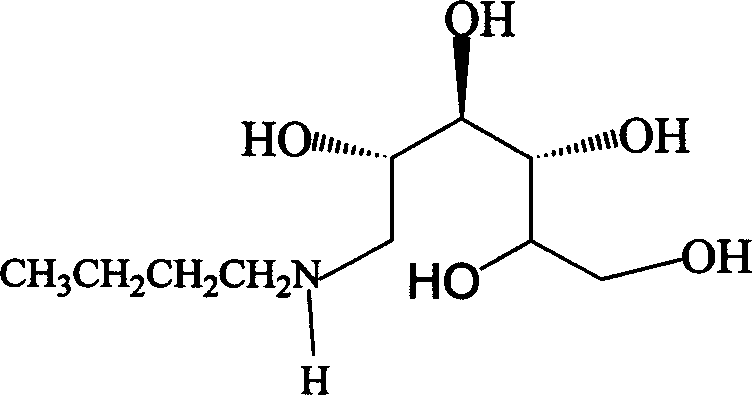
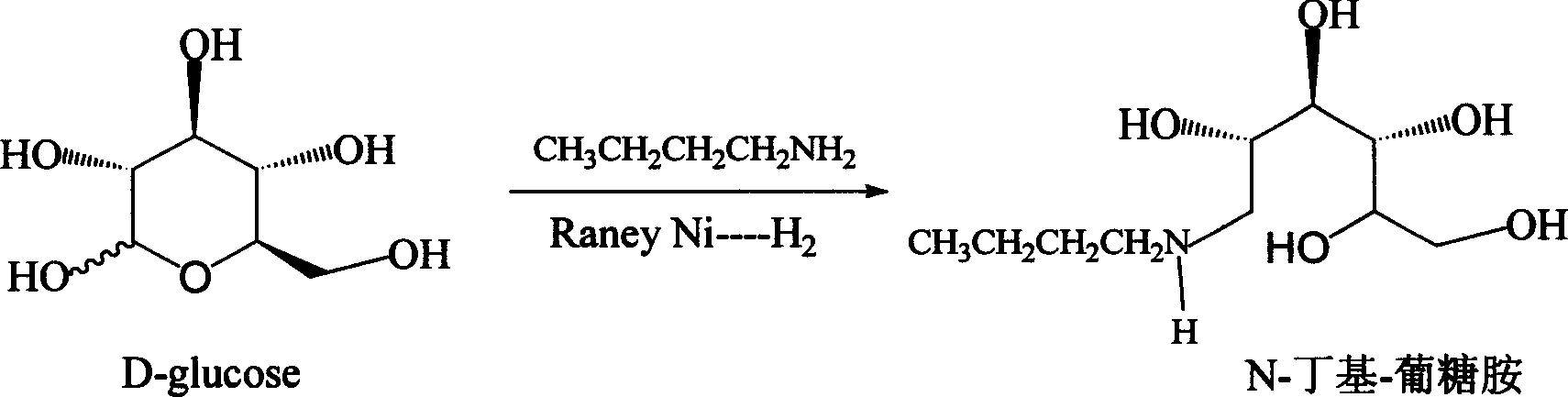Method for synthesizing N-butyl-glucosamine
A synthesis method and glucosamine technology, applied in the field of synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates, can solve the problems of many by-products, low conversion rate, and low product yield, and achieve mild reaction conditions, easy reaction, and good product quality Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] Embodiment 1: the preparation of active nickel catalyst
[0017] Add 250 g of 20-40 mesh aluminum-nickel alloy (containing 50% nickel) and 2 L of deionized water into a 5 L beaker. Cool the temperature in the beaker to below 5°C with ice-salt water. Slowly add 400 g of analytically pure sodium hydroxide, and control the feeding rate so that the reaction temperature does not exceed 5°C. After the addition, the reaction was continued at -5 to 5°C for 30 minutes. Alkaline water was replaced with deionized water until the pH was 7; and then replaced with absolute ethanol 6 times to obtain 120 g of the required active nickel.
Embodiment 2
[0018] Example 2: Synthesis of N-butyl-glucosamine
[0019] A) Feeding: In a 1L autoclave, add 100 g (0.5 mol) of D-glucose monohydrate, 38 g (0.53 mol) of n-butylamine, and then add 800 ml of a solvent of 90% methanol (containing 10% water). After nitrogen replacement, 5 g of the active nickel catalyst prepared in Example 1 was added, and high-purity hydrogen was blown in to keep the hydrogen pressure at 2-3 MPa. Slowly heat up to 35°C for reaction.
[0020] B) Reaction: Control the reaction temperature to 35-45° C., the hydrogen pressure to 2-4 MPa, and react for 10 hours. TLC is used to track the reaction. The glucose point disappears, and the reaction is terminated.
[0021] C) post-treatment: after the reaction is finished, release the hydrogen pressure and replace with nitrogen. The material is discharged and filtered, and the filter residue is spent active nickel catalyst, which is stored in deionized water and recovered for mechanical use after treatment. The light ...
Embodiment 3
[0022] Example 3: Synthesis of N-butyl-glucosamine
[0023] A) Feeding: In a 2L autoclave, add 199g (1mol) of D-glucose monohydrate, 80g (1.09mol) of n-butylamine, and then add 1500ml of 85% isopropanol solvent (containing 15% water). After nitrogen replacement, 15 g of the active nickel catalyst prepared in Example 1 was added, and high-purity hydrogen was blown in to keep the hydrogen pressure at 2-3 MPa. Slowly heat up to 35°C for reaction.
[0024] B) Reaction: Control the reaction temperature to 35-45° C., the hydrogen pressure to 2-4 MPa, and react for 12 hours. The reaction was followed by TLC, and the glucose spot disappeared, and the reaction was terminated.
[0025] C) post-treatment: after the reaction is finished, release the hydrogen pressure and replace with nitrogen. The material is discharged and filtered, and the filter residue is spent active nickel catalyst, which is stored in deionized water and recovered for mechanical use after treatment. The light re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com