A method and kit for detecting the early onset of renal tubular cell injury
A technology of renal tubular cells and kits, which can be used in biological testing, material testing, etc., and can solve problems such as Cyr61 detection problems.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
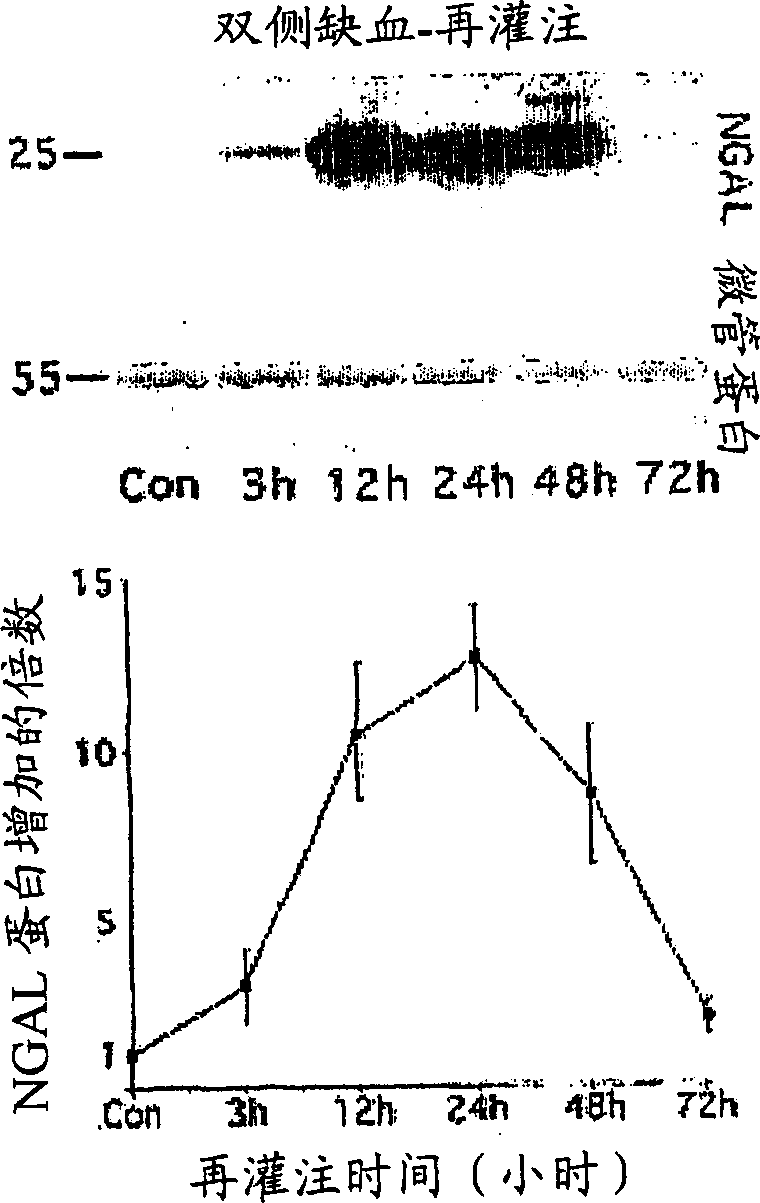
[0099] NGAL is a small protease-resistant, secreted polypeptide that can be detected in urine. Significant upregulation of NGAL mRNA and protein levels has been shown early after renal ischemia in mice. NGAL protein expression was mainly detected in the proximal tubule cells, which resembled a secreted protein with a punctate distribution in the cytoplasm. Indeed, in mouse and rat models of ARF, NGAL is readily and rapidly detectable in urine (in the first urination) after ischemic injury, when no renal leukocytes are observed penetration. The origin of NGAL from tubular cells was further confirmed in cultured human proximal tubular cells subjected to in vitro ischemic injury, where NGAL mRNA was significantly and immediately Inside, NGAL protein was readily detectable in the culture medium. Our results illustrate that NGAL may represent a new early urinary biomarker of ischemic kidney injury.
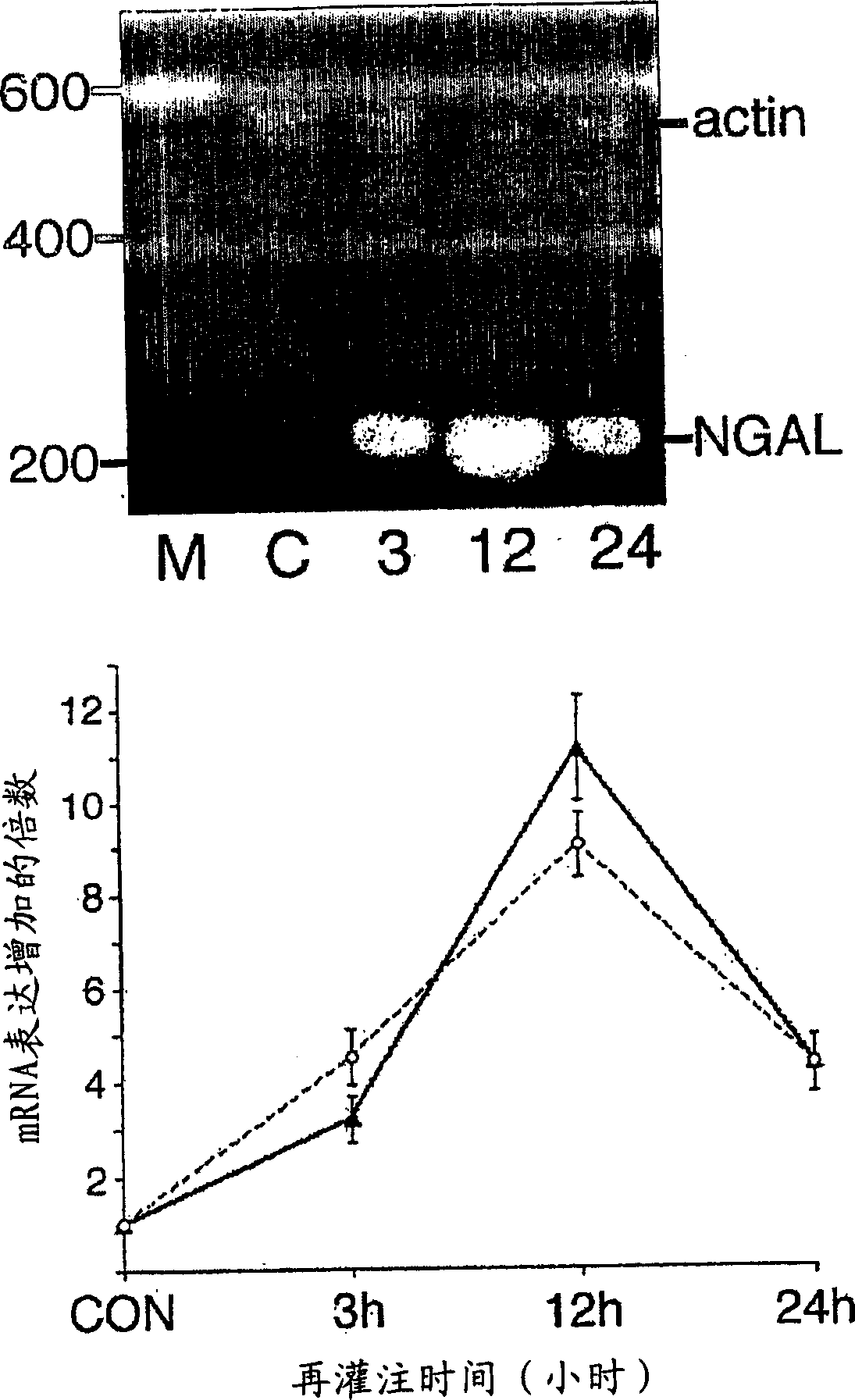
[0100] Identification of novel genes upregulated early after renal ischemia-re...
Embodiment 2
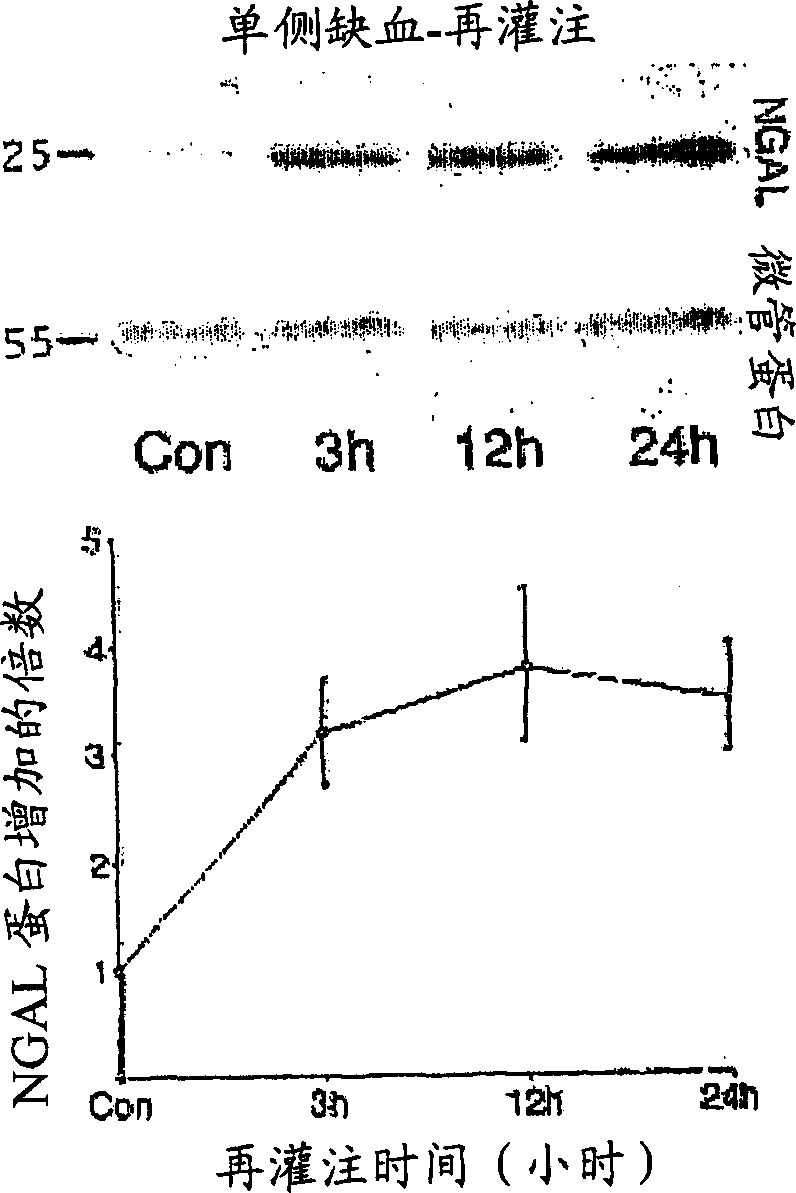
[0114] NGAL protein was readily detected in urine immediately after induction of ARF in rats:
[0115] Because of the debate regarding species differences in the response to renal artery occlusion, we below examined the behavior of NGAL in a different animal model, an established rat model of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Urinary creatinine concentrations were used to make loading consistent, and NGAL was absent in urine prior to renal ischemia in rats. In marked contrast, NGAL showed 25 kDa immunoreactivity within 3 hours of injury (in the first post-ischemic urine effusion), as shown in Figure 6 shown. In comparison, serum creatinine in this model of ischemic injury was elevated only after 24 hours of reperfusion (not shown). Again, NGAL was detectable in as little as 1 [mu]l of untreated urine and persisted throughout the period examined (24 hours of reperfusion).
Embodiment 3
[0117] NGAL mRNA is induced in cultured human proximal tubule cells after early minimal ischemia:
[0118]To confirm the source of NGAL from ischemic proximal tubular cells, we modified a previously described procedure for in vitro ischemia induced by ATP depletion in cultured human proximal tubular cells (RPTEC). Incubation in 1 μM antimycin produced a mild partial ATP depletion, which became about 83±3% of the control within 1 hour and decreased more slowly to about 75±3% of the control by 6 hours (from four Mean + / - SD of experiments). The morphological consequences of this mild ATP depletion were not discernible. NGAL mRNA is barely detectable in resting cells. However, after partial ATP depletion, a rapid duration-dependent induction of NGAL mRNA was clearly visible by RT-PCR, as shown in Figure 7 shown.
[0119] NGAL protein was readily detected in culture medium following early ischemia in vitro:
[0120] We next examined NGAL protein expression in RPTEC cells and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com