Process for preparing europium oxide doped inorganic lighting material
A technology of luminescent materials and europium oxide, which is applied in the direction of luminescent materials, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of harsh reaction conditions and cumbersome operation process, and achieve the effects of easy control of conditions, high reaction efficiency and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
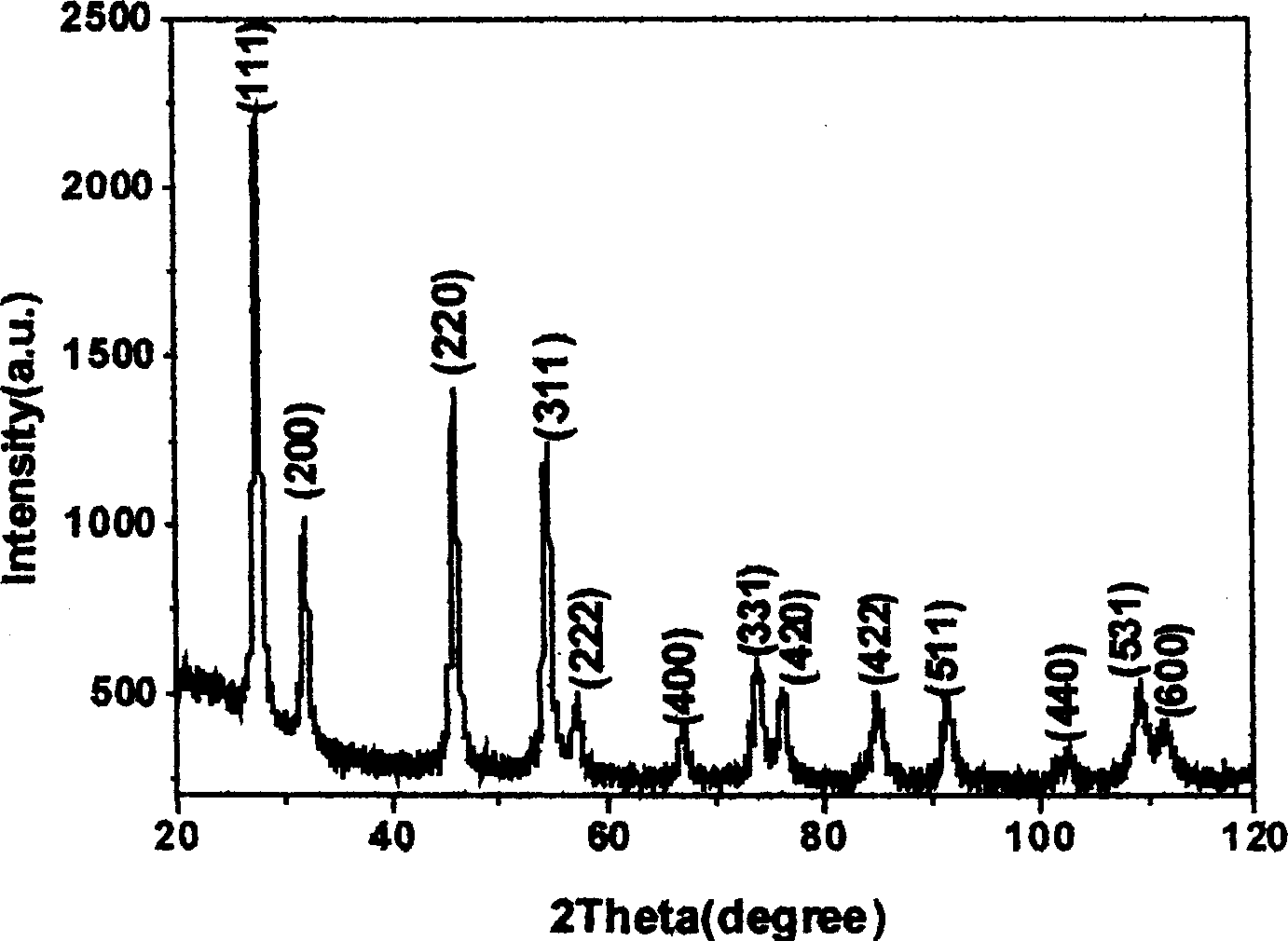
[0017] Weigh 1.00 g of thorium nitrate tetrahydrate and 0.02 g of europium oxide in a beaker. Add 10ml of distilled water, add dropwise 0.03g of nitric acid, and stir to obtain a clear solution. In order to avoid sputtering during calcination in a muffle furnace, the water in the solution can be evaporated to dryness in an oven. Calcined at 500°C for 2h in a muffle furnace to obtain the final target product.
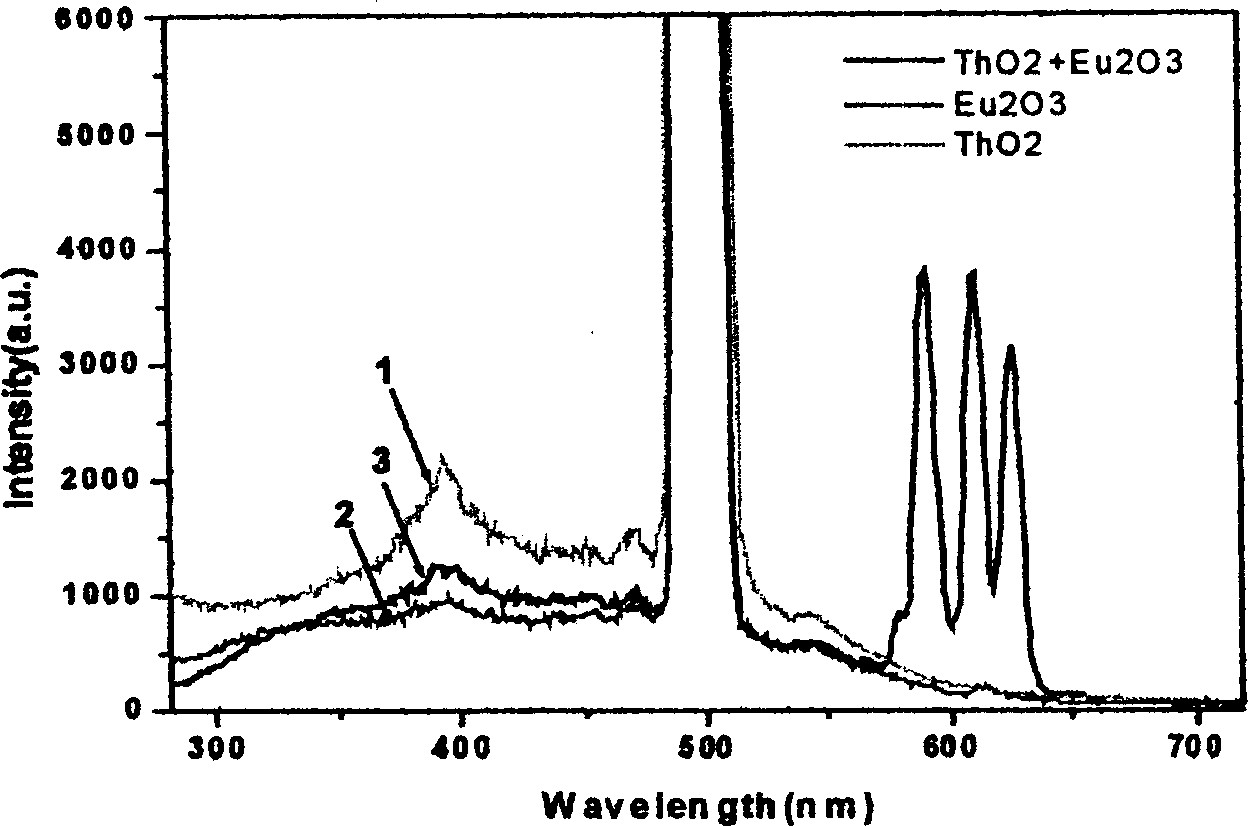
[0018] The final product was tested in a F4500 fluorescence instrument, and 250nm was selected as the excitation wavelength to measure the fluorescence emission spectrum, see figure 1 .
Embodiment 2
[0020] Weigh 1.00 g of thorium nitrate tetrahydrate and 0.08 g of europium oxide in a beaker. Add 20ml of distilled water, add dropwise 0.12g of nitric acid, and stir to obtain a clear solution. In order to avoid sputtering during calcination in a muffle furnace, the water in the solution can be evaporated to dryness in an oven. Calcined at 450°C for 3h in a muffle furnace.
Embodiment 3
[0022] Weigh 1.00 g of thorium nitrate tetrahydrate and 0.05 g of europium oxide in a porcelain crucible. Add 30ml of distilled water, add dropwise 0.08g of nitric acid, and stir to obtain a clear solution. In order to avoid sputtering during calcination in a muffle furnace, the water in the solution can be evaporated to dryness in an oven. Calcined at 550°C for 3h in a muffle furnace.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com