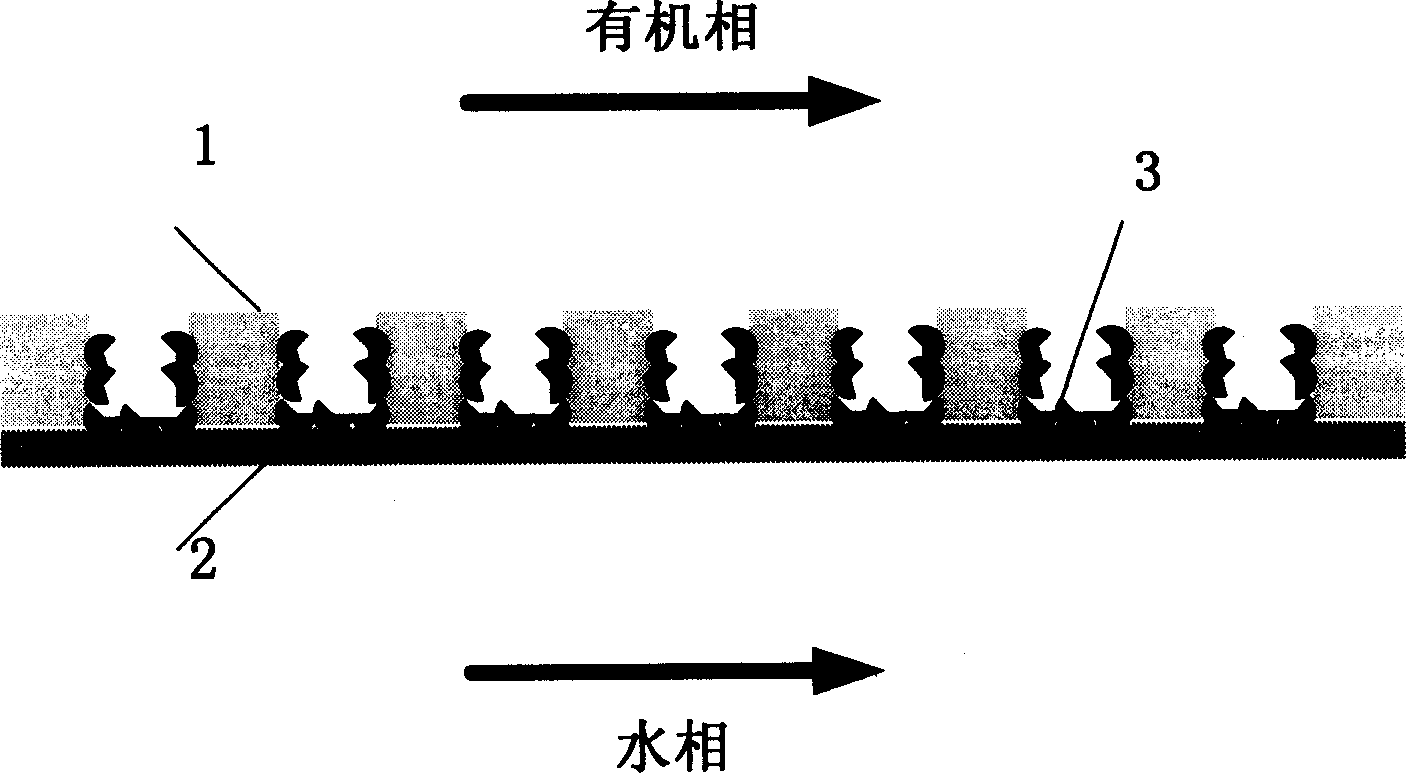
Method for immobilizing lipase using microstructure in hydrophilic/ hydrophobic composite membrane
A technology of immobilized lipase and composite membrane, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, immobilized on/in organic carriers, hydrolytic enzymes, etc. High cost and other issues, to achieve the effect of easy loading, high energy recovery rate and simple method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] A polytetrafluoroethylene membrane with an average pore diameter of 0.1 μm, a porosity of 50%, and a thickness of 85 μm was used as the hydrophobic layer. The mass fraction of the film-making solution for the hydrophilic layer is 15%, and the thickness of the cellulose acetate hydrophilic layer is controlled to 65 μm. It is volatilized at a temperature of 25°C and a humidity of 40% for 20 minutes, and then immersed in a deionized hydrogel bath to solidify and form a film. The lipase was dissolved in 0.05M sodium phosphate buffer solution with pH 7.5 to obtain a lipase solution with an enzyme protein concentration of 167mg / L. Set the area to 26cm 2 The membrane is loaded into a filter, 15ml of lipase solution is added, and the filter is carried out at 0.6MPa. The composite membrane has a primary filtration rejection rate of lipase of 20%, and the lipase protein loading is 0.0201mg / cm 2 immobilized lipase membrane.
[0020] The immobilized enzyme membrane is packed int...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Example 2: A polytetrafluoroethylene membrane with an average pore diameter of 0.1 μm, a porosity of 50%, and a thickness of 85 μm was used as the hydrophobic layer. The mass fraction of the film-making solution for the hydrophilic layer is 15%, and the thickness of the cellulose acetate hydrophilic layer is controlled to 135 μm. It is volatilized at a temperature of 25°C and a humidity of 40% for 20 minutes, and then immersed in a deionized hydrogel bath to solidify and form a film. The lipase was dissolved in 0.05M sodium phosphate buffer solution with pH 7.5 to obtain a lipase solution with an enzyme protein concentration of 167mg / L. Set the area to 26cm 2 The membrane is loaded into a filter, 15ml of lipase solution is added, and the filter is carried out at 0.6MPa. The primary filtration rejection rate of the composite membrane to lipase is 22%, and the lipase protein load is 0.0212mg / cm 2 immobilized lipase membrane.
[0022] The immobilized enzyme membrane is ...
Embodiment 3
[0024] A polytetrafluoroethylene membrane with an average pore diameter of 0.1 μm, a porosity of 50%, and a thickness of 85 μm was used as the hydrophobic layer. The mass fraction of the film-making solution for the hydrophilic layer is 10%, and the thickness of the cellulose acetate hydrophilic layer is controlled to 65 μm. It is volatilized at a temperature of 25°C and a humidity of 40% for 20 minutes, and then immersed in a deionized hydrogel bath to solidify and form a film. The lipase was dissolved in 0.05 M sodium phosphate buffer solution with pH 7.5 to obtain a lipase solution with an enzyme protein concentration of 84 mg / L. Set the area to 26cm 2 The membrane is put into a filter, 10ml of lipase solution is added, and the filter is performed at 0.3MPa. The primary filtration rejection of lipase by the composite membrane is 14.3%, and the lipase protein loading is 0.0046mg / cm 2 immobilized lipase membrane.
[0025] Put the immobilized enzyme membrane into a two-phas...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com