Method of dynamic changing user location frequency in LBS
A technology that dynamically changes and locates the frequency, applied in electrical components, wireless communication and other directions, can solve the problem that the positioning interval cannot provide service quality, the delay cannot meet the service quality of LBS users, and the positioning interval is short, etc., to reduce system utilization. rate effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0015] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
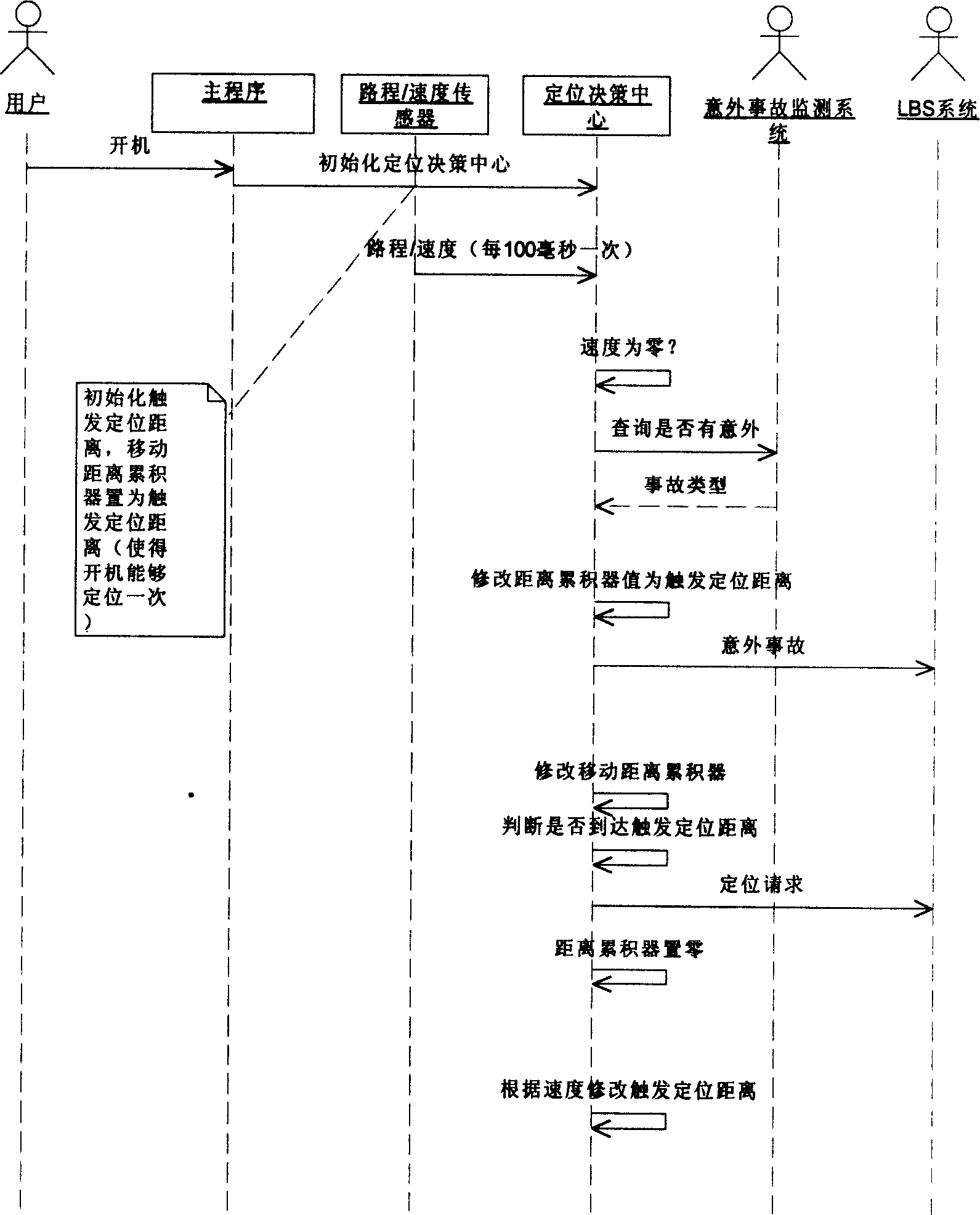
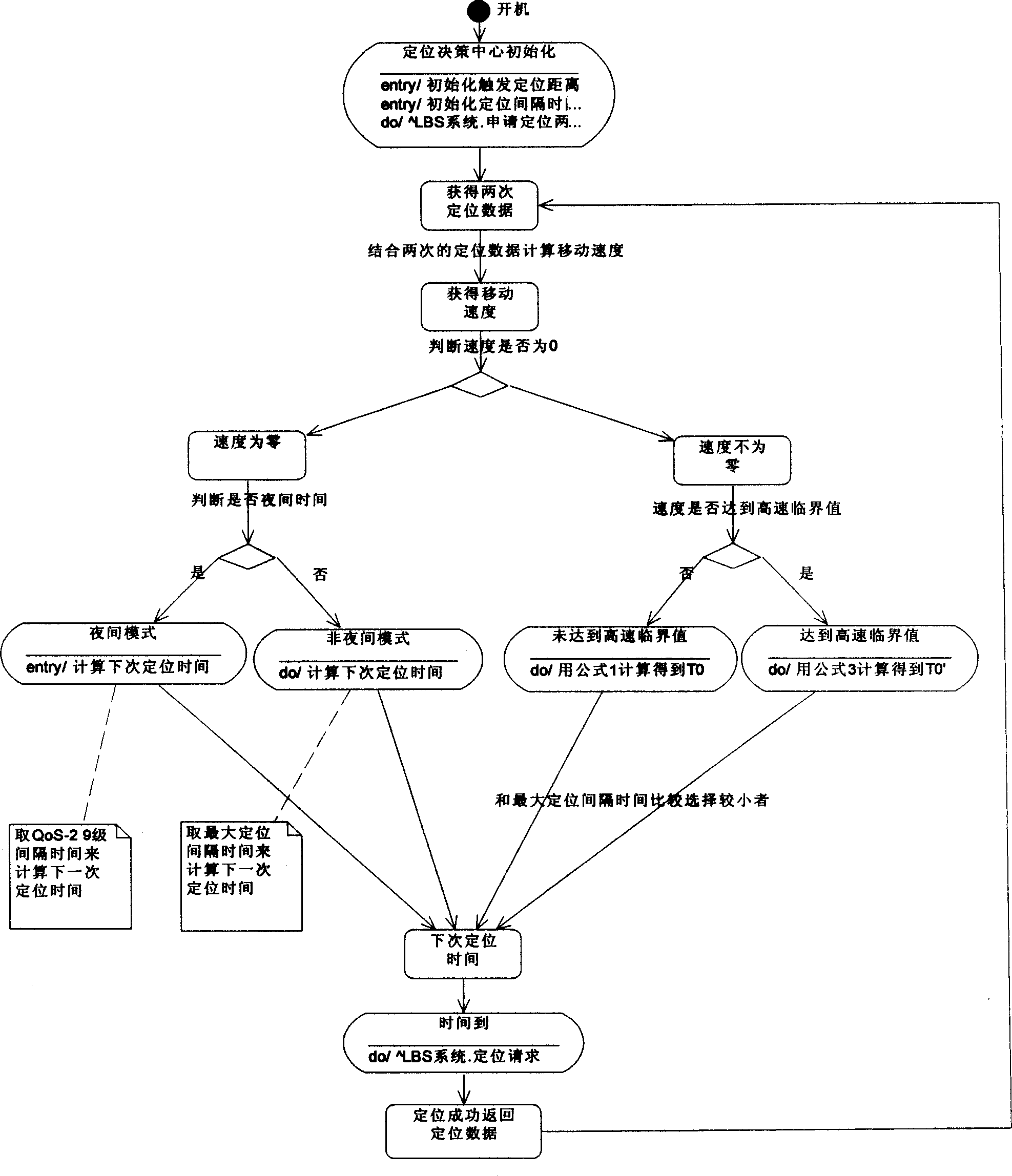
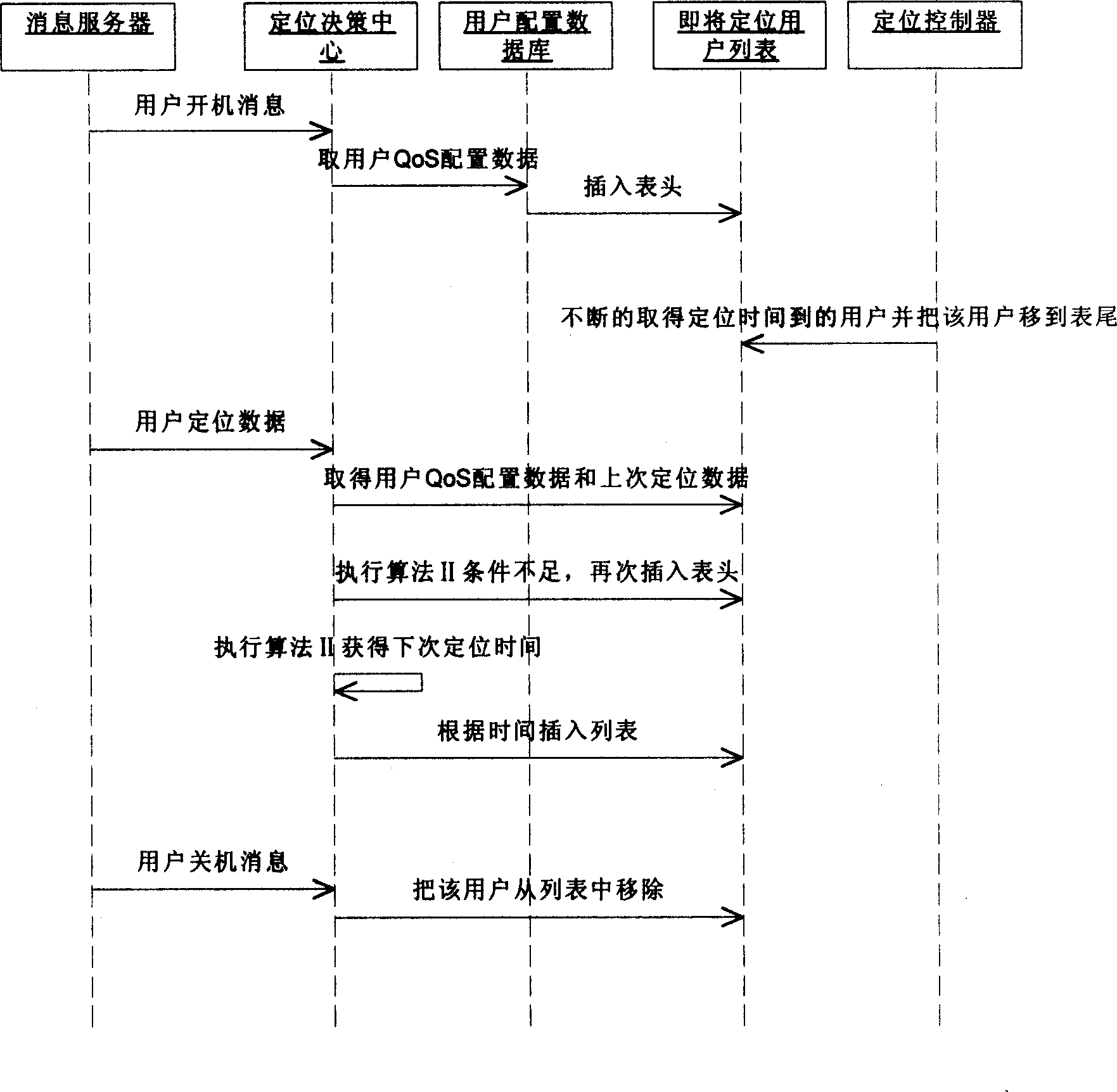
[0016] The best way to record the path traveled by the user at equal density is to locate and record the location every time the user moves a certain distance. The faster the user moves, the higher the frequency of positioning, and the slower the speed. The lower the frequency, the specific distance is called the trigger positioning distance. Since different users may need different trigger location distances to meet their needs, the system defines a QoS about the trigger location distance for users to choose. For example, car users can choose a trigger location distance of 20 meters, while ship users may choose a trigger location distance of 100 meters.
[0017] The above method is the most ideal positioning method, but not every user can obtain their own moving distance continuously. Assuming that such users who cannot continuously obtain their own ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com