Compositions and methods for treating emphysema
A composition and alveolar technology, applied in drug combination, drug delivery, pharmaceutical formulation, etc., can solve problems such as impaired quality of life, increased frequency of hospitalization, and decreased functional capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3 describes a variety of surface membranes, and Table 1, which summarizes many of the biophysical characteristics of these surface membranes, demonstrates that similar biophysical behavior can be produced using a variety of unique lipid profiles.
[0053] Table 1
[0054] Composition k 1 k 2 gamma min gamma *
[0055] m 2
[0056] DAPC(0.7)+PG(0.2)
[0057] +DPPC(0.05)+AA(0.05) 6×10 5 6 <0.5 38
[0058] 170
[0059] DAPC(0.7)+DPPC(0.2) 2 <0.5 45
[0060] +AA(0.05)+PA(0.05) 6×10 5
[0061] 170
[0062] DPPC(0.7)+PG(0.2) 10 <0.5 43
[0063]+AA(0.075)+Chol(0.025) 3×10 5
[0064] 170
[0065] DAPC(0.65)+PG(0.15)
[0066] +AA(0.1)+PA(0.08)+ 6×10 5 8 <0.5 51
[0067] 170
[0068] Synthetic SPC(0.02)
[0069] Although the compositions shown here are mixtures comprising almost exclusively lipid components, naturally occurring proteins or synthetic peptides may also be included. Indeed, inclusion of these prot...
Embodiment 1
[0083] Example 1: Tissue-based model of emphysema.
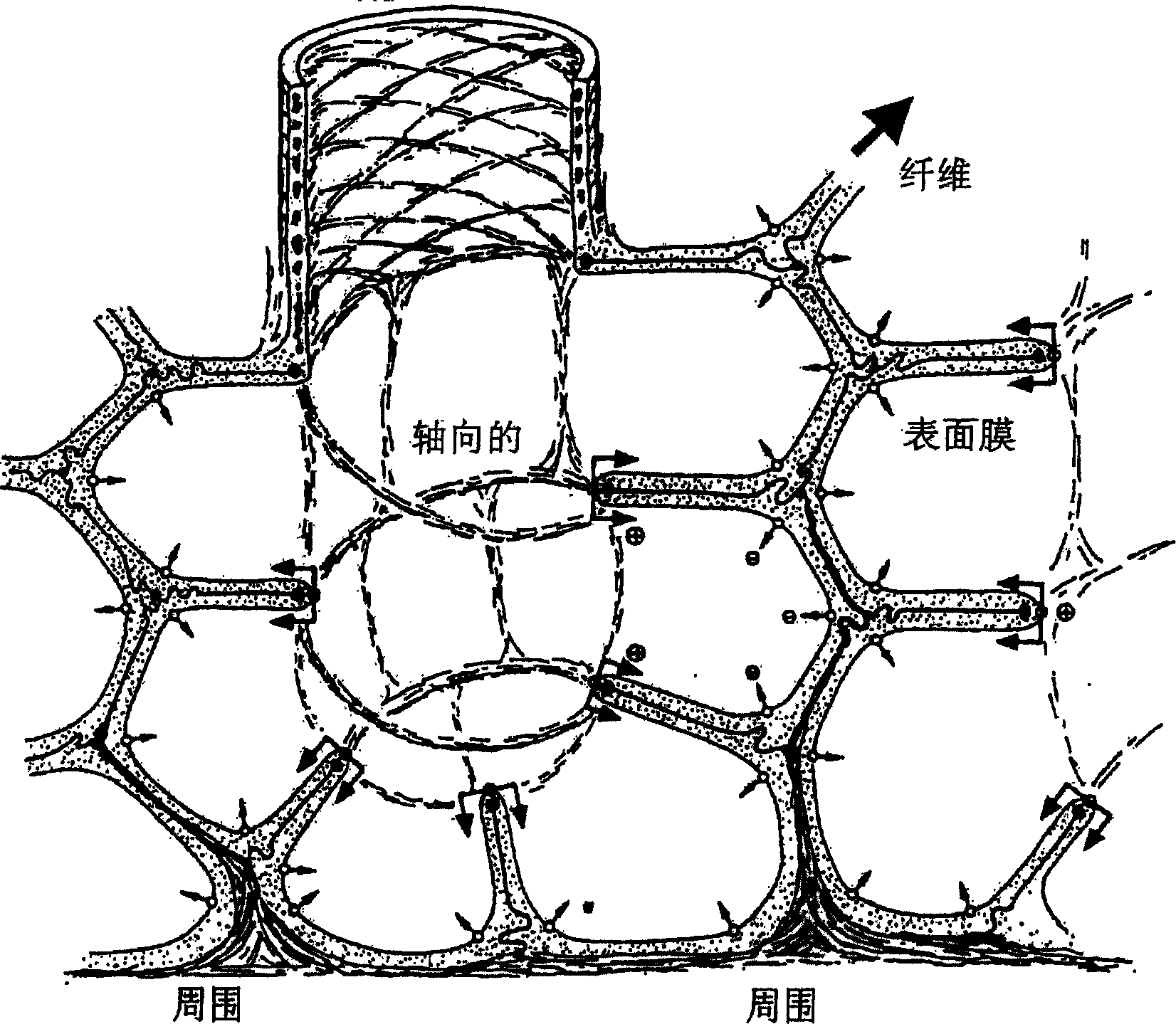
[0084] Collagen and elastic fibers in the alveolar walls are observed in many cases and can be examined in a variety of ways (see e.g. figure 2 ). For example, lung tissue comprising alveoli can be obtained from a healthy animal (including a human patient) or from a human or other animal with enlarged alveoli as a result of a natural or experimentally induced disease process such as emphysema. Tissue can be mechanically stretched as a result of being subjected to forces mimicking the forces experienced by tissue during in vivo respiration (including shallow, normal or deep respiration), and it can be stretched in the presence or absence of pharmaceutical compositions such as known surfactants or in the case of surface films of the invention were stretched to evaluate the ability of those compositions to reduce fiber breakage.
[0085] As mentioned above, as the alveoli enlarge, fiber rupture occurs at tensions close to no...
Embodiment 2
[0087] Example 2: Computer-Based Emphysema Model Showing Decreased Lung Volumes.
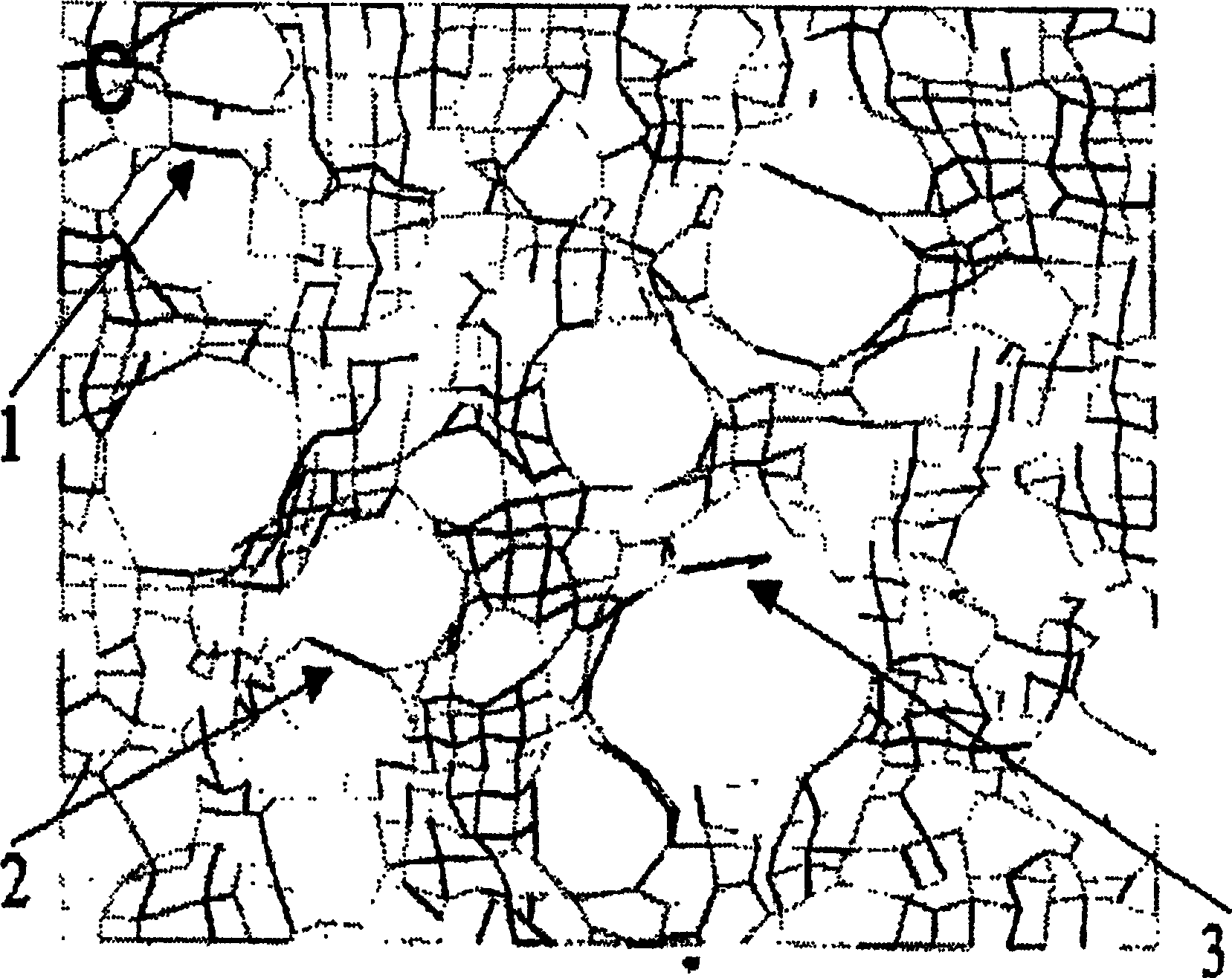
[0088] A finite element computer model was used to simulate the lung consisting of a network of tension-supporting fibers equivalent to collagen and elastic fibers in the alveolar walls. Using parameter values representative of human lung physiology, this model identifies foci of concentrated hypertension that tend to distribute along alveolar edges. Under stretching, fibers under high tensile stress (shown in image 3 And marked as fibers 1, 2, 3) were broken, resulting in enlargement of the alveoli and expansion of focal tension concentrations. This process becomes self-propagating as disruption leads to further weakening. The net results were similar to those seen in clinical practice and consistent with observations made after LVRS. Despite initial improvement, rapid decline in lung function occurs after LVRS. The procedure is performed to enhance tissue retraction, but at the same tim...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface tension | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com