Wheat disease-resistant gene Lr-L1 and its use
A disease-resistant gene, wheat technology, applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve the problem of less research on wheat disease-resistant gene isolation, cloning and disease-resistant response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
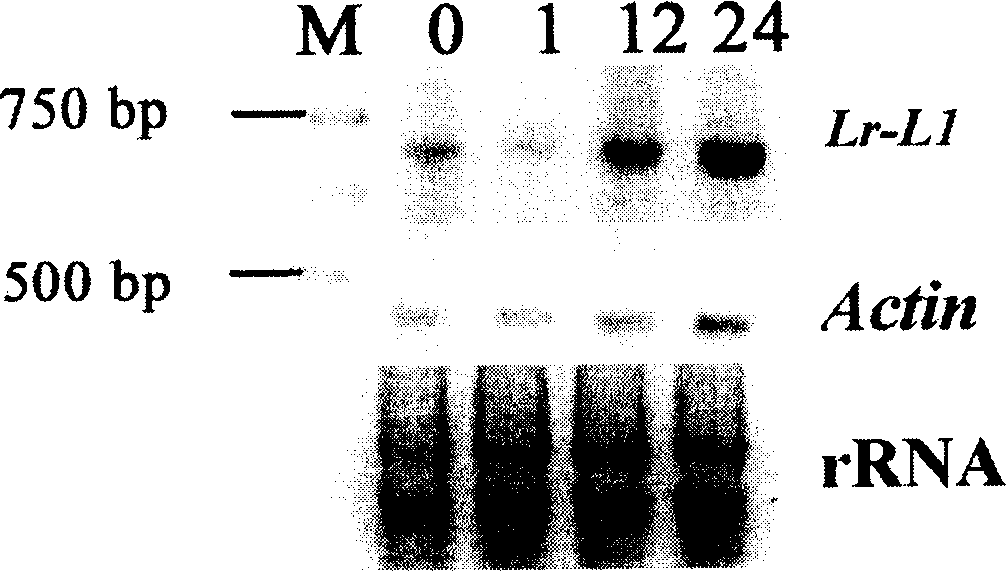
[0071] Example 1: Cloning process of wheat disease resistance gene Lr-L1:
[0072] Wheat Lr-L1 gene was isolated from a new wheat disease-resistant line "99-2439" with high resistance to powdery mildew and rust. Total RNA (ribonucleic acid) was extracted from leaves 22 hours after powdery mildew induction, and mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) was further isolated, and mRNA was transcribed into cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) by reverse transcription, and the cDNA was used as a template Perform gene cloning. A degenerate primer (sequence: 5'-GTGAGGCTT(G / A)A(T / C)(G / A)TC(A / G)AA(G / A) T(G / A)GAG(G / A)ATGCG-3'), many products were obtained by rapid amplification of cDNA end technology (5'-RACE), and an amplification product of about 1500bp was recovered. It was cloned on the pGEM-T Eseay vector, and sequence analysis proved that this cDNA fragment was a part of the receptor-like protein kinase gene after sequencing.
[0073] Amplification was performed using a special ...
Embodiment 2
[0145] Embodiment two: Transgenic disease-resistant breeding:
[0146] Digest the Lr-L1 gene from the pGEM-T easy vector, or amplify it with high-fidelity Taq-DNA polymerase and gene-specific primers. Use T4-DNA ligase to connect Lr-L1 to the downstream of maize ubiquitin high-efficiency promoter Ubi (Ubiquitin-1), and then insert it into the pCAMBIA-Bar plant expression vector to construct the pCAMBIA-Ubi-Lr-L1 expression vector plasmid. The expression vector is transformed into Escherichia coli DH10B bacterial strain for propagation, and the plasmid of the vector is extracted to carry out transgenic disease-resistant breeding. Transform the pCAMBIA-Ubi-Lr-L1 expression vector plasmid into the callus of immature embryos of wheat varieties with high yield and high quality but poor disease resistance by gene gun (such as Bio-Rad’s high-pressure helium gene gun, PDS-1000 / He) middle. Using the selection marker gene on the expression vector—the herbicide-resistant gene Bar, the...
Embodiment 3
[0147] Embodiment three: design and synthesis of new disease resistance gene:
[0148] Modern DNA synthesis technology has been able to synthesize full-length genes. Therefore, according to the difference between the Lr-L1 gene and the LRK10 gene, the cDNA encoding the 1-180 amino acid residues of the LRK10 gene is synthesized and connected with the 176 amino acid residues encoded by the Lr-L1 gene to the end of the gene cDNA, thus synthesizing the Brand new genes. Then, the correct coding frame (ORF) of the synthetic gene was verified by sequencing. The verified gene can be further constructed into a plant expression vector, and the disease resistance of the synthetic gene can be tested by transgenic technology. Synthetic genes with good disease resistance can be used in the breeding of new transgenic disease-resistant wheat varieties (the construction of plant expression vectors and the specific operations of transgenes are as described in (1)).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com