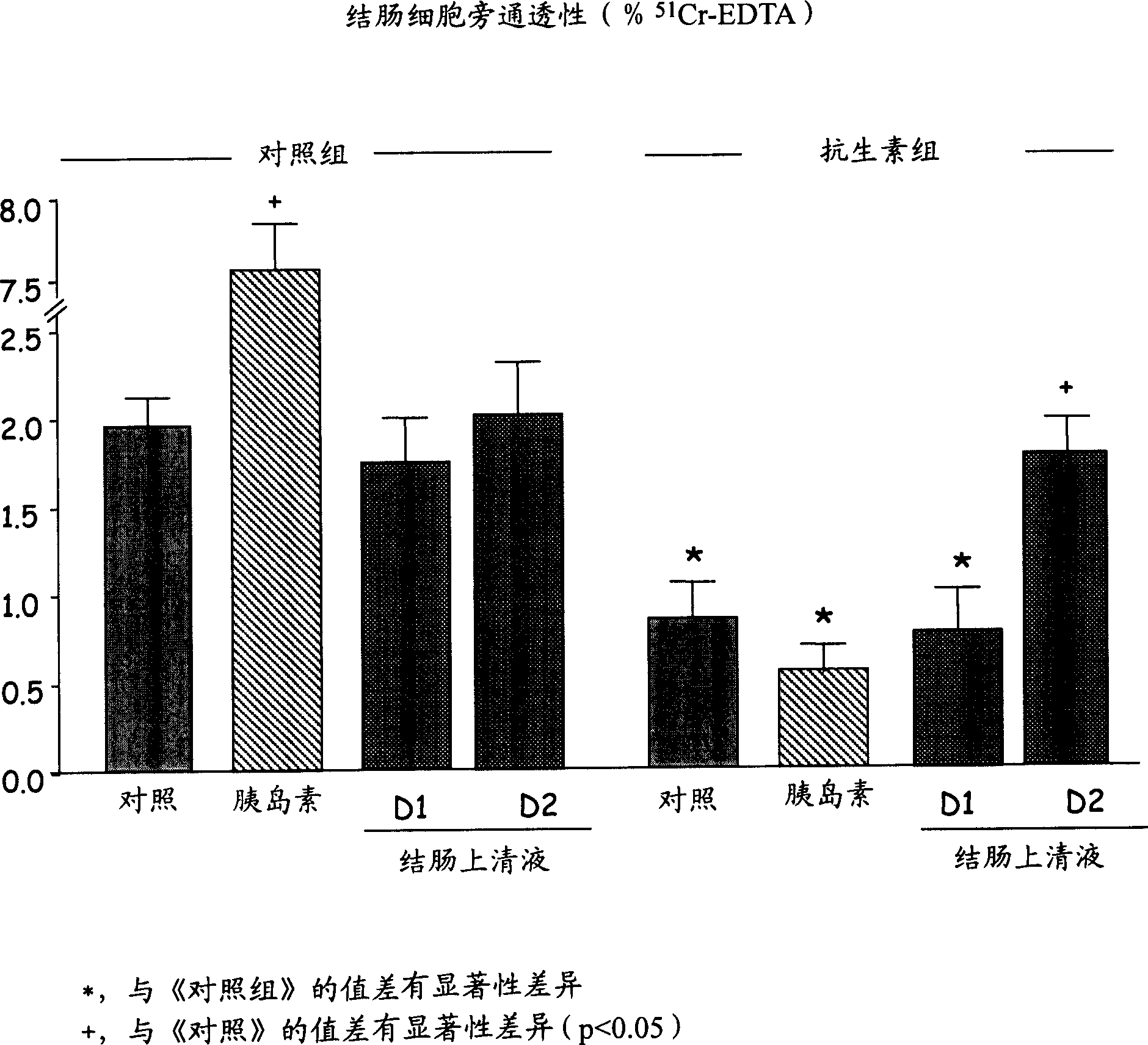
[0050] Example 3: Changes in the paracellular permeability of the colon of mice induced by intraluminal infusion of insulin and supernatant of colonic contents, and after treatment with a cocktail of antibiotics.
[0051] Groups of 10 male Swiss mice (Janvier-France) each weighing 25-30 g were used for this study. The effects of intracolonic infusion of insulin (50 μL, 600 U) and the supernatant of colon contents from control mice on the paracellular permeability of the colon were evaluated under baseline conditions, and were performed on one day (D1) or two consecutive days ( D2) Intracolonic infusion (250 μl / h) was administered for 3 hours. The same infusion was then repeated 12 days after treatment with an oral antibiotic cocktail (Neomycin 2 mg / kg / day + Ampicillin 1 mg / kg / day). The results showed that: 1) antibiotic treatment decreased colonic permeability, 2) the increase in permeability caused by insulin disappeared after antibiotic treatment, which may cause the loss o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com