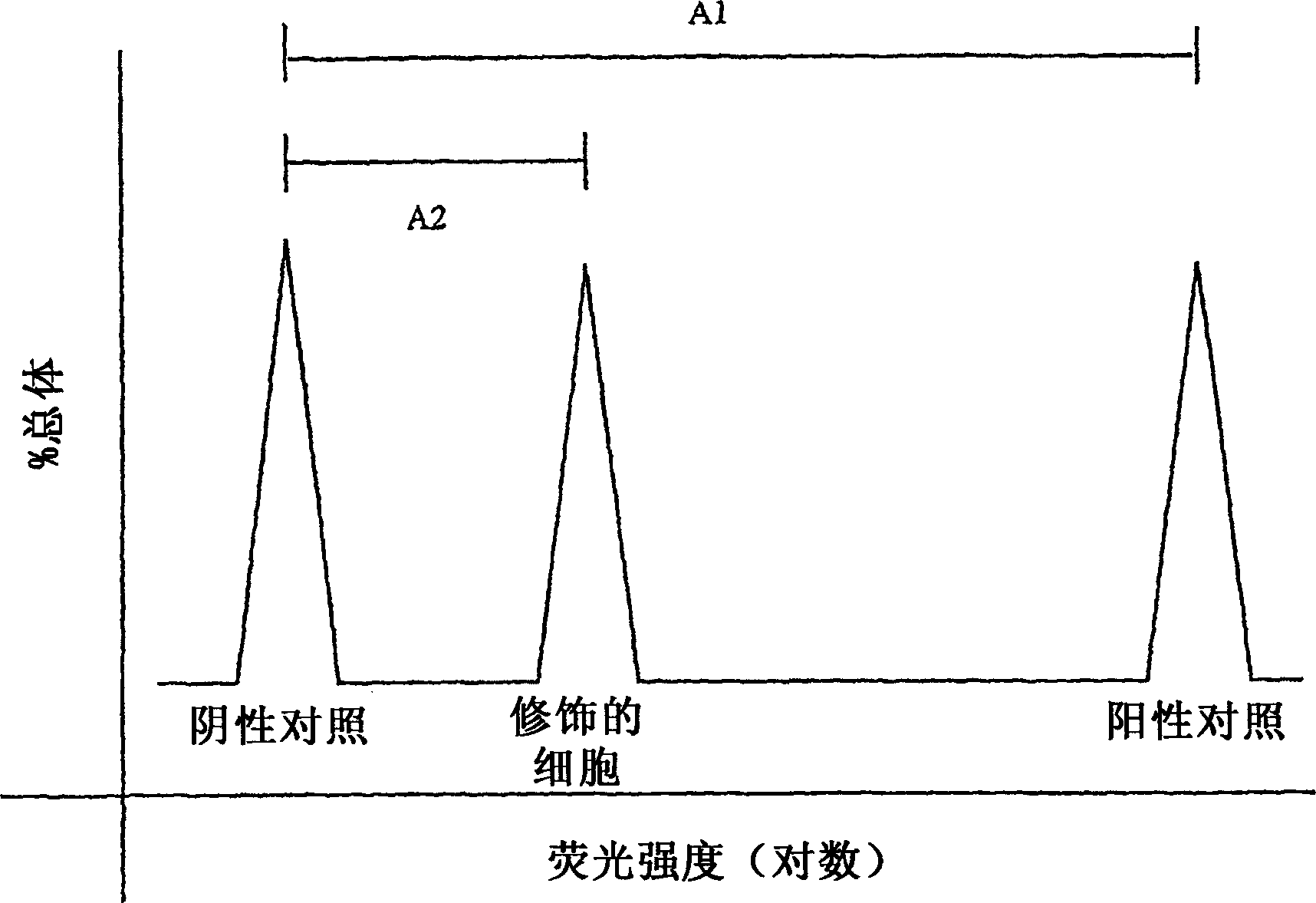
Preparation of pathogen inactivated solution of red blood cells having reduced immunogenicity
A technology for red blood cells and pathogens, which can be used in extracellular fluid diseases, organic active ingredients, antibacterial drugs, etc., and can solve problems such as formation and heterologous sensitization.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0088] EXPERIMENTAL SECTION EXAMPLE 1: DETERMINATION OF THE INACTIVATION OF R17 BY THE COMPOUNDS AND METHODS OF THE INVENTION
[0089] This example describes a method for assaying the inactivation of bacteriophage R17 by compounds and methods of the invention. This method is used to determine the inactivation potency of compounds of the invention in different processing steps. Specifically, compounds and methods for inactivation and compounds and methods for masking erythrocyte immunogenicity are analyzed separately. All methods of producing less infectious and less immunogenic red blood cell compositions were also analyzed. Since R17 immunogenicity may be masked simultaneously with RBC immunogenicity, it is important to evaluate this separately. The purpose of this example was to determine whether the compounds and methods of the invention also inactivated R17.
[0090]The assay measures the ability of phages to infect bacteria and inhibit their gro...
Embodiment 2
[0091] To demonstrate the efficacy of compounds that mask immunogenicity of erythrocytes and the efficacy of the overall method of preparing the treated erythrocyte compositions, R17-Adsol solutions were treated appropriately and then plated as described above. Inactivation titers were assessed by adding appropriate solutions (without inactivating or antigen-masking compounds) to appropriate controls as described above. This assay can also be supplemented with other solutions instead of Adsol. Embodiment 2: Determination of the inactivation of the compounds and methods of the present invention to HIV
[0092] Cells infected with HIV in TC culture medium (Popovic et al., Science, 224:497 (1984): H9-IIIb cells were suspended in tissue culture medium to obtain a plaque-forming unit / mL assay titer Suspension. To a 2 mL aliquot of test medium in a 15 mL conical test tube was added sufficient pathogen-inactivating compound solution to obtain the desired concentration of active subs...
Embodiment 3
[0095] To demonstrate the efficacy of compounds that mask the immunogenicity of erythrocytes, as well as the efficacy of the overall method of preparing the treated erythrocyte compositions, HIV solutions were treated appropriately and then titrated as described above. Inactivation titers were assessed by adding appropriate solutions (without inactivating or antigen-masking compounds) to appropriate controls as described above. This assay can also be supplemented with other solutions instead of Adsol. Embodiment 3: Determination of the inactivation of compounds and methods of the present invention to Yersinia enterocolitica
[0096] Yersinia enterocolitica (California Department of Health Services, Laboratory of Microbial Diseases, Berkeley, CA) was grown overnight at 37°C in LB-broth on a shaker at 180 rpm. To determine the titer, measure the optical density diluted 1:100 in Adsol (10 8 OD at bacteria / mL 610 = 0.2). The bacterial stock was then diluted 1:100 into either s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com