Methods of diagnosing cervical cancer
A kit and papilloma virus technology, applied in the field of HPV E6 protein composition, can solve the problems of expensive, difficult to detect E6 protein, and inability to recognize E6 protein
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 5
[0097] Example 5 lists representative PDZ domain sequences cloned in a vector (PGEX-3X vector) for the generation of GST-PDZ fusion protein (Pharmacia). An extended list of PDZ domains cloned in pGEX vectors for the generation of GST-PDZ fusion proteins is given in US Patent No. 09 / 724553.
[0098] As discussed in detail herein, the PDZ proteins listed in Table 2 are native PDZ domain-containing proteins. Only important interactions are shown in this table. Therefore, the present invention is particularly directed to the detection and regulation of the interaction between PDZ protein and PL protein. PDZ domains that bind other pathogens can be used in a similar fashion for the diagnosis of infection. Additional examples of pathogenic PL proteins suitable for diagnosis are included in Table 8, although this is not meant to limit the scope of the invention.
[0099] In another embodiment of the present invention, cell abnormalities or diseases can be diagnosed by detecting im...
Embodiment 1
[0357] Sequence analysis of HPV E6 protein to determine oncogenic potential
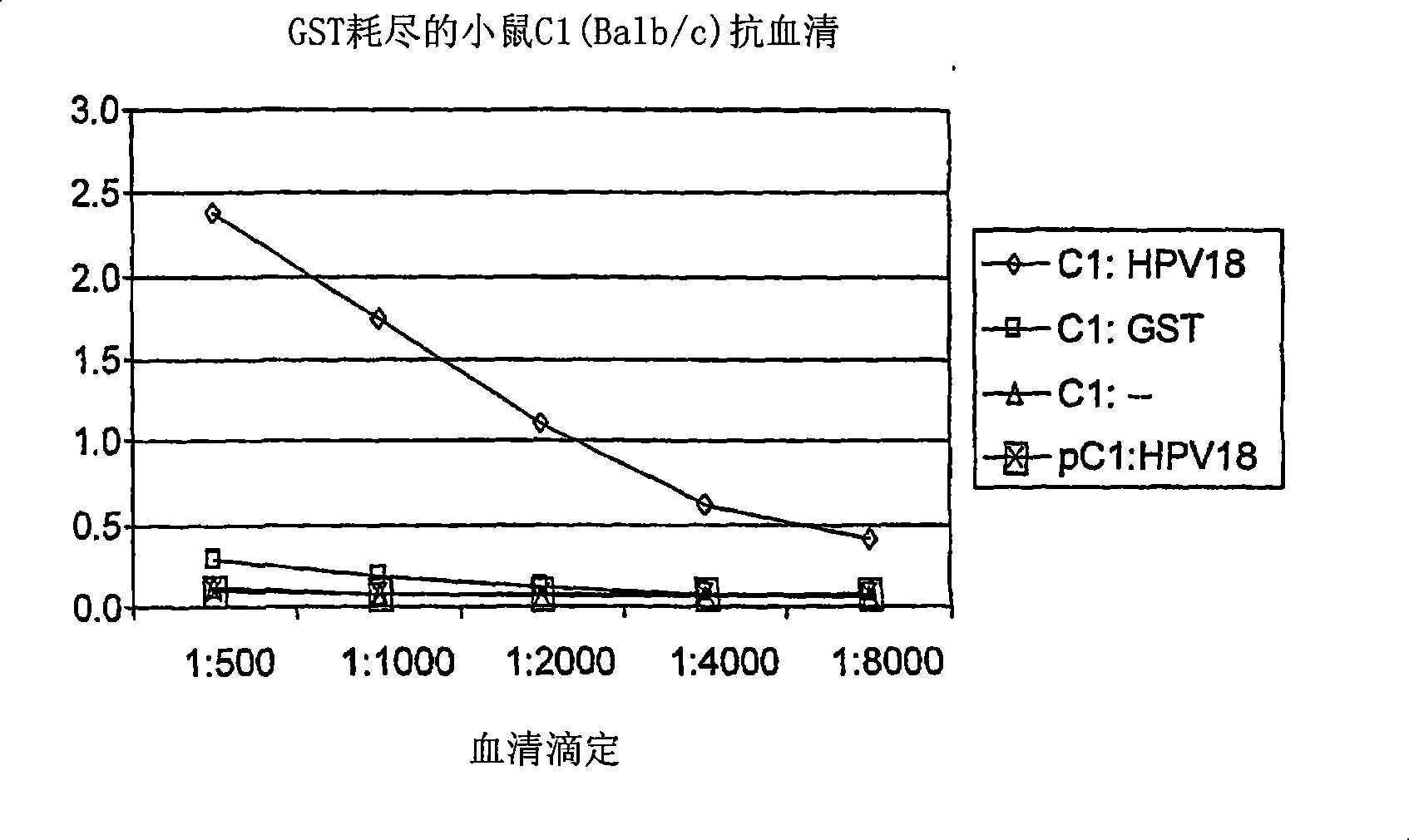
[0358] PDZ proteins are known to bind to the carboxy-terminal sequence (PL) of certain proteins. The PL sequences that bind PDZ domains are predictable and are described in detail in US Patent Applications 09 / 710059, 09 / 724553 and 09 / 688017. A group of proteins ending with the sequence -X-(S / T)-X-(V / I / L) is one of the important classes of PL motifs. We have examined the C-terminal sequence of the E6 protein from several HPV strains. All oncogenic virus strains identified by the National Cancer Institute share a common PDZ-binding sequence. Those non-oncogenic E6 proteins from papillomavirus strains were not predicted to bind PDZ domain sequences, thus implying that the interaction with PDZ proteins is a prerequisite for their cancer-causing in humans. In the sequences examined (Table 3A), there was a 100% correlation between the presence of PL and the initiation of cancer. In theory, using the PL...
Embodiment 2
[0368] Identification of PDZ domains that interact with the C-terminus of oncogenic E6 proteins
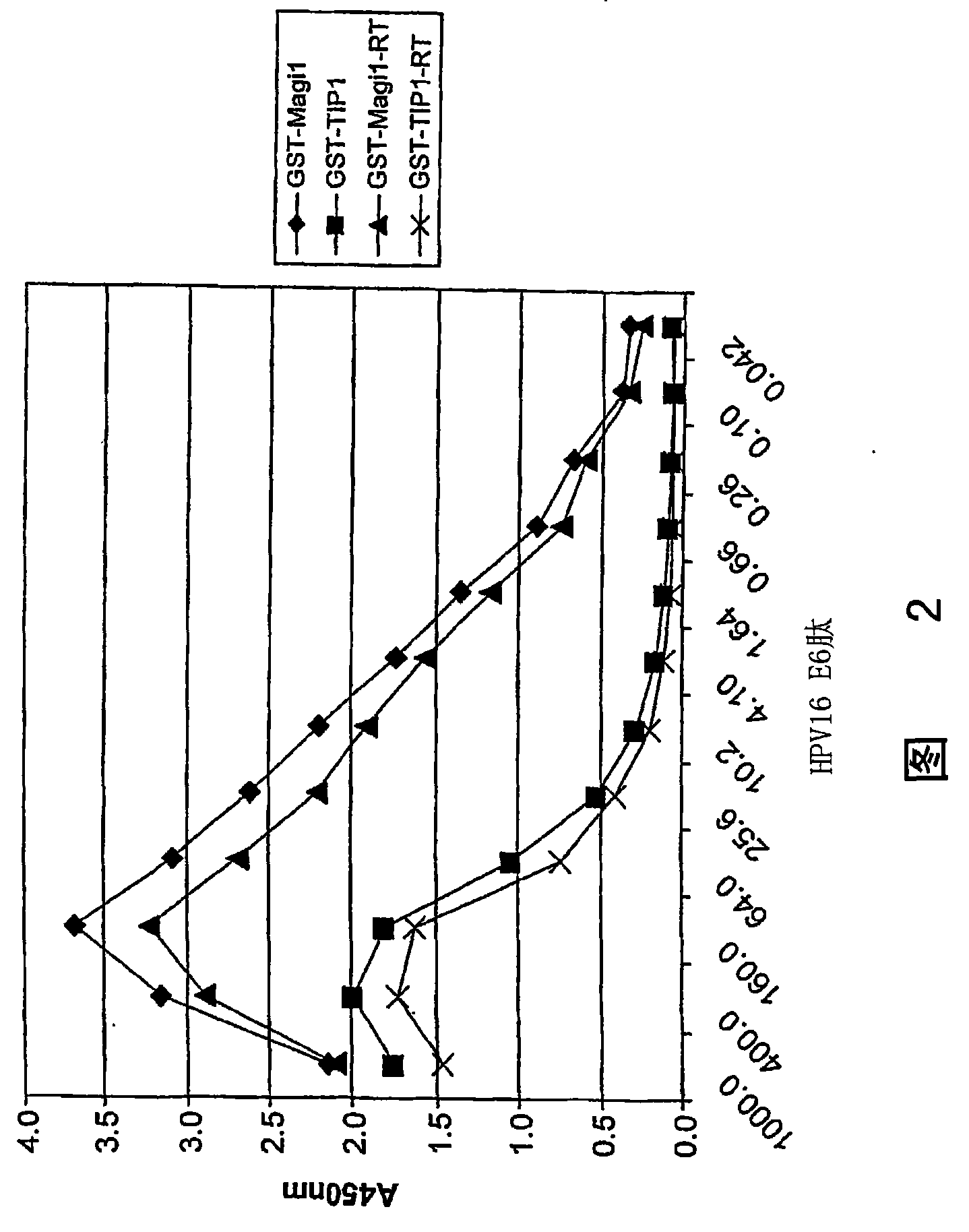
[0369] To identify PDZ domains that can be used to detect oncogenic E6 proteins in diagnostic assays, the 'G test' (described above) was used to identify interactions between E6PL and PDZ domains. Peptides were synthesized according to the C-terminal amino acid sequence of the E6 protein from an oncovirus strain of human papillomavirus. The ability of these peptides to bind the PDZ domain was assessed using the G assay described above and the PDZ domain synthesized from the expression constructs detailed in US Patent Applications 09 / 710059, 09 / 724553 and 09 / 688017. The results of these assays showing high binding affinities are listed in Table 4 below.
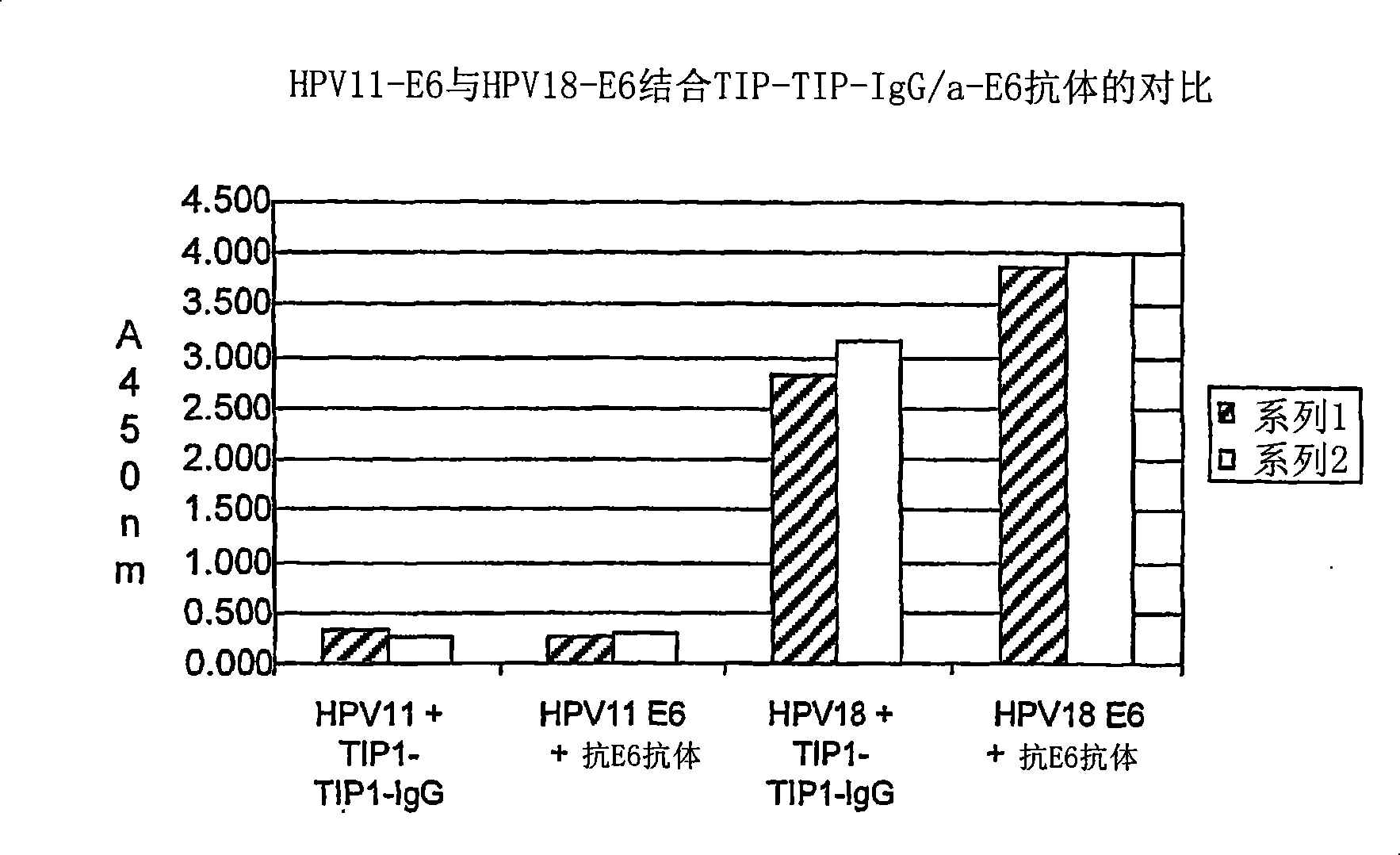
[0370] As we will see below, there are a large number of PDZ domains that bind some oncogenic E6 proteins. However, it appears that only the second PDZ domain of MAGI-1 binds all tested oncogenic E6PLs. The PDZ domain of TIP-1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com