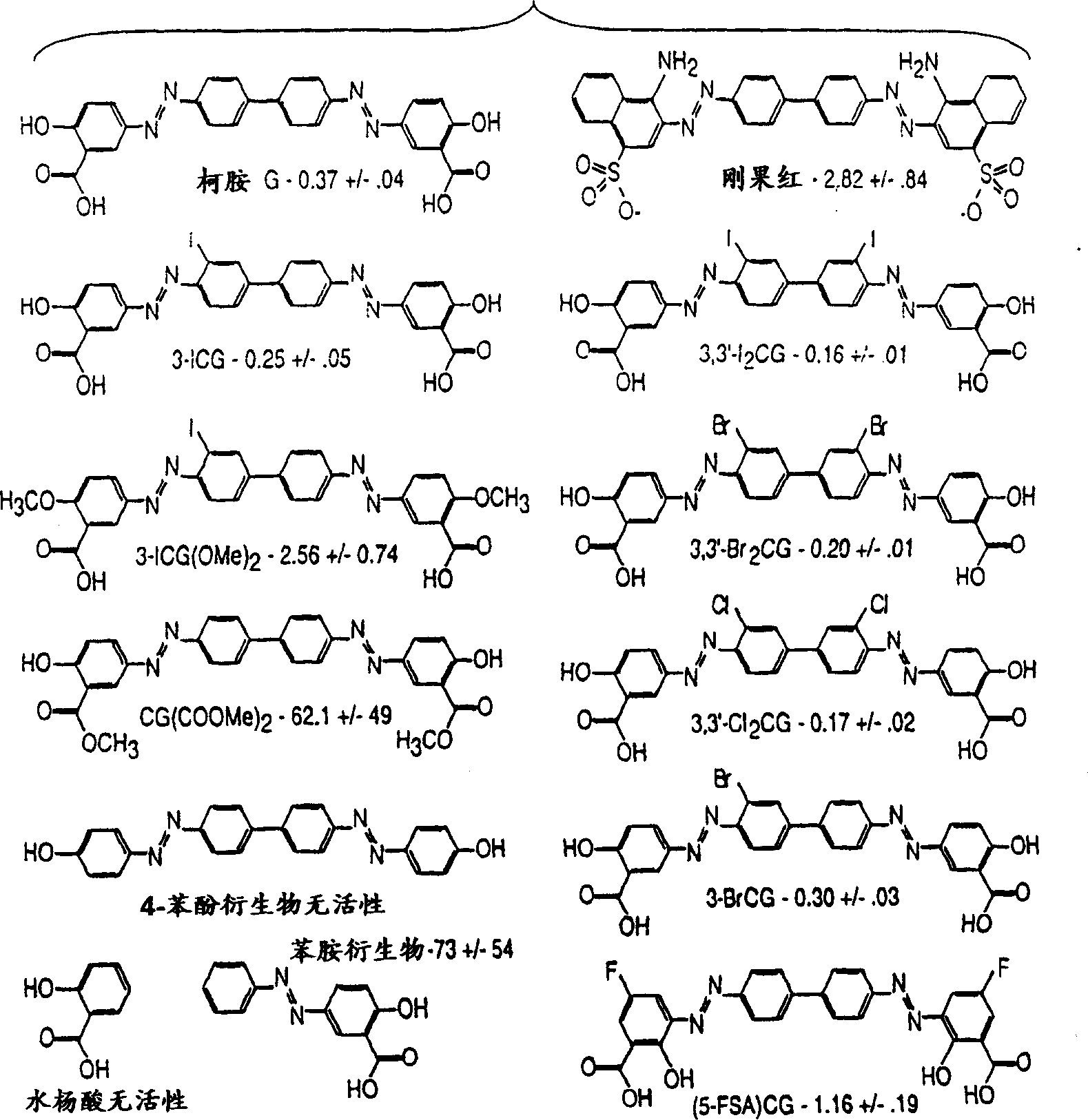Compound for antemortem diagnosis of alzheimer's disease and i(IN VIVO) imaging and prevention of amyloid deposition
A compound and amyloid protein technology, applied in the preparation of tin organic compounds, organic compounds, preparations for in vivo tests, etc., can solve problems such as low bioavailability and difficulty in passing through macromolecules
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
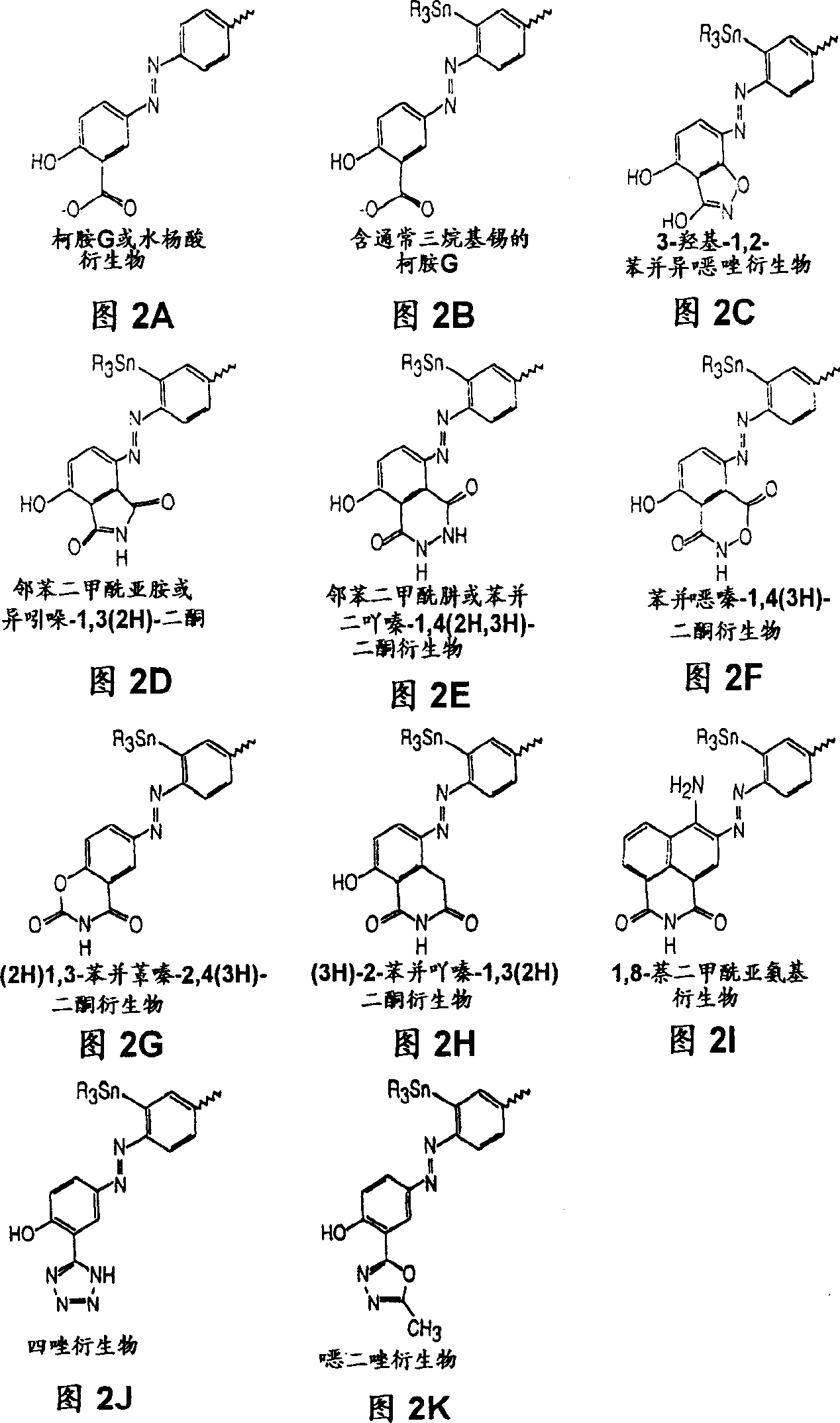
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0138] Embodiment 1. Synthesis of Chrysamine G and derivatives thereof
[0139] Synthesis of Chrysamine G
[0140]The synthesis of Chrysamine G (ie 4,4'-bis(3-carboxy-4-hydroxyphenylazo)-biphenyl) requires the following reaction steps. These reaction steps should be referred to as "chrysamine G synthesis" conventional methods. Benzidine·2HCl (28.9 mg, 0.11 mmole, Sigma Chemical Company, St. Louis, MO) was added to a 50 mL round bottom flask containing 1.5 mL of 1:1 dimethylsulfoxide:distilled / deionized water. The individual reaction steps were performed at 0°C unless otherwise stated. 29 μl of concentrated hydrochloric acid was added and a clear solution was obtained after stirring. Add 15.5 mg (0.22 mmole) NaNO dropwise to the biphenyl gum solution 2 In 300 μl 1:1 DMSO / H 2 solution in O. The pH of the resulting solution was about 2-3. The reaction mixture was stirred for 45 minutes. Then in this benzidine tetrazide mixture, dissolve in 2.0ml containing 250m...
Embodiment 2
[0230] Example 2 Binding specificity of Chrysamine G and Chrysamine G derivatives to Aβ
[0231] Binds to synthetic Aβ(10-43)
[0232] Chrysamine G binds well to synthetic Aβ(10-43) peptides in vitro. Figure 4A shows Scatchard analysis of Chrysamine G binding to A[beta](10-43). Its higher affinity component has a K D is 0.257 μM, and Bmax is 3.18 nmol Chrysamine G / mg Aβ(10-43). These data alone are not sufficient to define the lower affinity components well, but show that their K D 4.01 μM, B max It is 18.7 namol Chrysamine G / mg Aβ(10-43). This low-affinity fraction represents the high concentration of Chrysamine G binding to a different low-affinity site rather than binding to an impurity in the preparation. Since the in vivo injected amount of Chrysamine G was so low that there was no binding of the low affinity components. At very low concentrations, the ratio of high-affinity binding to low-affinity binding is very large.
[0233] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the a...
Embodiment 3
[0251] Example 3 Using Chrysamine G to Distinguish Normal Brain and Alzheimer's Brain
[0252] Chrysamine G binding to AD brain features
[0253] To understand the enhanced binding of Chrysamine G to AD brain, Scatchard analysis was performed on AD brain samples bound to Chrysamine G and its derivatives (Fig. 4B, Table 1). Under the conditions applied, control and AD brains showed a single binding component. K in the AD brain D 16% lower than in the control group, but the difference was not significant (p=0.29). B in the AD brain max It was 36% higher than that in the brain of the control group, but the difference also did not reach significance (p=0.09). Thus, the increased binding in AD brains was primarily due to the presence of more bound components in control brains, rather than the presence of a single component.
[0254] KD(μM) Bmax(pmol / μg port) Control group (n=6) 0.47±0.049 0.576±0.092 AD (n=5) 0.39±0.048 0.784±0.061
[0255] The...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com