Non-volatile semiconductor memory device and rewriting method
A non-volatile, storage device technology, applied in information storage, static memory, read-only memory, etc., can solve long-term problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] figure 1 is a block diagram showing the main part of the structure of the nonvolatile semiconductor memory device 10 according to the present invention.
[0080] exist figure 1 Among them, the non-volatile semiconductor storage device 10 includes: a storage array 1 with a plurality of storage units, each of which can store two or more data values; whether the voltage value of the memory cell is higher or lower than a reference value preset between the maximum value and the minimum value of the voltage range corresponding to the data value; and the rewriting part 3, according to the determination result of the determination part 2, Rewriting data into the memory cell increases the margin between two adjacent voltage ranges, thereby improving data retention characteristics.
[0081] Here, the memory array 1 includes memory cell transistors as memory cells. It should be noted that the memory cells in the memory array 1 are not limited to the memory cell transistors in...
Embodiment 2
[0114] In the rewriting operation of Embodiment 1, a write signal is repeatedly applied under a specific condition. Thus, it sometimes takes a relatively long time to complete the rewriting operation. In Embodiment 2 of the present invention, an example in which the data rewriting operation is completed in a short time will be described.
[0115] In Embodiment 2, the rewriting operation of the following types of memory cells will be described. When data is read from the memory cell immediately before the rewriting operation performed in Embodiment 2, the same data value as that of the written data is read. When data is read from the memory cell after a certain period of time, due to the drift of the threshold voltage of the memory cell, a data value different from that of the written data may be read.
[0116] Figure 6 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the rewrite operation according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
[0117] In step S21, the threshold volta...
Embodiment 3
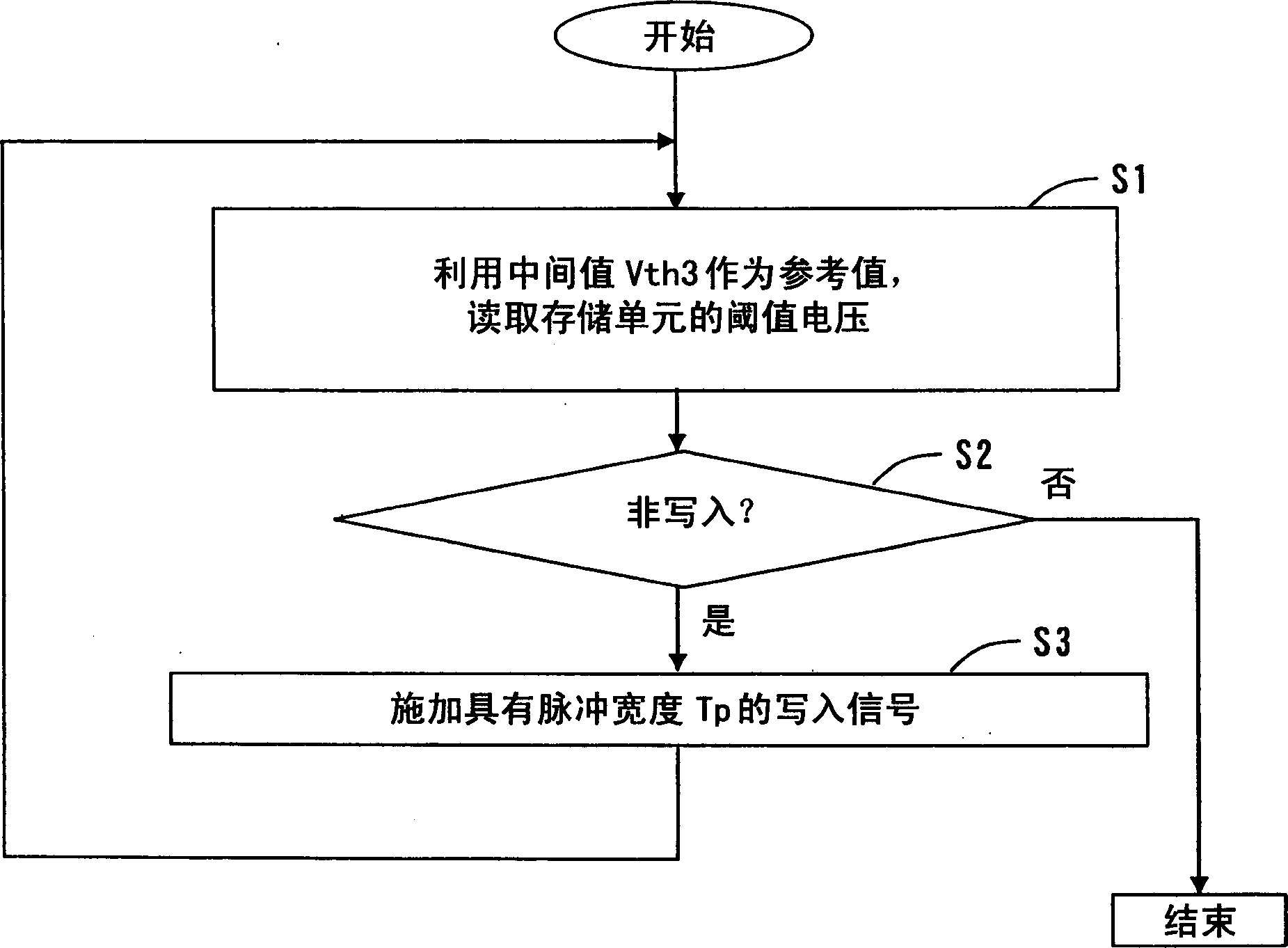
[0135] In Embodiment 3, an example in which the rewriting operation can be performed even more quickly will be described.
[0136] Same as Embodiment 2, in Embodiment 3, the rewriting operation of the following types of memory cells will be described. When data is read from the memory cell immediately before the rewriting operation performed in Embodiment 3, the same data value as that of the written data is read. When data is read from the memory cell after a certain period of time, due to the drift of the threshold voltage of the memory cell, a data value different from that of the written data may be read.
[0137] Figure 8 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the rewrite operation according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
[0138] In step S31, the threshold voltage of a memory cell (for example, a memory cell transistor) is read out, wherein the middle value Vth3 of the threshold voltage range corresponding to the written data value in the memory cell is us...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com