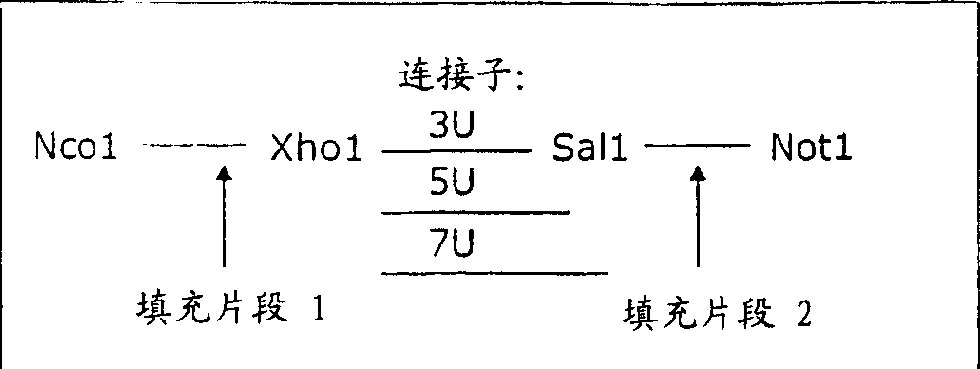
Dual specific single domain antibodies specific for a ligand and for the receptor of the ligand
A bispecific and specific technology, applied in the field of dual specific ligands, can solve problems such as poor stability, lack of light chain partners, and limited therapeutic value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0251] Preparation of immunoglobulin-based multispecific ligands
[0252] The dual-specific ligands of the present invention can be prepared according to the technologies previously established and applied to antibody engineering, regardless of whether they are in an open or closed conformation according to the expected configuration of the invention. Such as the preparation of scFv, phage antibodies and other engineered antibody molecules. Examples of techniques for preparing antibodies, particularly bispecific antibodies, are described in the following reviews and references: Winter & Milstein, (1991) Nature 349:293-299; Plueckthun (1992) Immunological Reviews 130:151-188; Wrightetal., (1992) Crti. Rev. Immunol. 12: 125-168; Holliger, P. & Winter, G. (1993) Curr. Op. Biotechn. 4, 446-449; Carter, et al. (1995) J. Hematother. 4, 463-470; Chester, KA & Hawkins, RE (1995) Trends Biotechn. 13, 294-300; Hoogenboom, HR (1997) Nature Biotechnol. 15, 125-126; Fearon, D. (1997) Nature Bi...
Embodiment 1
[0405] Example 1. Screening of bispecific scFv antibody (K8) specific for human serum albumin (HSA) and β-galactosidase (β-gal)
[0406] This example explains the method of preparing bispecific antibodies specific to β-gal and HSA. According to the ability to bind β-gal, it is selected as a dummy V H The Vκ variable region library connected to the Vκ region is selected based on the ability to bind HSA to select the V H Variable area library. Then combine the selected variable V H HSA and Vκβ-gal regions, and antibodies are selected based on their ability to bind β-gal and HAS. HSA is a half-life enhancing protein found in human blood.
[0407] Four human phage antibody libraries used in this experiment.
[0408] Antibody Library 1 Germline Vκ / DVT V H 8.46×10 7
[0409] Antibody Library 2 Germline Vκ / NNK V H 9.64×10 7
[0410] Antibody Library 3 Germline V H / DVTVκ 1.47×10 8
[0411] Antibody Library 4 Germline V H / NNKVκ 1.45×10 8
[0412] All antibody libraries are ba...
Embodiment 2K8
[0418] Example 2. Characteristics of K8 antibody binding performance
[0419] First, the monoclonal phage ELISA method was used to describe the binding characteristics of the K8 antibody. Use HSA, β-gal with alkaline phosphatase (APS), bovine serum albumin (BSA), peanut agglutinin (peanutagglufinin), lysozyme and cytochrome C at a concentration of 10μg / ml (to prevent cross-reaction ) 100 μl PBS 4°C overnight to coat a 96-well plate. The phagemid from the K8 clone was rescued with KM13, as described in Harrison et al. (1996), and the phage-containing supernatant (50 μl) was directly analyzed. Then a standard ELISA procedure (Hoogenboom et al., 1991) was carried out, using the detection method of bound phage with anti-M13-HRP conjugate. When the absorption signal displayed on the surface of the phage was greater than 1, the bispecific K8 antibody was found to bind to HAS and β-gal (Figure 4). Strong binding to BSA can also be observed (Figure 4). Since HSA and BSA are 76% homologous...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com