Method for supporting operation system of storage compression
A memory and real memory technology, applied in the field of computing systems, can solve problems such as physical memory exhaustion, no dynamic change of compression ratio, system crashes, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
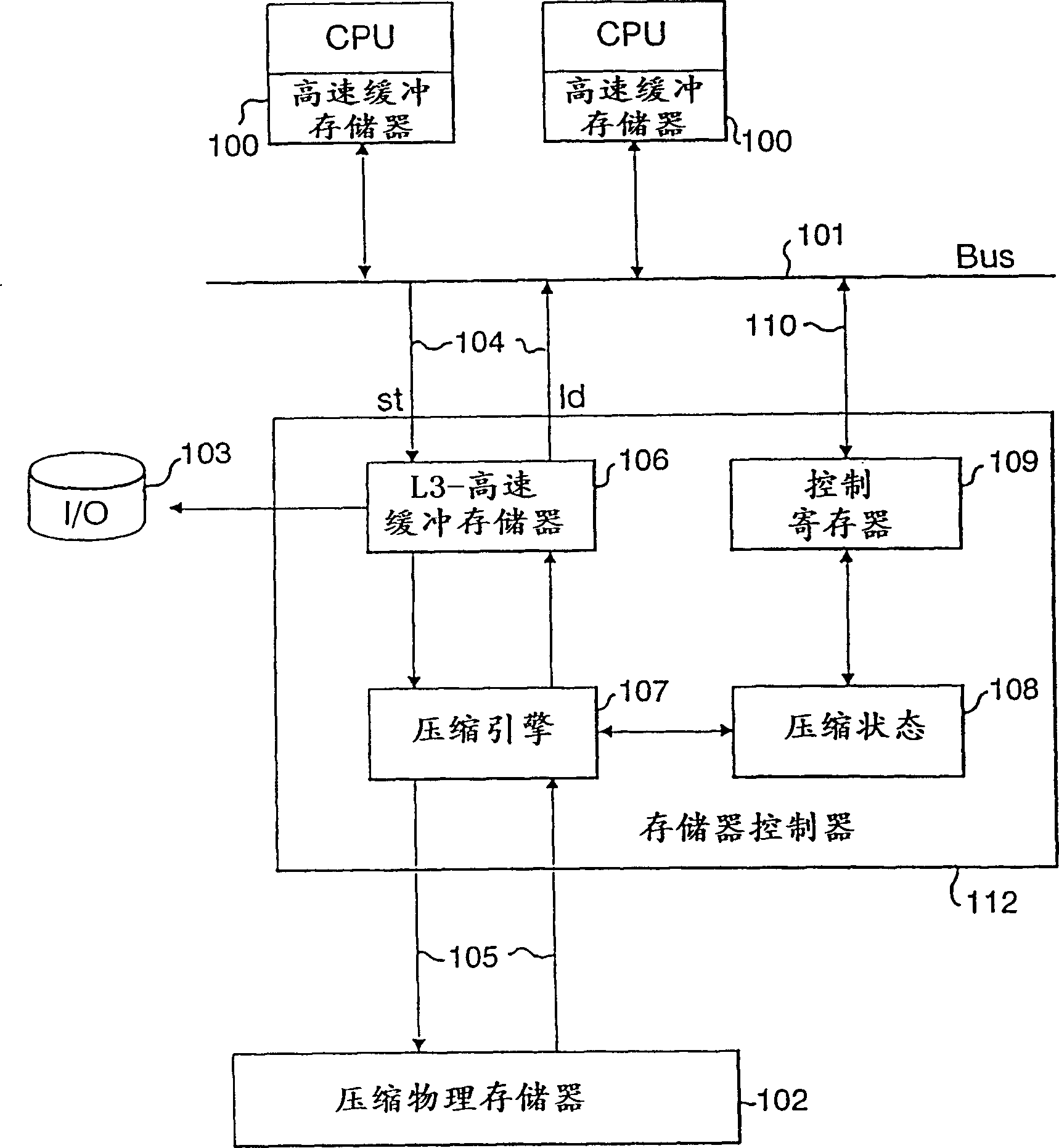
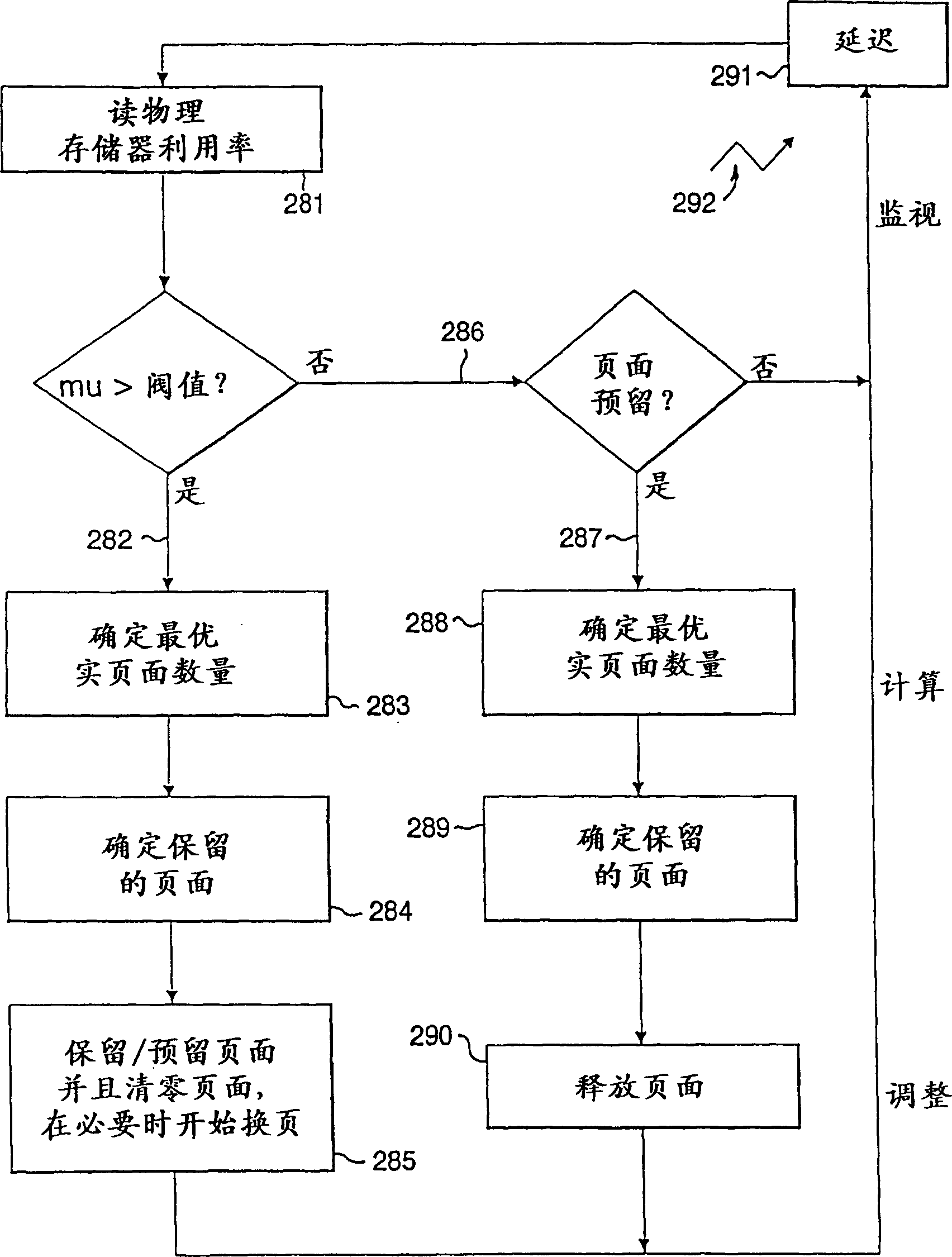
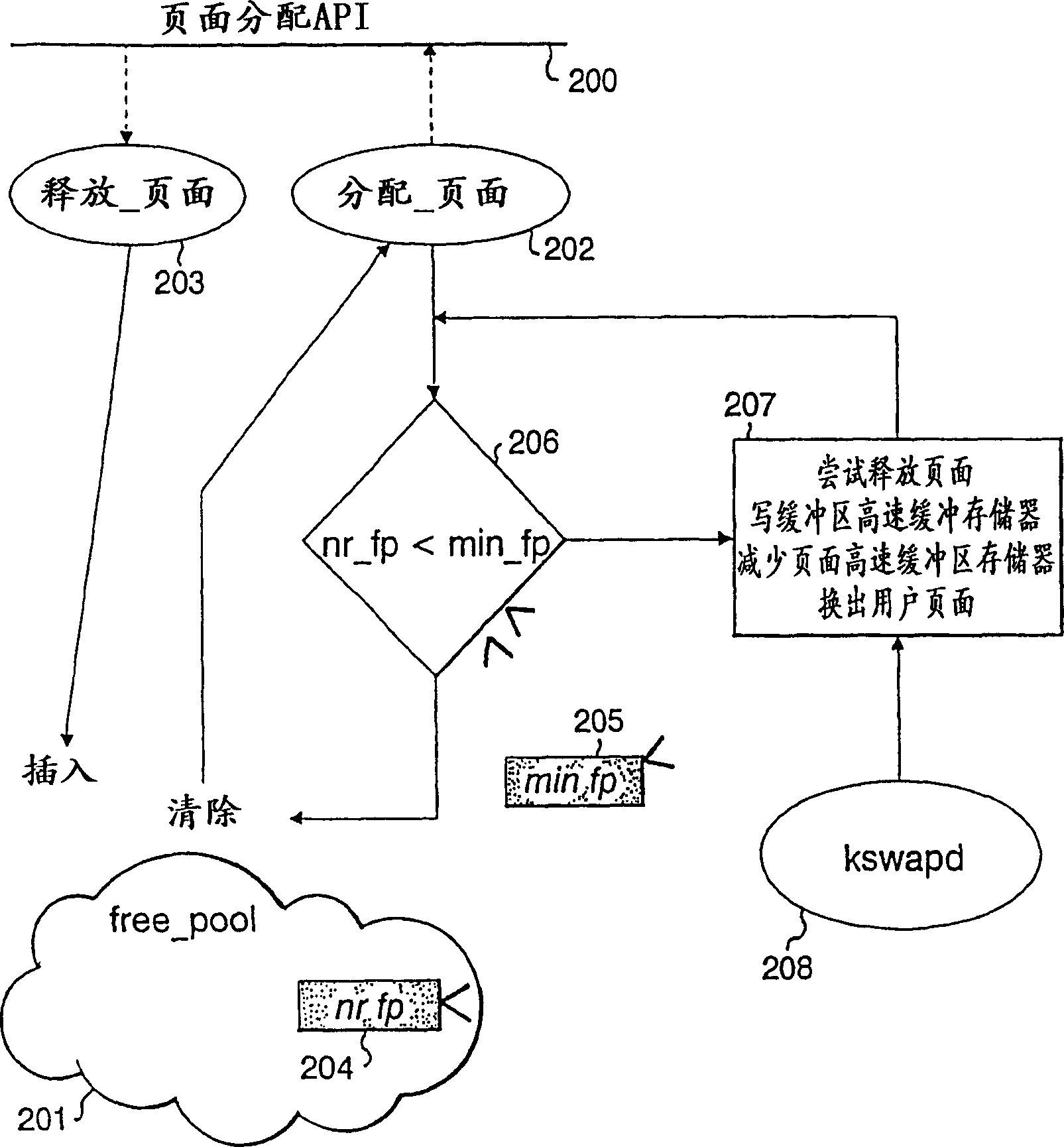
[0030] The introduction of memory compression requires that the utilization of physical memory never exceed 100%. If it exceeds, the data cannot be written back to the physical memory, which usually leads to a system crash. The amount of effective real memory RM(t) that can be provided at a given time tOS is defined by the following data compression ratio CR(t): RM(t)=CR(t)*PM. When the compression ratio is reduced, the operating system may overcommit physical memory by allocating pages to applications, so the operating system must be prepared to take action to reduce physical memory utilization when the memory controller indicates to the OS that its memory utilization has reached a critical level. Unfortunately, no direct assumptions or control can be made about data compressibility or physical memory utilization.
[0031] Equation Eq-1 shows that there are two basic ideas to reduce physical memory utilization, (1) increase compressibility, and (2) reduce effective real memor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com