Non-volatibility semiconductor memory
A non-volatile, semi-conductive technology, applied in semiconductor devices, static memory, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, etc., can solve problems such as working speed and wrong work
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
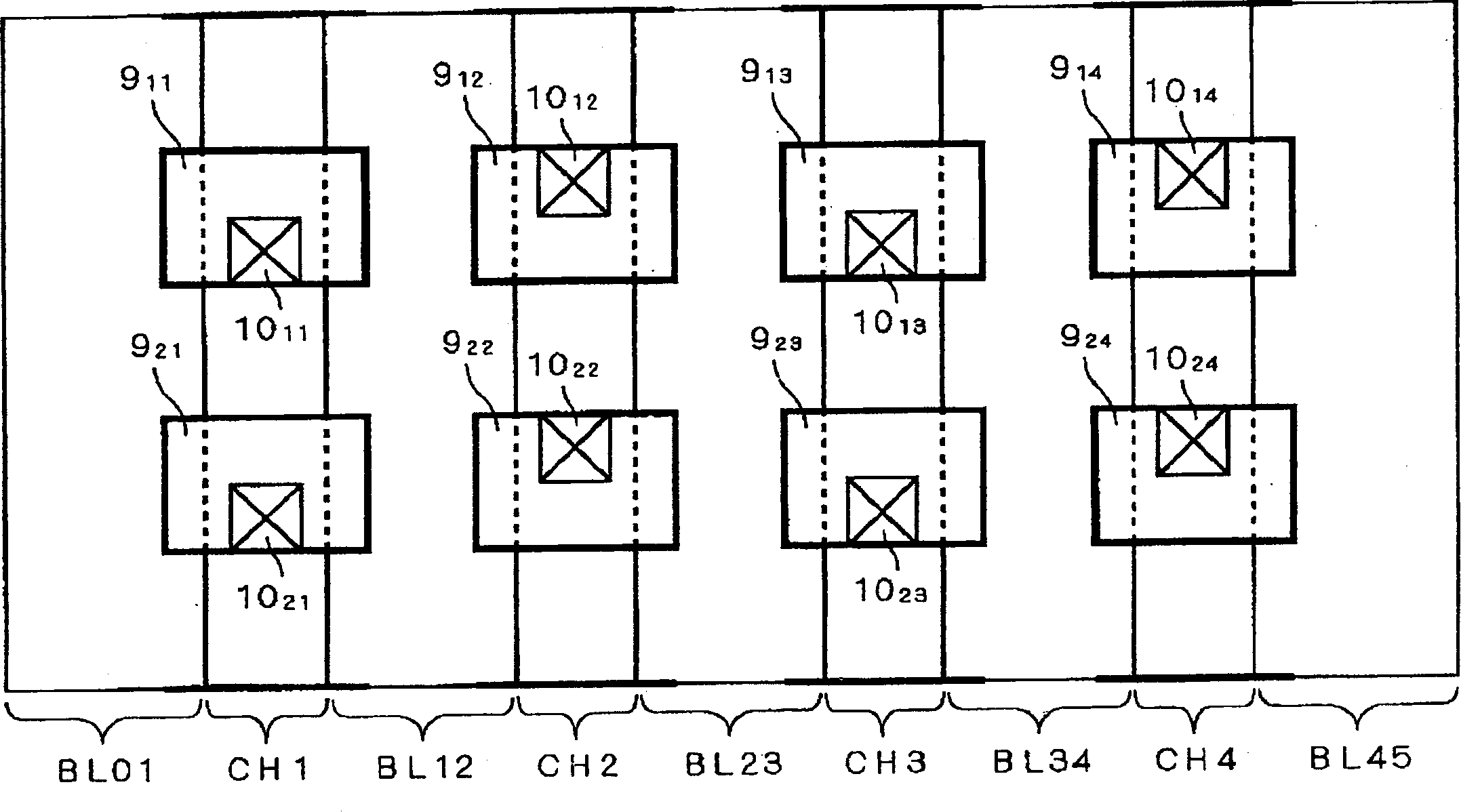
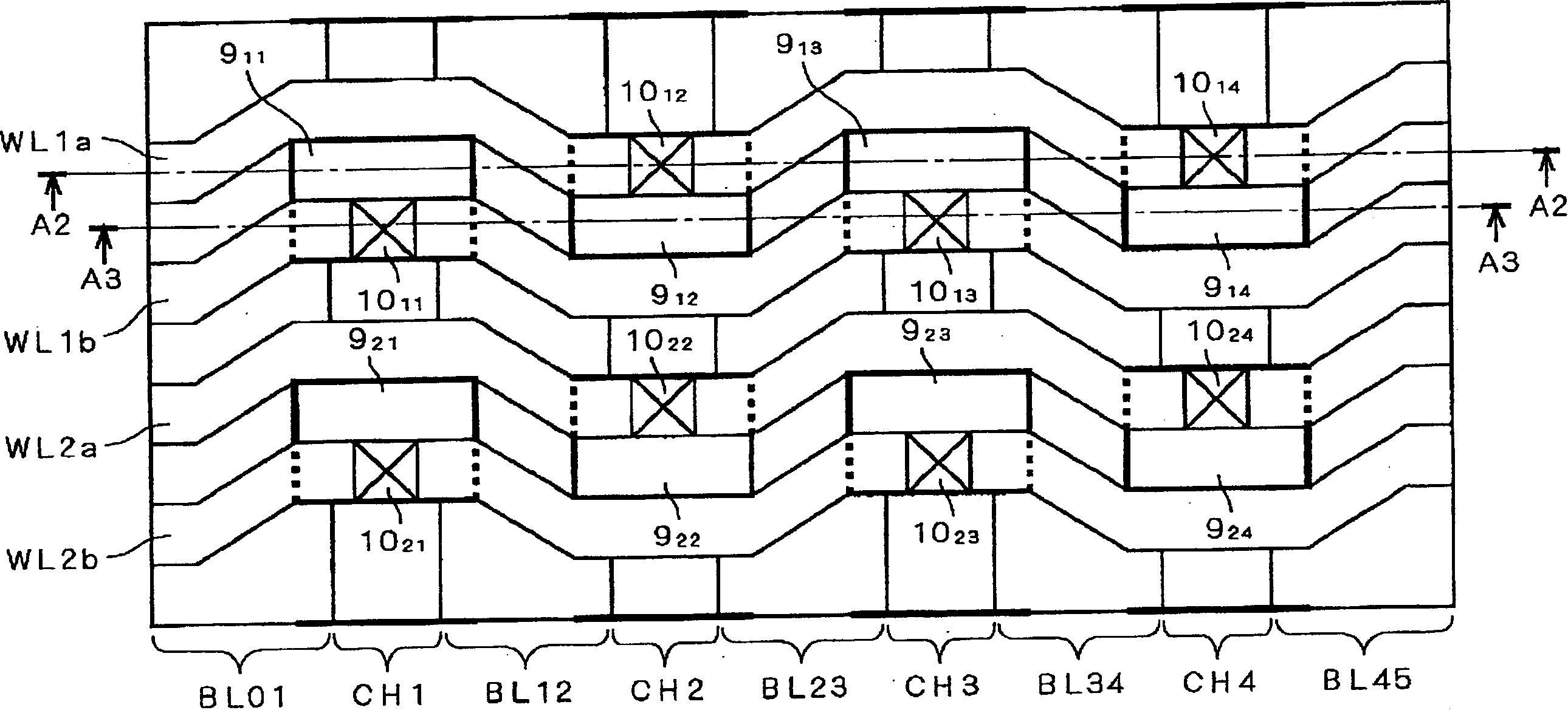
[0116] figure 1 It is a plan view schematically showing the structure of the nonvolatile semiconductor memory according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. A nonvolatile semiconductor memory includes a memory cell array portion in which a plurality of memory cell transistors are formed in a matrix in a semiconductor substrate. figure 1 In , the structure of a part of the above-mentioned memory cell array unit is extracted and shown. In addition, in figure 1 In , description of word lines is omitted. bit line BL (at figure 1 In , codes BL01, BL12, BL23, BL34, BL45) are formed extending in the column direction of the above-mentioned matrix.
[0117] Channel region CH (in figure 1 , denoted by symbols CH1 to CH5) are formed extending between adjacent bit lines BL in the column direction. A gate electrode 9 is formed on the channel region CH (in figure 1 , marked with symbol 9 11 ~9 14 ,9 21 ~9 24 ). Gate electrode 9 11 ~9 14 and 9 21 ~9 24 are the gate...
Embodiment 2
[0142] Figure 25 It is a plan view schematically showing the structure of the nonvolatile semiconductor memory according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. In addition to the nonvolatile semiconductor memory described in the description of the prior art, the nonvolatile semiconductor memory of the present embodiment 2 (refer to Figure 61 , 62 ), also has metal wiring ML (in Figure 25 , marked with symbols ML01, ML12, ML23, ML34, ML45) and bolt 20. The metal lines ML are formed to extend in the column direction corresponding to the bit lines BL. In addition, metal wiring ML is connected to bit line BL via plug 20 .
[0143] Figure 26 is shown along with Figure 25 The sectional view of the sectional structure related to the position of the line A4-A4 shown in . and Figure 25 The conductive film 9 corresponding to the word lines WL1 and WL2 has a structure in which a doped polysilicon film 25 , a tungsten silicide film 26 , a tungsten nitride film 27 and a tun...
Embodiment 3
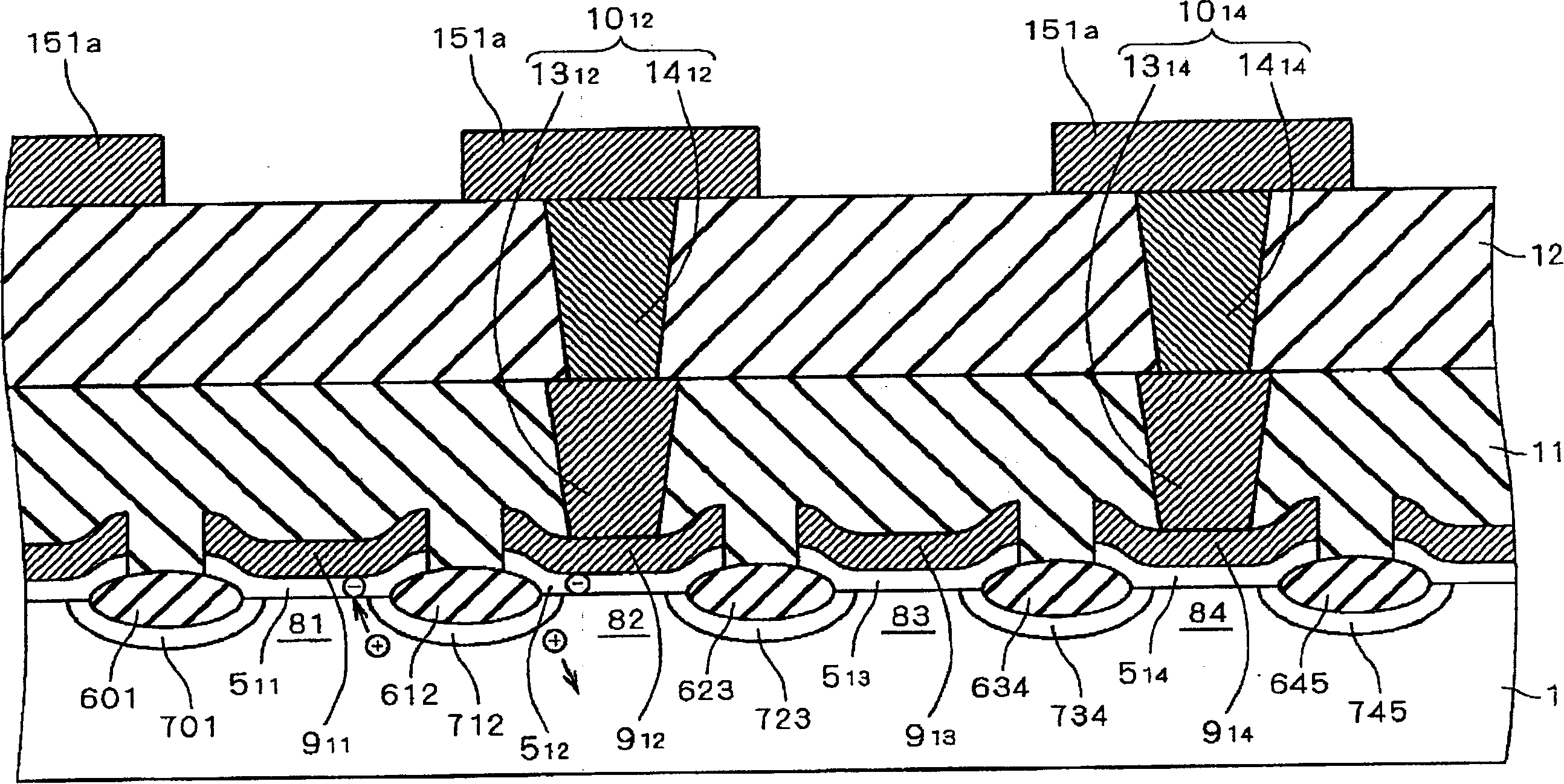
[0160] Figure 34 It is a cross-sectional view showing the structure of a memory cell transistor related to the nonvolatile semiconductor memory according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. A polysilicon film 51 is formed in a gate insulating film 50 made of a silicon oxide film. Under the element isolation insulating film 6, impurity diffusion regions 7 functioning as source and drain regions of memory cell transistors are formed. Polysilicon film 51 is formed only in the end portion of gate insulating film 50 close to impurity diffusion region 7 . The polysilicon film 51 functions as a floating gate of the memory cell transistor, and can store electrons inside.
[0161] Writing is performed by injecting hot electrons into the polysilicon film 51 . Erasing is performed by injecting hot holes induced by the interband tunneling current into the polysilicon film 51 . Reading is performed by monitoring the leakage current or the leakage voltage and detecting the thresh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com