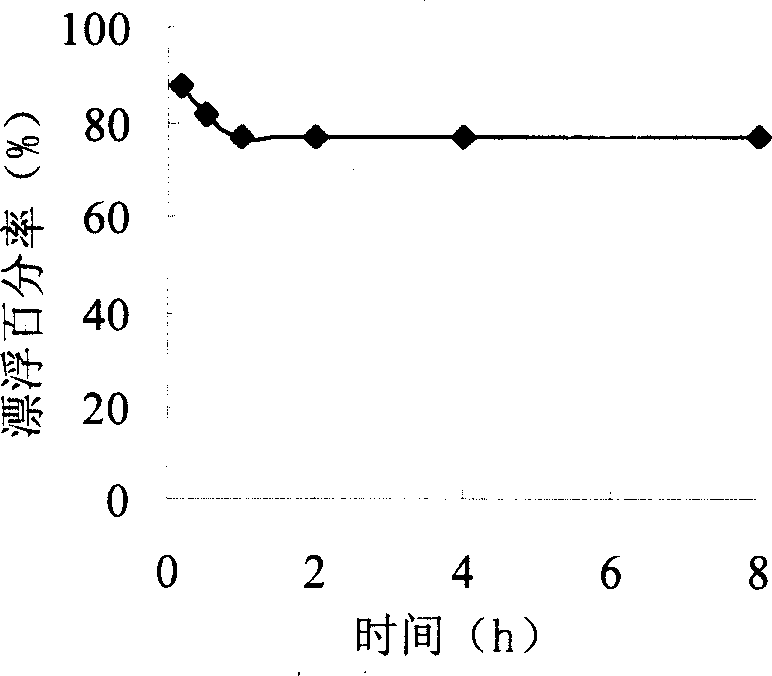
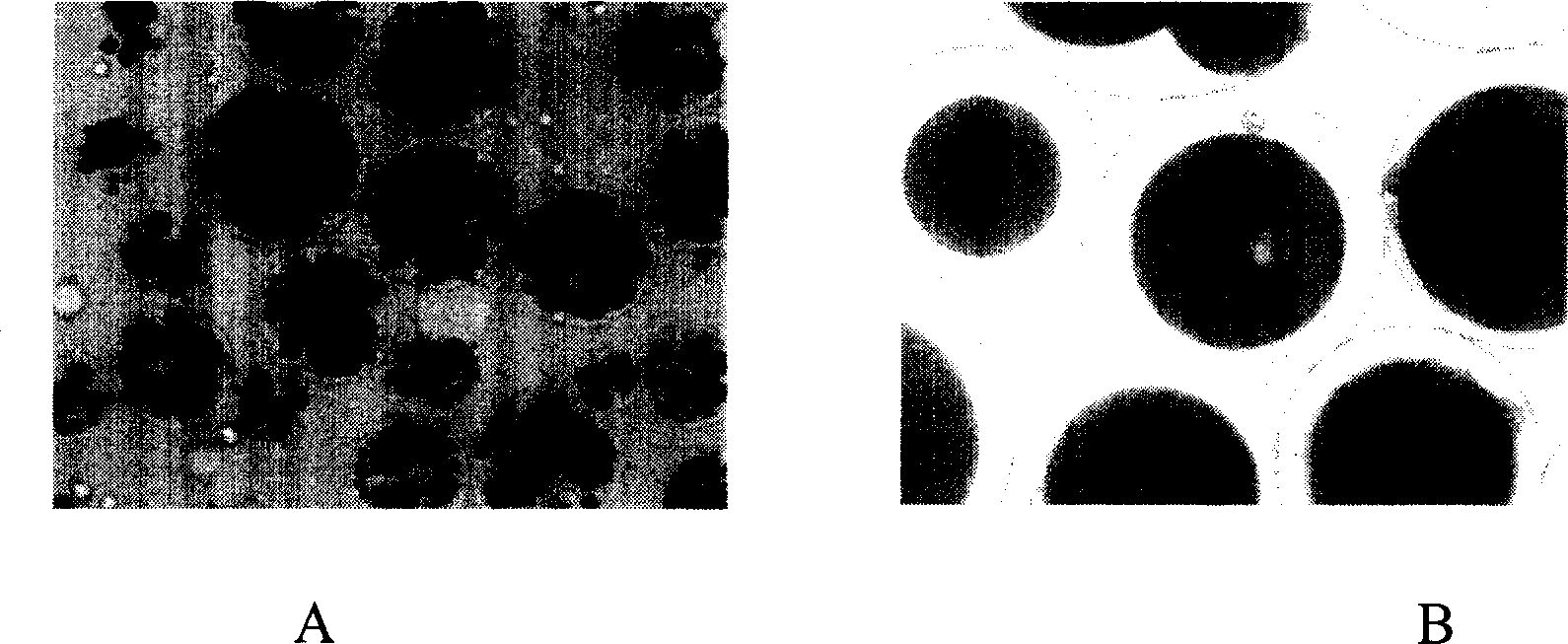Method for preparing floating-biological adhesion synergistic microparticle
A bioadhesion and microparticle technology, which is applied in the direction of non-active ingredient medical preparations, pharmaceutical formulations, block delivery, etc., can solve the problems of decreased adhesion performance, premature drug release, and microsphere shedding, so as to reduce toxicity , short time, good biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Embodiment 1: take dichloromethane as solvent, the ethyl cellulose solution of concentration 4% (w / v) is as dispersed phase (O), with concentration 0.5% (w / v) polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and concentration 0.01 % (w / v) sodium dodecylsulfonate aqueous solution is used as the continuous phase (W), the O / W ratio is 1:40, the temperature is controlled at 20°C, the stirring speed is 1200rpm, and the stirring time is 5h. ~100 μm ethylcellulose microspheres. Evenly disperse the prepared ethylcellulose microspheres and 0.05mol / L insoluble calcium salt into a 0.5% (w / v) sodium alginate solution, and then disperse the mixed solution to a solution containing 0.5% (w / v) sodium In the liquid paraffin of Span80 (Span80) and 0.5% (w / v) Tween 20 (Tween20), the water-oil phase volume ratio is between 1:4, add 0.2ml of 10% (v / v) glacial acetic acid, continue Stir for 20 minutes and control the temperature at 20°C to obtain sodium alginate-ethylcellulose microparticles. Disperse the prepared...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Embodiment 2: take chloroform as solvent, the ethyl cellulose solution of concentration 15% (w / v) is as dispersed phase (O), with concentration 10% (w / v) polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and concentration 0.2% ( w / v) Sodium dodecylsulfonate aqueous solution is used as the continuous phase (W), the O / W ratio is 1:10, the temperature is controlled at 40°C, the stirring speed is 600rpm, the stirring time is 2h, and the prepared particle size is 100~200μm ethylcellulose microspheres. Evenly disperse the prepared ethylcellulose microspheres and 0.3mol / L insoluble calcium salt into a 3% (w / v) sodium alginate solution, and then disperse the mixed solution into a solution containing 2.5% (w / v) sodium alginate In the liquid paraffin of Pan 80 (Span80) and 2.5% (w / v) Tween 20 (Tween20), the water-oil phase volume ratio is between 1:10, add 10ml of 50% (v / v) glacial acetic acid, and continue to stir 5min, the temperature is controlled at 20°C, and sodium alginate-ethylcellulose microparti...
Embodiment 3
[0026] Embodiment 3: take normal hexane as solvent, the ethyl cellulose solution of concentration 1% (w / v) is as dispersed phase (O), with concentration 2% (w / v) polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and concentration 0.1% (w / v) Sodium dodecylsulfonate aqueous solution is used as the continuous phase (W), the O / W ratio is 1:6, the temperature is controlled at 30°C, the stirring speed is 900rpm, and the stirring time is 4h. 150 μm ethylcellulose microspheres. Evenly disperse the prepared ethylcellulose microspheres and 0.2mol / L insoluble calcium salt into a 1.5% (w / v) sodium alginate solution, and then disperse the mixed solution into a solution containing 1% (w / v) sodium alginate In the liquid paraffin of Pan 80 (Span80) and 1% (w / v) Tween 20 (Tween20), the water-oil phase volume ratio is between 1:6, add 5ml of 30% (v / v) glacial acetic acid, continue to stir After 15 minutes, the temperature is controlled at 30°C to obtain sodium alginate-ethylcellulose microparticles. Disperse the prepa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com