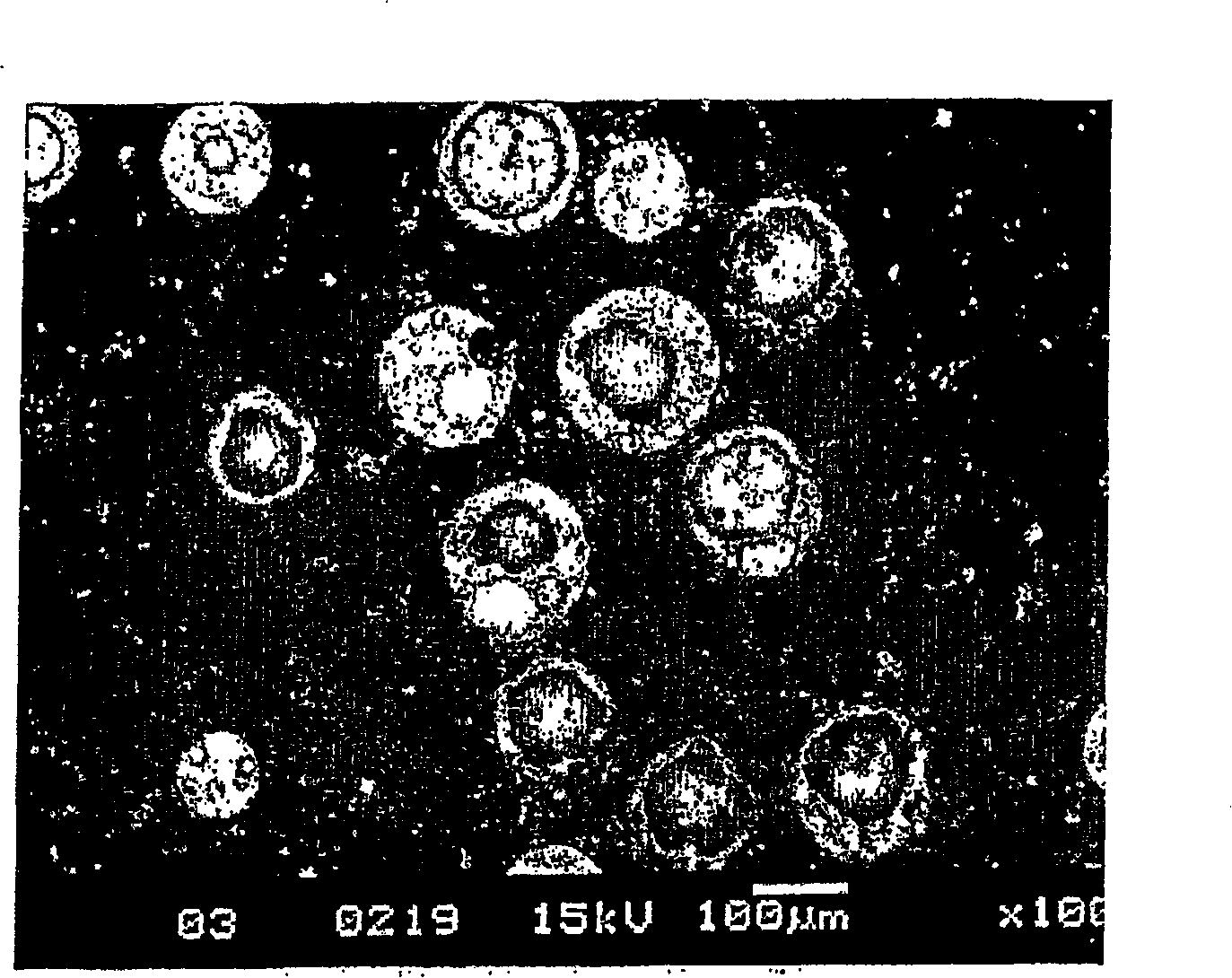
Methods for producing low density products
A low-density material and particle size technology, which is applied in the field of synthetic production engineering expanded particles, can solve problems such as difficult foaming agent matching, and achieve the effect of increasing the scope of use and reducing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0164] This example illustrates the production of expansive microinclusions from a formulation consisting of basalt and sodium hydroxide.
[0165] The formulation is prepared by mixing ground basalt with solid sodium hydroxide and water. Blowing agents were added in combination or separately with various mixtures of control agents including silicon carbide, sugar, carbon black, and coal. The formulations are listed in Table 1. The composition of the basalt is listed in Table 2.
[0166] Formulation 1A
[0167] This recipe illustrates the production of expanding microinclusions from a recipe consisting of basalt, sodium hydroxide, and sugar as a blowing agent.
[0168] The sample was obtained by grinding 92 grams of basalt (ground to d 50 The particle size is about 2 microns) and 5 grams of solid sodium hydroxide (tablets), 3 grams of technical sugar and 23 ml of water are prepared. The formulations are listed in Table 1.
[0169] Recipe 1B
[0170] This recipe illus...
Embodiment 2
[0193] This example illustrates the production of expansive microinclusions from formulations consisting of various silicate compounds, sodium hydroxide, and various blowing agents.
[0194] Expanded microinclusions were prepared from blends of soda-lime waste glass and various silicate materials. These blends also contain a mixture of a primary blowing agent and a control agent, such as a mixture of silicon carbide and a control agent silicon carbide, sugar and / or carbon black. The formulations are listed in Table 4. The composition of the waste glass used in this work is listed in Table 5.
[0195] Formulation 2A
[0196] This recipe illustrates the production of expanding microinclusions from a recipe consisting of glass, sodium hydroxide and silicon carbide as blowing agent and carbon black as control agent.
[0197] The sample was prepared by grinding 95.6 grams of glass (ground to d 50 A particle size of about 1 micron) was prepared by mixing 3 grams of solid sodiu...
Embodiment 3
[0224] This example illustrates the production of expansive microinclusions from formulations consisting of varying amounts of pozzolan, sodium hydroxide, a mixture of blowing and control agents, and other minor additives.
[0225] Formulation 3A
[0226] The sample was prepared by mixing 78.2 grams of pozzolan (ground to d 50 The particle size is about 3 microns) and 20 grams of solid sodium hydroxide (tablets), 0.8 grams of technical grade silicon carbide as the main blowing agent, 1 gram of technical grade carbon black as the control agent, and 43 milliliters of water.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com